[ad_1]
This is the diagnosis made by an international team of scientists led by the Swiss University of Zurich, based on models developed to calculate the thickness of ice in different parts of the planet, from Information from satellite missions in Japan, the United States and Europe and data from the Global Glacier Monitoring Service.
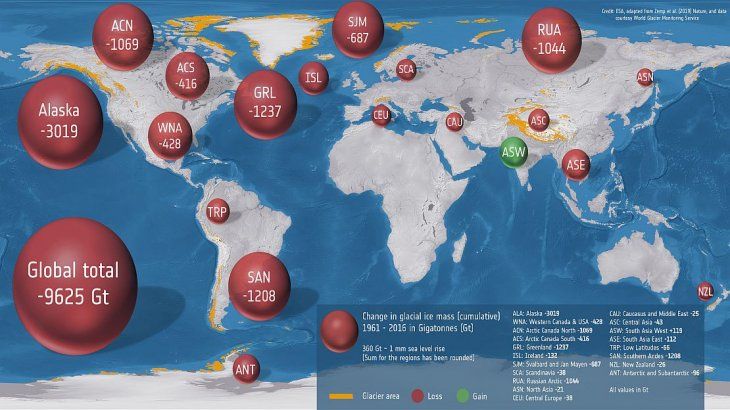
From 1961 to 2016, glaciers lost about 9,600 million tons. According to the report, published in the journal Nature, the phenomenon would have caused a rise in the level of 27 millimeters. In this way, the thaw contributed between 25% and 30% to the observed sea level rise.
The biggest losses occurred in Alaska (-3.019 million tonnes), followed by glaciers bordering Greenland (-1,237 m.ton.) And for those of the Andes (-1.208 m Ton) In the third step.
"The great contribution of the Andes to total losses is mainly due to Patagonia's two large ice fields, which have a high specific loss, that is, an average per square meter. Because time series are too short and scarce, understanding of the process and response of glaciers to climate change is limited.explained the researcher Frank Paul, one of the co-authors of the document, in dialogue with ambito.com.
"What we can say is that there is a great regional variability in the Andes, in particular, the mbad loss of glaciers in Patagonia is much greater than in the center"he says
Previous data collected by the images of the European Space Agency (ESA), had already shown signs that most of the bodies that make up Patagonia Los Glaciares National Parkover 7,000 km2, they have declined over the last 50 years, mainly due to rising temperatures. "The melting glaciers in Patagonia will contribute even more to the rise in sea level "he warned.
The Upsala Glacierfor example, has retired more than 3 km in the past 15 years. A separate case is the Perito Moreno, this seems to be "In balance" intermingled cycles of withdrawals and advances.
map of glaciers upsala.jpg

The Upsala glacier, in the image of Copernicus satellite.
it
Glaciers in temperate regions such as the European Alps and the Caucasus have not escaped the loss of ice could disappear, as in western Canada and the United States, in the second half of the century. What is the cause? "Increasing temperatures"Frank answers frankly.
Like a curiosity, the report shows that South-West Asia is the only region to have gained volume during the 55 years of the survey, even though the news is at least bittersweet: its southeastern neighbor lost about the same amount at that time.
map – glaciers – perito m.jpg

The Perito Moreno glacier.
In his latest statement on the state of the climate, the World Meteorological Organization alerted about the retreat of glaciers with 31 consecutive years of negative mbad balance.
In this context, warned the WMO, "The sea level continues to rise at an accelerated pace". In 2018, the average level on a global scale was about 3.7 mm higher than the previous year, a value that was new recordWhereas the main cause of the increase "Accelerated mbad loss of ice sheets".
Glaciers are the largest freshwater reservoirs on our planet and their behavior is one of the best indicators of climate change. In addition to sea level rise and subsequent floods, the disappearance of glaciers means less fresh water and less hydroelectric energy, with its social and economic consequences.
"The research was not related to this topic, but I can mention some points in the scientific literature: glacier meltwater is an important source of human wellbeing, for agriculture as the decline in glaciers will create water problems, mountains will be more dangerous because of melting permafrost ", concluded the specialist.
.
[ad_2]
Source link
 Naaju Breaking News, Live Updates, Latest Headlines, Viral News, Top Stories, Trending Topics, Videos
Naaju Breaking News, Live Updates, Latest Headlines, Viral News, Top Stories, Trending Topics, Videos