
[ad_1]

Image Credit: File / Gulf News
Strong points
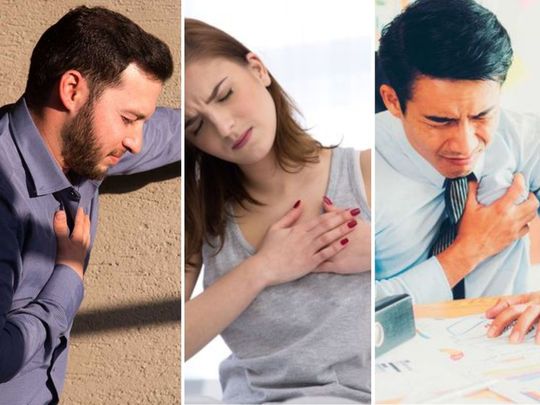
- Cholesterol levels are dangerously high in UAE patients, doctors say; citing the latest data from 30,000 patients
- High levels of bad cholesterol are a major risk factor for cardiovascular disease, which kills 4 times more each year than COVID-19 in 20 months
- Cardiologists weigh in on many factors, including lifestyle, stress, and heredity, that lead to heart disease.
- Know the dos and don’ts to reduce the risk of CVD.
Cardiovascular disease (CVD) is a key risk factor for COVID-19. But in and of itself, CVD is much more deadly – with nearly 400% more deaths each year, compared to COVID.
For the background, the deadly pandemic has so far claimed 4.55 million lives in nearly 20 months (from January 2020 to September 2021), according to figures from Johns Hopkins University.
Reality: CVD kills an average of 17.9 million per year (3.93 times more than COVID), making it the leading cause of death worldwide, according to WHO data.

Image Credit: Jay Hilotin / Gulf News / Photo provided
Amid reports of dangerously high cholesterol levels in UAE patients, three cardiologists intervene:
What is the main cause of cardiovascular disease (CVD)?
There are several causes, instead of just one. Dr Anil Prahalada Rao Kumar, consultant cardiologist at Aster Jubilee Medical Center in Bur Dubai, describes CVD as a “range of disorders” that affect the heart and blood vessels.
- Hypertension
- Stroke
- Atherosclerosis
- Peripheral artery discomfort
- Diseases of the veins
Who are the main contributors to CVD?
Dr Srinivasan Kandasamy, cardiologist at Zulekha Hospital, says “fatty plaques” (or atherosclerosis) are the main driver of CVD. Doctors point to the usual suspects behind cardiovascular disease:
- Unhealthy lifestyle
- Bad eating habits
- Lack of exercise
- Obesity
- Hypercholesterolemia, arterial hypertension
- Excessive consumption of alcohol
- Smoking
- Stress
“An unhealthy lifestyle ranges from smoking and eating unhealthy to eating foods high in salt or foods with excess calories, leading to obesity. They are the biggest contributors to the increase in deaths from cardiovascular disease, ”said Dr Kandasamy.

Image Credit: Jay Hilotin / Gulf News / Photo provided
Which CVD risk factors are out of control?
Two factors – age and heredity – are beyond your control.
At what age does heart disease usually start?
The risk of heart disease increases around age 45 in men and age 55 in women.
Does heredity play a role in CVD risk factors?
Yes. Your risk may be higher if you have close family members who have a history of heart disease.
How does it start?
Current scientific evidence shows that chronic inflammation is a starting point for CVD, Dr. Kumar said. Chronic inflammation plays a key role in the “pathogenesis” (disease development) of CVD and coronary heart disease. This chronic inflammation, also known as “atherosclerosis”, is a major contributor to the incidence and death of CVD.

