
[ad_1]
By Natalia Concina
Is there community circulation of the Delta variant of the coronavirus in Argentina? Why is your income so affected? Is the third wave coming? So many questions that have resonated this week since the confirmation of five cases with this worrying variant unrelated to travelers and which were answered by two of the specialists who know the most about the subject in the country.
First identified in India in October last year, the Delta variant – defined by the World Health Organization (WHO) as one of the four worrisome variants – has been the driving force behind a new wave in various parts of the world due to its greater contagion capacity.
In Argentina there are two groups that carry out the genomic surveillance of the coronavirus, that is, they carry out the genetic sequencing of local samples of patients to determine which variants are circulating: one is the ANLIS Institute- Malbrán and the other is Inter-Argentina. SARS-CoV-2 Institutional Genomics Project (PAIS).
This week, the Ministry of Health published a work carried out by the two in which it learned of the detection of five cases of residents of the city of Buenos Aires who had the Delta variant whose link with travelers did not had not been determined.
Meanwhile, on Friday, he reported that so far “there are 174 cases with a sequenced Delta variant (travelers, travelers-related and 5 unrelated cases), plus 21 close positive COVID contacts of confirmed cases of Delta variant “.
In this context, the virologist Carolina Torres, member of the PAIS project, and the biochemist Josefina Campos, coordinator of the genomics and bioinformatics platform ANLIS-Malbrán, explained to Telam what these detections involve and the variables that intervene to think about different futures. scenarios related to the pandemic in Argentina.
– What are the variants currently circulating in the country at Community level?
– Carolina Torres: At the country level, among the new cases, there is a predominance of the Gamma variant (identified for the first time in Manaus), except in the area of the Metropolitan Area of Buenos Aires (AMBA) where it There is a similar prevalence between Gamma and the variant defined by WHO as Lambda of interest (known as Andina).
Regarding the Alpha group (known as the United Kingdom), some cities still have them but we see very little in Argentina.
– From the cases detected with Delta unrelated to travelers, can we say that there is community traffic?
– CT: What the detection of these cases implies is that there are local chains of transmission, but we are still not talking about community circulation because it is a concept defined by the Ministry of Health of the Nation taking into account several factors.
Basically what it takes to define “community transmission” is that there is a high risk of contracting this variant at the community level.
So far, these are isolated cases; the new ratios therefore always correspond to the variants we mentioned previously: Gamma and Lambda.
This is because the transmission chains can be cut, and each detection of a case unrelated to a traveler will not necessarily result in community traffic; it is an intermediate step.
– How was Delta’s behavior in other countries of the world?
– Josefina Campos: Delta has so far been detected in 142 countries and 90 percent of the new sequenced cases that were reported in July worldwide to GISAID (Global Initiative on Sharing All Influenza Data – global initiative to share virus data influenza- ) corresponded to this variant.
In most of the places it entered, it quickly became predominant and this is due to its high transmissibility index which has been shown in several studies; it means that one person infects more than one.
– CT: In the world, he had a similar behavior in the countries where he entered. What happened was between two and four weeks of sporadic detections and after it became between 1 and 5 percent of the detections, after a month it was over 50% and in six to eight weeks, it became 90% of new cases.
This range of weeks is linked to the situation in the countries where it has arrived; For example, if these were places where there were fewer restrictions, the mandatory use of chin straps had been removed, massive events had been allowed, or there was no control over entry into the country.
In addition, it was observed that initially the variant entered the unvaccinated population and then spread to the rest.
What can happen in Argentina
– What will happen in Argentina?
– JC: What happens in the country will depend on multiple factors such as how Delta interacts with the other variants. You should know that in Argentina the predominant ones are Gamma and Lambda, not Alpha as is the case in the United Kingdom or the United States.
Another factor is, in the event that Delta’s community circulation begins, what situation the population is in with regard to vaccination and how Delta is responding to vaccines that are in the country.
And it will also have to do with the public health measures that are taken and social behavior, both for general care and for respecting the isolation of those entering from abroad.
– CT: Referring to how it interacts with other variants, the behavior we mentioned in the previous answer has occurred in Alpha-predominant populations. In South Africa, which had a predominance of the Beta variant, it also quickly became predominant.
Gamma is predominant in most countries of South America, with the exception of Peru (where lambda predominates) and Colombia (with one variant that is monitored).
In Brazil, Peru, Paraguay, Colombia, Chile and Ecuador, they have already reported cases unrelated to travelers. And in Brazil precisely, where community circulation has been announced in Rio de Janeiro and São Paulo, the Delta already represents 60% of the new cases reported.
Third wave
– Is a third wave inevitable?
