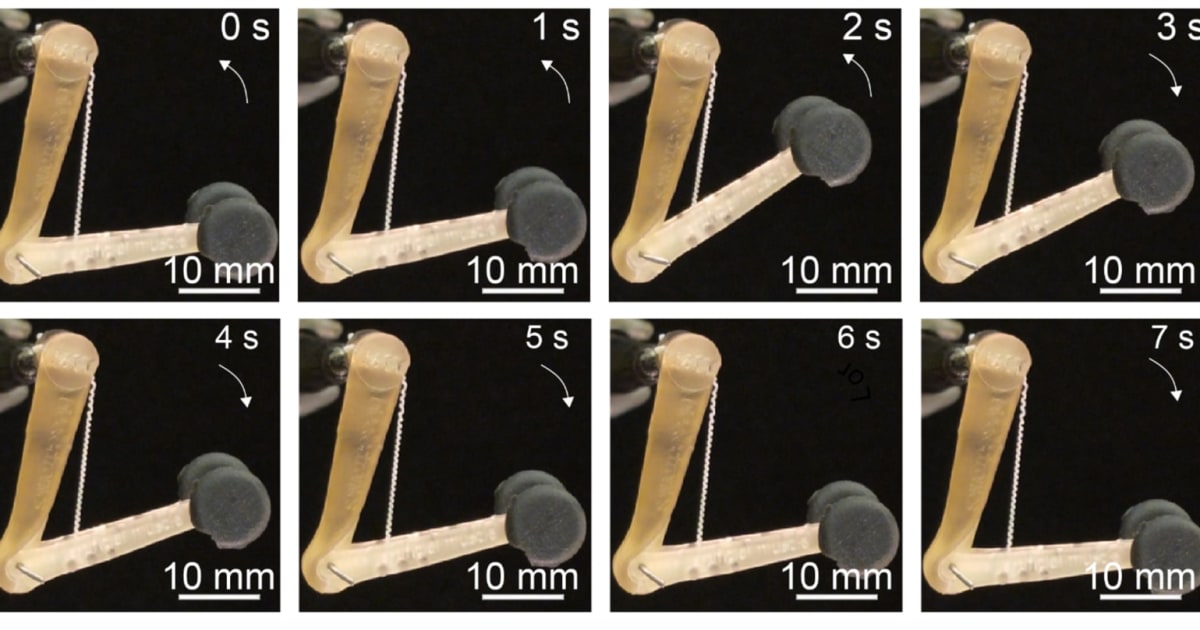
[ad_1]
The fibers can range from a few micrometers in thickness to a few millimeters, and their length can reach several hundred meters. You can also weave other elements into the fiber, such as nanowires (as researchers have done to measure the voltage), electrodes or optical fibers. A robotic member would not need external and bulky heat sources to activate the fibers. And if you bundle the fibers, they could provide automated and accurate control.
Although it is still a laboratory experience, there is a lot of potential. Tiny medical robots could work on your body from the inside, while the big robots could be muscular, fast or both. This could be especially vital for prosthetic limbs, where hydraulics and other machines can hinder them. An artificial limb could not only be more natural, but offer a more comparable response time.
Source link