Image Credit: Gulf News / Photo provided
What does “atherosclerosis” lead to?
The inflammatory processes involve the subendothelial area of the arterial wall, accumulating fat and fat-laden macrophages, among other cell types, Dr Kumar said.
Inflammation is just the answer, said Dr Kumar. “What promotes inflammation is the disruption of endothelial function. Inflammation also leads to the formation of thrombi and multiple pathological consequences such as calcification, stenosis, rupture or hemorrhage.
In its advanced form, atherosclerosis is a major risk factor for coronary heart disease, stroke, peripheral artery disease, heart failure or sudden death.
Is there anything we can do about stress?
There is good and bad stress. “Stress is a part of almost everyone’s life,” said Dr Kumar. “Sometimes it’s not easy to recognize stress because we are caught up in the flow of life.
The good news: Oxidative stress (an imbalance between free radicals and antioxidants in your body) and systemic inflammation are modifiable through nutrition.
“We can also control these risk factors: excessive food intake and physical inactivity, which contribute to the secretion of pro-inflammatory cytokines,” said Dr Kumar.
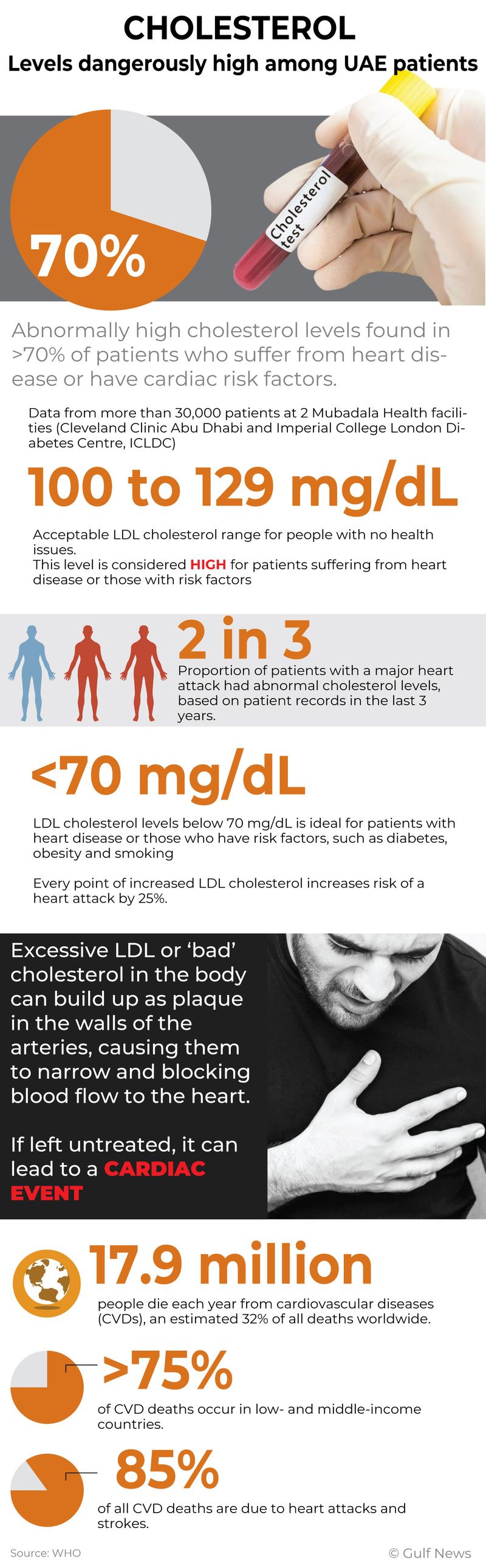
Image Credit: Seyyed dela Llata / Gulf News
Does High Fat / Meat Diet Increase CVD Risk Factor?
“Consuming foods high in trans fats increases the amount of harmful LDL cholesterol in the blood,” Dr. Kumar said. “It reduces the amount of beneficial HDL cholesterol. Trans fats create inflammation, followed by heart disease, stroke, diabetes, and other chronic illnesses.
“They also contribute to insulin resistance, which increases the risk of developing type 2 diabetes. Even small amounts of trans fats can be harmful: for every 2% of calories from trans fats consumed daily , the risk of heart disease increases by 23%.
Dr Brajesh Mittal, Consultant Cardiologist, Medcare Hospital Al Safa, said: “A diet high in fatty foods and meats definitely increases the risk of CVD. These (types of food) lead to an increase in the blood levels of bad cholesterol deposited in the arteries. – causing blockages. “
23%
2% increased risk of heart disease for calories from trans fat, says Harvard Medical School cardiologist Dr. Dariush Mozaffarian
What are the main sources of trans fat?
Trans fats can be found in:
- Bakery products, such as cakes, cookies and pies.
- Shortening.
- Popcorn in the microwave.
- Frozen pizza.
- Refrigerated dough, such as cookies and rolls.
- Fried foods including French fries, donuts, and fried chicken.
- Non-dairy coffee cream.
- Margarine stick.
What’s wrong with red meat?
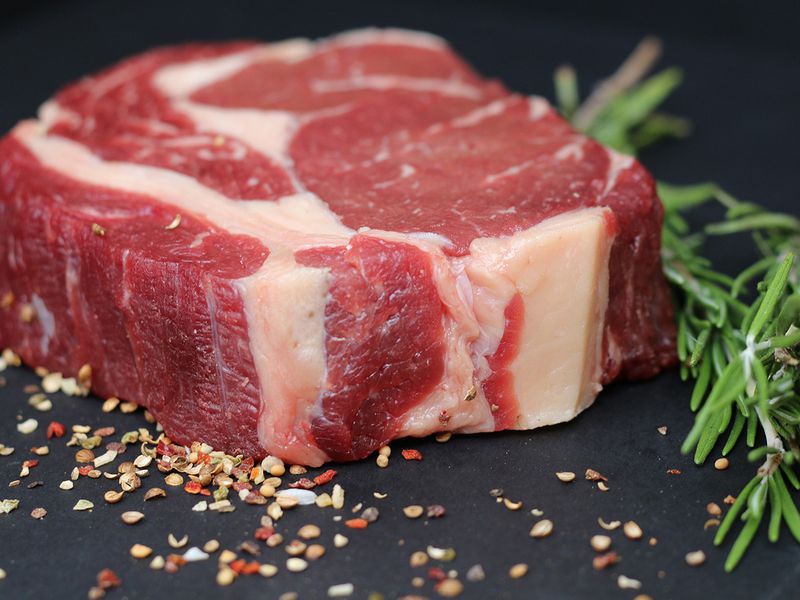

