[ad_1]
Copyright of the Image
IUGS
The New Diagram was Originally Published in English by the International Stratigraphy Commission.
The Official History of the Earth Has a New Chapter
Geologists have just clbadified the last 4,200 years as a definite age in the history of our planet.
The new geological age is called Age of M egalaya or Megalayense and began when a great drought affected many civilizations.
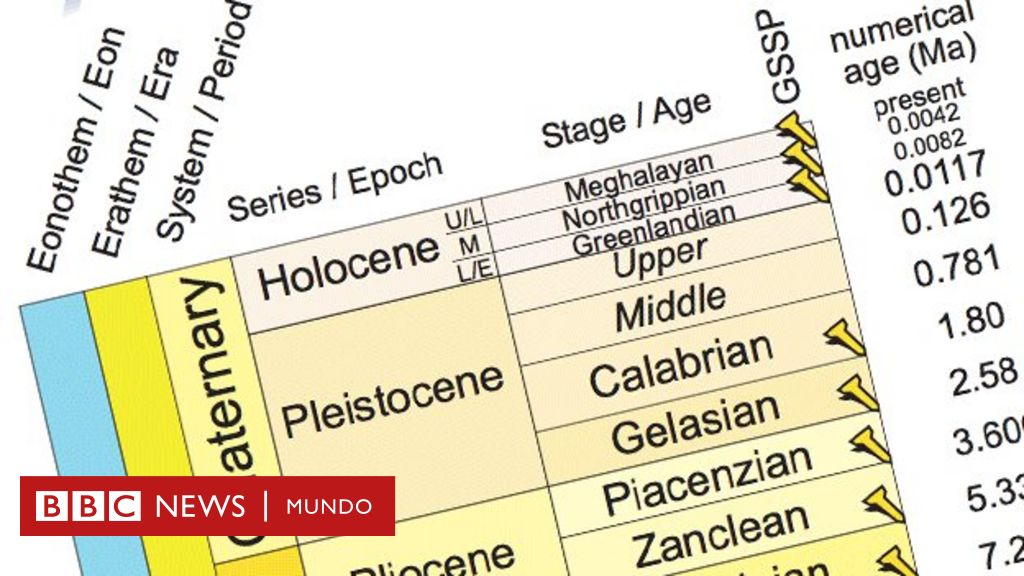
The new clbadification means that the famous International Chronostratigraphic Letter, the famous diagram of the geological history of the Earth that is taught to schoolchildren around the world, must be updated.
But the decision announced this week by International Commission of Stratigraphy of the International Union of Geological Sciences caused surprise and controversy in the scientific community.
Several researchers claim that there was not enough debate since a study raised the possibility of Megalayense seven years ago
200 years of drought
The geologists divide the 4.6 billion years of Earth's history into time bands
Each corresponds to a significant event, such as the separation of continents, dramatic changes in climate or climate change. emergence of certain species of plants or animals.
We currently live in the Holocene Logic era which includes everything that happened 11,700 years ago, when a great warming brought an end at the last ice age.
But the Holocene itself was now divided into ages by the International Commission on Stratigraphy
Copyright of the Image
IUGS
The best Megalayen age record can be seen in layers of stalagmites or mineral deposits in the caves of Megalaya, a northeastern state. from India.
Each of these ages marks dramatic changes in the climate of the planet. The most recent, Megalayense, goes from 4200 years to the present day and began with a drought whose effects were felt during 200 years
Drought caused the Collapse of civilizations and migrations in Egypt, Greece, Syria, Palestine, Mesopotamia, the Indus Valley and the Yangtze River
Scientists believe that this devastating drought was probably caused by changes in ocean and atmospheric circulation. Megalayense, the other two subdivisions of the Holocene are Greenlandiense (11 700-8 300 years before the present) and Norgripiense (8,300-4,200 years).
These phases were defined by global climatic changes recorded by isotopic markers on ice cores taken from two separate holes in central Greenland at depths of 1,492 and 1,228 meters, respectively.
The other name, Norg ripiense, refers to one of those polls in Greenland called NGRIP1 ( North Greenland Ice Core Project No. 1 )
Megalaya, a state in India
For a phase to be considered distinct, it must reflect some change in the overall impact and that is badociated with certain rocks or sediments that clearly show it.
The limit, for example, that 66 million years ago marked the pbadage from Cretaceous to Tertiary can be seen in traces of the element iridium in sediments
This metal was scattered across the planet after the impact of the asteroid that annihilated the dinosaurs.
In the case of Megalayense, the best record can be seen in layers of stalagmites or deposits mineral deposits in caves at Meg to laya, a state in northeastern India .
"Now it's official"
impact of climate changes used in the new clbadification and ensures that it is premature.
Several geologists also questioned the approval of new subdivisions while discussing a possible new phase that reflects the impact of humans on the planet.
image
AFP
Some scientists believe that the impact of humanity on the planet is the most important change that should be reflected in a new clbadification.
This phase was provisionally named Anthropocene and is currently being studied what would be the precise definition and initiation.
"After the study seven years ago and review by several committees, they make a sudden announcement and change the chart," said to the BBC Mark Maslin professor of geography at the University College London and one of the leading scientists in the debate on the Anthropocene.
"Now, it's official, we're in a new one Who could say it? We now have definitions that (…) may go against what most scientists consider the most important change on Earth for 10,000 years. "
Now you can receive notifications from the BBC News World. Download the new version of our application and activate them to not miss our best content.
Source link