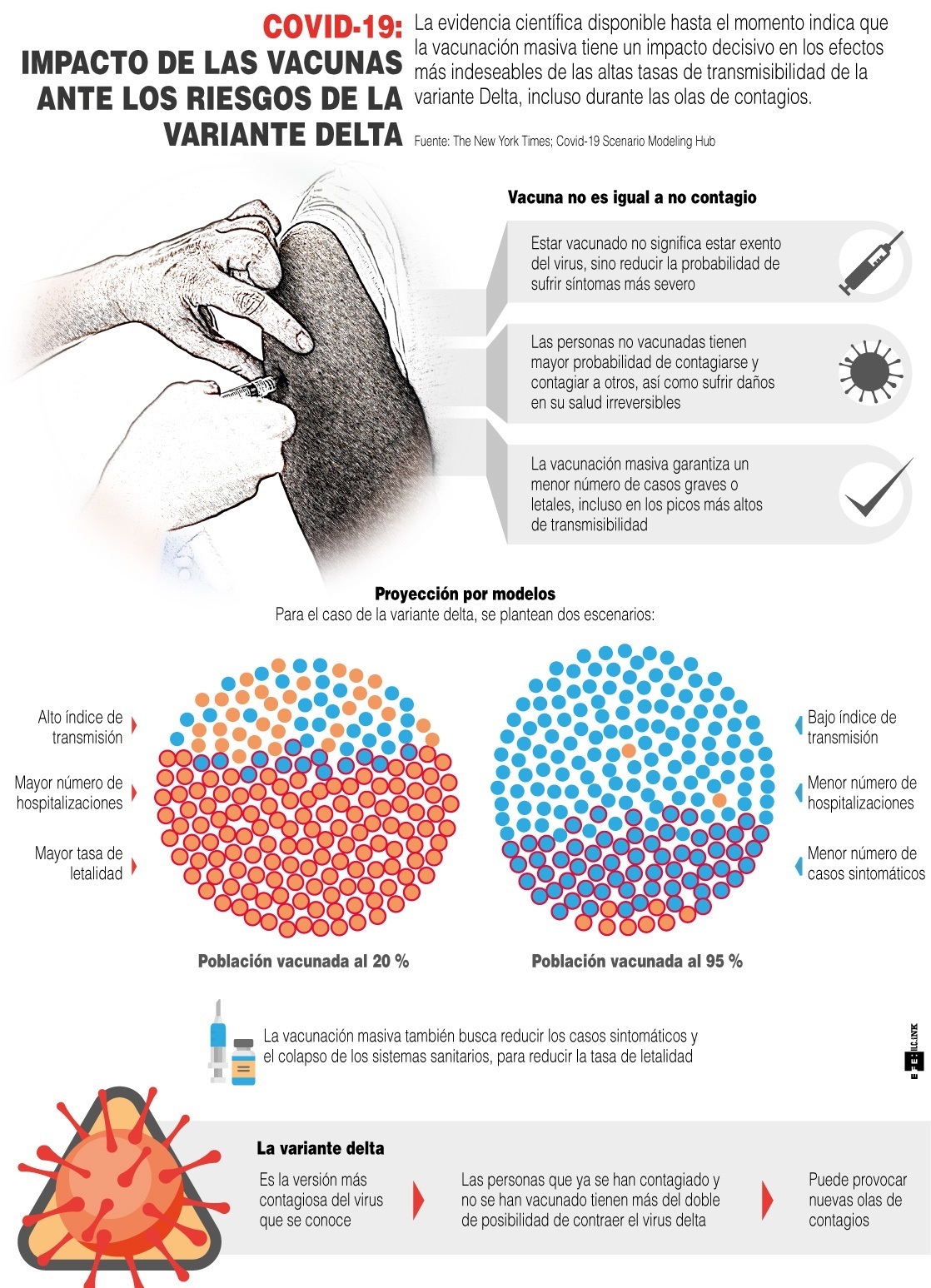
– JC: It will depend on how all of the factors we mentioned earlier are combined. What is important is that it is necessary to move forward with the complete immunization schedules to obtain greater protection against this variant and any variants that may arise; as well as continuing care measures such as correct use of mask, ventilation and distance, as this also depends on the increase or not of cases.
– CT: It is very difficult to predict what may happen. What has happened so far is that sooner or later the variant enters, but its impact depends on many factors, including vaccination. If the vaccination campaign succeeds in completing the schedules of a large percentage of the population, even if Delta enters and infections increase, it is highly likely that we would have fewer severe cases and fewer deaths.
Telam.
[ad_2]
Source link
 Naaju Breaking News, Live Updates, Latest Headlines, Viral News, Top Stories, Trending Topics, Videos
Naaju Breaking News, Live Updates, Latest Headlines, Viral News, Top Stories, Trending Topics, Videos