Greater consumption of total, unprocessed and processed red meat is known to be associated with a higher risk of CVD – independent of other dietary and non-dietary CVD risk factors, said consultant cardiologist Dr Anil Prahalada Rao Kumar at the Aster Jubilee Medical Center in Bur Dubai.
“There is evidence that red meat alters the gut microbiome, leading to higher levels of certain pro-inflammatory metabolites and cytokines in the blood, which in turn have been linked to an increased risk of heart disease,” he said. -he adds.
Dr Kandasamy said studies show that “fried foods high in fat, high in calories and high in red meat in any form, whether vegetarian or not, contribute to heart disease.”
What processes are behind the consumption of red meat that contributes to a higher risk of CVD?
Several mechanisms contribute to an adverse effect of red meat consumption on CVD risk, Dr Kumar said.
- Increased low density lipoprotein (LDL) cholesterol levels in the blood.
- Red meat is low in polyunsaturated fats.
- Excessive iron intake could catalyze several cellular reactions involved in the production of reactive oxygen species, thereby increasing levels of oxidative stress.
- Scientists hypothesized that N-glycolylneuraminic sialic acid in red meat generates a pro-inflammatory atherogenic state (promotes the formation of fatty plaques in the arteries) in humans.
- The high sodium content of processed meats may increase the risk of coronary heart disease – by increasing blood pressure and vascular resistance.
What advice do you give people to reduce the risk of CVD?
Dr Kumar:
“Heart disease is a leading cause of death, but it’s not inevitable. While you can’t change some risk factors, such as family history, gender, or age, there are many other ways you can lower your risk.
Dr Mittal:
“Maintain a healthy lifestyle – a healthy diet, foods low in fat and calories, with fruits and salads, regular exercise, weight maintenance, yoga / meditation, adequate sleep, periodic check-ups after 40 years. Also watch blood pressure, diabetes and cholesterol.
Dr. Kandasamy:
“As a cardiologist, I advise people to maintain a healthy lifestyle, to avoid smoking, to take in fewer calories and less fatty foods – every now and then is good, but not as a diet. routine food. Try to eat less salt and lower calorie foods. Take sugar / candy, carbs. Consume more protein, consume foods rich in dietary fiber, try to control your risk factors like diabetes, hypertension or any other risk associated with chronic morbidities.
People who eat more meat have smaller ventricles, poorer heart function, and stiffer arteries, all markers of poorer cardiovascular health.
WHAT IS THE POLYPILL STRATEGY?
- In a landmark study published in 2003, researchers found that it was possible to reduce the risk of ischemic heart disease (IHD) by up to 80%. The study, published in the BMJ, said that the “polypill strategy” results in a proportional reduction in ischemic heart disease (IHD) events and strokes, the prevalence of side effects and the years of life gained.
- The ‘polypill strategy’ study was led by NJ Wald of the Department of Environmental and Preventive Medicine, Wolfson Institute of Preventive Medicine, University of London. In randomized trials, they found that the polypill strategy largely prevented heart attacks and strokes if taken by anyone aged 55 and over – and anyone with existing cardiovascular disease.
- The formulation includes: a statin [i.e. atorvastatin (daily dose 10 mg) or simvastatin (40 mg)]; 3 antihypertensive drugs [for example, a thiazide, a β blocker, and an angiotensin converting enzyme inhibitor], each at half the standard dose; folic acid (0.8 mg); and aspirin (75 mg).
- Safety: Researchers have shown that Polypill causes symptoms in 8-15% of people, depending on the formulation, and is “acceptably safe”.

Image Credit: Gulf News / Jay Hilotin
Source link