[ad_1]

A number of high-profile Android apps still use an unpatched version of Google’s widely used app update library, potentially putting the personal data of hundreds of millions of smartphone users at risk of being hacked. .
Many popular apps, including Grindr, Bumble, OkCupid, Cisco Teams, Moovit, Yango Pro, Microsoft Edge, Xrecorder, and PowerDirector, are still vulnerable and can be hijacked to steal sensitive data, such as passwords, financial details. and emails.
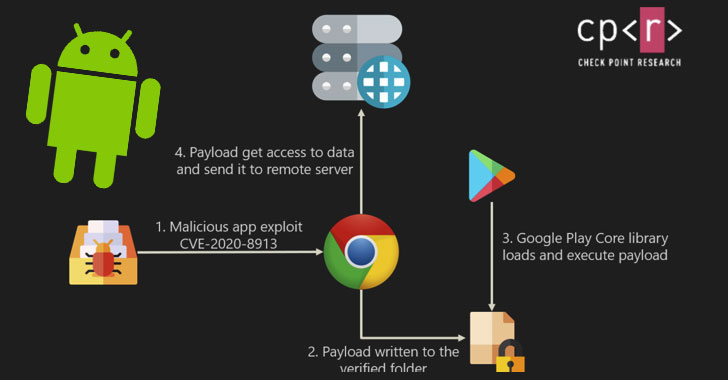
The bug, tracked as CVE-2020-8913, is rated 8.8 out of 10.0 for severity and impacts versions of Android’s Play Core library prior to 1.7.2.
Although Google patched the vulnerability in March, new findings from Check Point Research show that many third-party app developers have yet to integrate the new Play Core library into their apps to fully mitigate the threat.
“Unlike server-side vulnerabilities, where the vulnerability is completely patched once the patch is applied to the server, for client-side vulnerabilities, each developer must grab the latest version of the library and insert it into the application,” said said the cybersecurity firm said in a report.
Play Core Library is a popular Android library that allows developers to efficiently manage the delivery of new feature packs, trigger in-app updates at runtime, and download additional language packs.
First reported in late August by researchers at the Over-Secure Application Security startup, the issue allows a threat actor to inject malicious executables into any library-backed application, thereby granting the attacking full access to all resources like that of the compromised application.
The flaw stems from a path traversal vulnerability in the library that could be exploited to load and execute malicious code (for example, an APK file) on a target application in order to steal login information, passwords, etc. financial details and other sensitive information of users stored in it.
The consequences of successfully exploiting this flaw are enormous. It can be used to “inject code into banking apps to retrieve credentials, and at the same time have SMS permissions to steal two-factor authentication (2FA) codes”, retrieve messages from bank apps. chat, spy on user locations, and even gain access to corporate resources by spoofing corporate apps.
According to Check Point Research, of the 13% of Google Play apps analyzed as of September 2020, 8% of these apps had a vulnerable version.
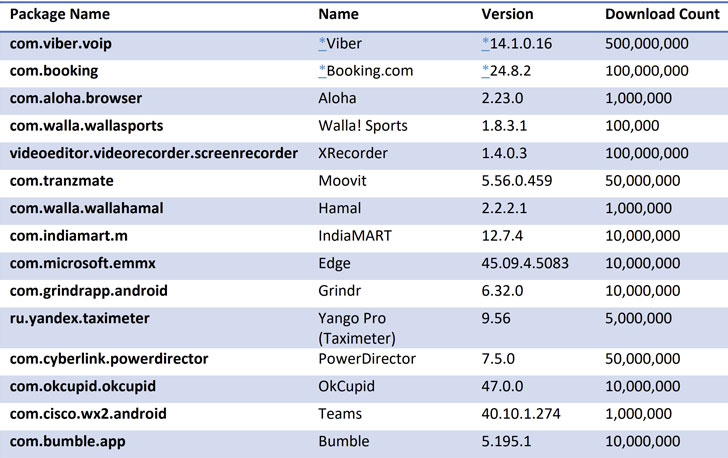
After the cybersecurity company responsibly disclosed its results, Viber, Meetup, and Booking.com updated their apps with the patched version of the library.
Researchers also demonstrated proof of concept using a vulnerable version of the Google Chrome app to siphon bookmarks stored in the browser through a dedicated payload.
“We estimate that hundreds of millions of Android users are at risk of security threats,” said Aviran Hazum, head of mobile research at Check Point. “Although Google has implemented a patch, many applications still use outdated Play Core libraries. The CVE-2020-8913 vulnerability is very dangerous, [and] the attack possibilities here are only limited by the imagination of a threatening actor. “
[ad_2]
Source link