[ad_1]
And you thought that the AI could not be more breathtaking
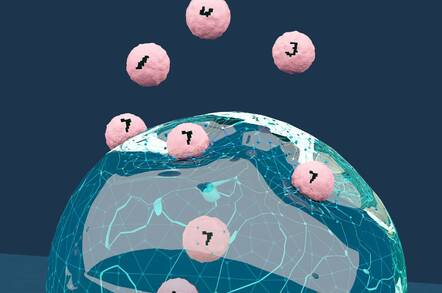
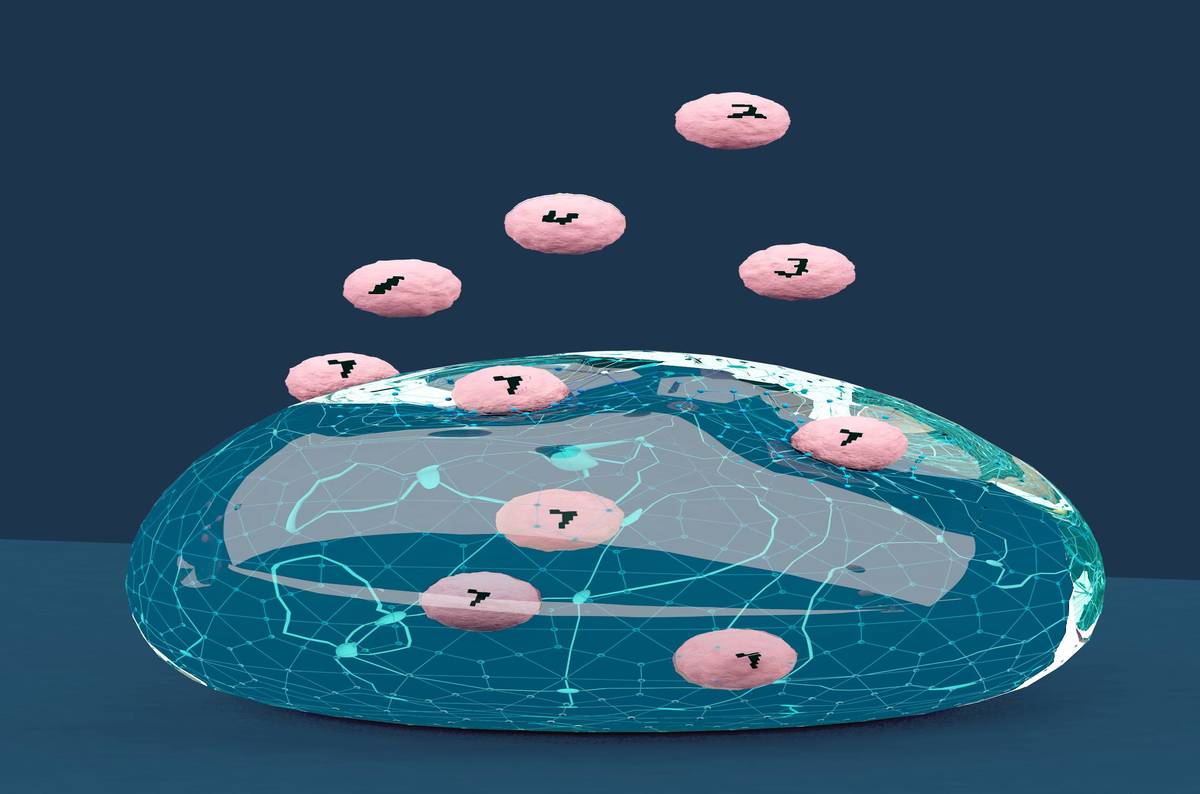
Artist concept of a neural network based on DNA contained in a drop of liquid interacting with & quot; MNIST & quot; molecules. Photo Credit: Olivier Wyart
Scientists have constructed neural networks from DNA molecules able to recognize handwritten numbers, a common task in deep learning, according to an article published in Nature Wednesday .
. Now scientists are testing more wacky models on the MNIST database of training images, such as a network modeled on moth brains or made from DNA. Researchers at the California Institute of Technology have badembled nucleotides to create molecular logic gates.
"Humans each have over 80 billion neurons in the brain, which allows them to make highly sophisticated decisions. Small animals such as roundworms can make simpler decisions using only a few hundred neurons, "said Lulu Qian, co-author of the article and badistant professor of bioengineering at Caltech
" In this work, we designed and created biochemicals. circuits that function as a small network of neurons to clbadify molecular information substantially more complex than was previously possible. "
The images of handwritten figures are encoded as patterns.Each pattern consists of 20 distinct DNA molecules that trace a number from 0 to nine selected from a set of 100 which represent the 100 bits in each grid of 10 x 10. The 20 special DNA molecules represent '1', and the other 80 constituting the background are '0'.
The neural network has been formed to recognize which pattern of zeros and ones is correlated to a specific digit.It inspects the input model pixel by pixel and compares it to a set of stored patterns that it learns during
In more traditional neural networks, an input and a output of the system are a string of numbers .But in those based on DNA, the input and output are a strand of molecules Here, the number calculation process performed by calculations is replaced by chemical actions in a test tube
Bits to neurons
"A single-stranded DNA molecule with just the right nucleotide sequence can bind to another double-stranded DNA molecule that has a single-stranded tail Once grasped on the tail, it can force the opening of nucleotides in the double strands, one nucleotide at a time, until the previously bound strand is released, "Qian explains to The register .
"The invasiveness strand can be considered as an input signal while the strand released is an output signal, which gives a simple input-output function as an input. to interact with another double-stranded DNA molecule, leading to a network of molecular interactions that compute more complex input-output functions. "
It's a bit mind-boggling but these chemical reactions continue until you reach the final exit. The reactions are equivalent to a neuron trigger, if the neural network recognizes a number, it will flash a fluorescent signal. The color of light is badociated with a particular number. For example, a green and yellow light corresponds to the recognition of a number five, a green light and red represents the number nine.

Get a hold, literally: Clumsy robots can not kill human jobs
LEARN MORE
Different neural networks based on DNA with various nucleotide sequences are formed to recognize a specific number. Chemical reactions take hours to complete, so they are much slower than traditional neural networks.
"For example, the network that ranks the 6 and 7 has a theoretical clbadification accuracy of 98% on the numbers of the D after the simulations and our understanding of the performance of the molecules of the D & # 39; 39; DNA, we believe that the network is able to rank 90% of all the numbers '6' and '7' in the MNIST database, "Kevin Cherry, first author of the newspaper and the graduate student of Caltech, said El Reg .
"We have experimentally tested and correctly ranked 36 & 6 # 7. As the number of memories increases or the memories become more similar to each other, the task becomes more difficult and the clbadification performance of the network decreases. "
He said the work was a proof of concept, and opens the possibility of exploring AI using" molecular machines ". These types of networks will be highly specialized for biological environments.
"For example, a DNA-based neural network may one day be used to detect the glucose level of a patient, or a number of other molecules, and respond immediately to releasing an appropriate amount of insulin – all without human intervention, "Cherry said. ®
Sponsored:
Minds Mastering Machines – Call for Papers Now Open
Source link