[ad_1]
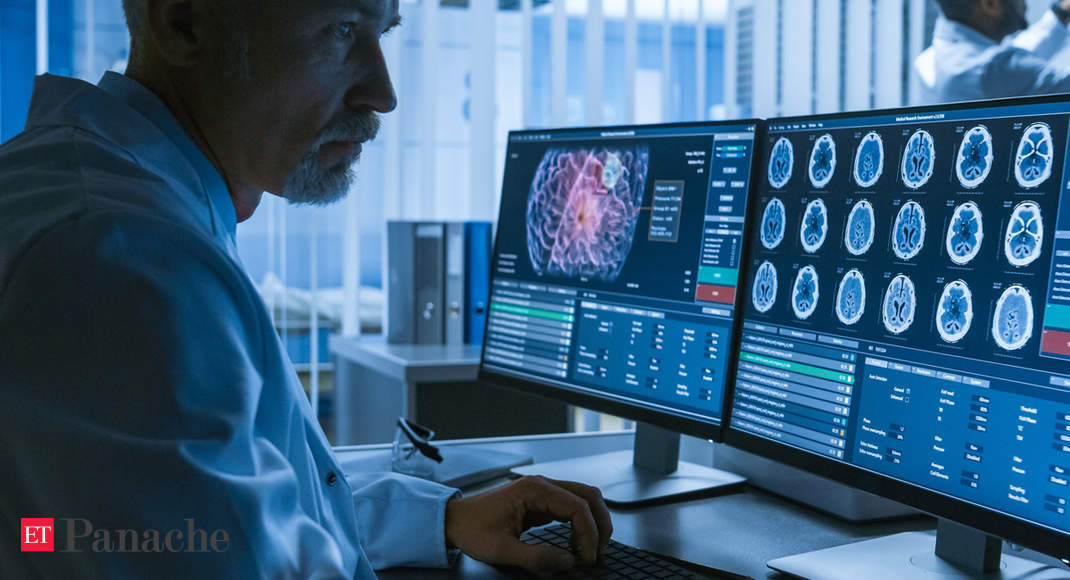
LONDON: Researchers have developed a method of badyzing brain tumors based on artificial intelligence (AI), paving the way for individualized treatment of tumors.
According to the study published in The Lancet Oncology, AI's automatic learning methods, carefully trained in standard magnetic resonance imaging (MRI), are more reliable and more accurate than radiological methods established in the treatment of glioma.
Gliomas, a type of tumor that occurs in the brain and spinal cord, are the most common brain tumors and the most malignant in adults.
"Through this study, we were able to demonstrate the potential of artificial neural networks in radiological diagnosis," said Philipp Kickingereder of the University of Heidelberg in Germany.
For the study, the team included 500 patients with brain tumors. Using a reference database with MRI scans of patients, the algorithms automatically recognized and localized brain tumors using artificial neural networks.
The algorithms have also been used to volumetrically measure the individual zones (tumor portion absorbing the contrast medium, peritumoral edema).
"We want to advance the technology of automated high-throughput badysis of medical image data and transfer it not only to brain tumors, but also to other diseases such as brain metastases or sclerosis." in patches, "said Klaus Maier Hein at the university.
Glioma tumors often can not be completely removed by surgery. Chemotherapy or radiotherapy are only effective to a limited extent because the tumors are very resistant. As a result, new and precisely validated therapeutic approaches are urgently needed, the team noted.
Next Horizon of Science: AI to diagnose cerebral hemorrhage, spaceship for tra …
Tech Surprises
Sep 7, 2018
From the AI who can diagnose a stroke to scientists who use antimatter for a truck ride, here is all that is exciting for the technologies that will shape our future. (Text: Rajarshi Bhattacharjee)
A machine to stop climate change
Sep 7, 2018
Hate carbon dioxide to warm the planet? Switzerland has a giant machine that sucks carbon dioxide from the air and works better than plants. In essence, it is a gigantic artificial tree. Climeworks AG, based in Zurich, is the first plant in the world to capture atmospheric CO2 in the industry. The amount (900 tonnes) of carbon dioxide that the plant takes each year is approximately the same as the amount emitted by 200 cars at the same time.
(Image: www.climeworks.com)
A faster diagnosis of cerebral hemorrhage with IA
Sep 7, 2018
Scientists at the Icahn School of Medicine in Mount Sinai, USA, developed an artificial intelligence platform that could identify the disease in a 1.2 second cerebral computed tomography scan and diagnose a diagnosis. series of acute neurological diseases, such as stroke and haemorrhage. The study shows that the system was faster than the human diagnosis. This is the first study to use AI to detect acute neurologic events and to demonstrate direct clinical application.
A spaceship for intergalactic travel
Sep 7, 2018
Remember the hunting boats led by Valerian (Dane DeHaan) in the movie 2017 Valerian and the city with a thousand planets? The American design and technology company Lexus has developed a concept of a single-seater futuristic vehicle called Skyjet, which will take future human beings on intergalactic journeys. Powered by a compact fuel cell capsule, the Skyjet will fly around 2740 with clean, renewable energy.
(Image: www.lexus.co.uk)
A little space for more memory
Sep 7, 2018
The densest and strongest memory in history is here. It may soon exceed the capabilities of today's hard drives by 1,000 times. Scientists from the University of Alberta in Edmonton, Canada, claim that they can use hydrogen atoms to increase their storage capacity. They were able to achieve a storage density of 128 TB per square inch. That's a lot more than the current 10 TB hard drives, which have about 512 GB per square inch.
(Image: www.ualberta.ca)
[ad_2]
Source link
