
[ad_1]
Engineers at the Jet Propulsion Laboratory (JPL) near Los Angeles said this successful landing was confirmed by signals relayed to Earth by one of two miniature satellites launched with InSight and flying over Mars upon his arrival shortly before 3 pm EST (2000 GMT).
? I would like you to be here! @NASAInSight sent his first picture after #MarsLanding: The view of InSight is flat, smooth … https://t.co/ZbbR0C9IgC
– NASA (@NASA) 1543262604000
Members of the mission control team applauded and cheered as they received data showing that the spacecraft had survived its dangerous descent to the Martian surface.
The landing completed a six-month journey to 301 million miles (548 million km) of the Earth, following its launch from California in May.
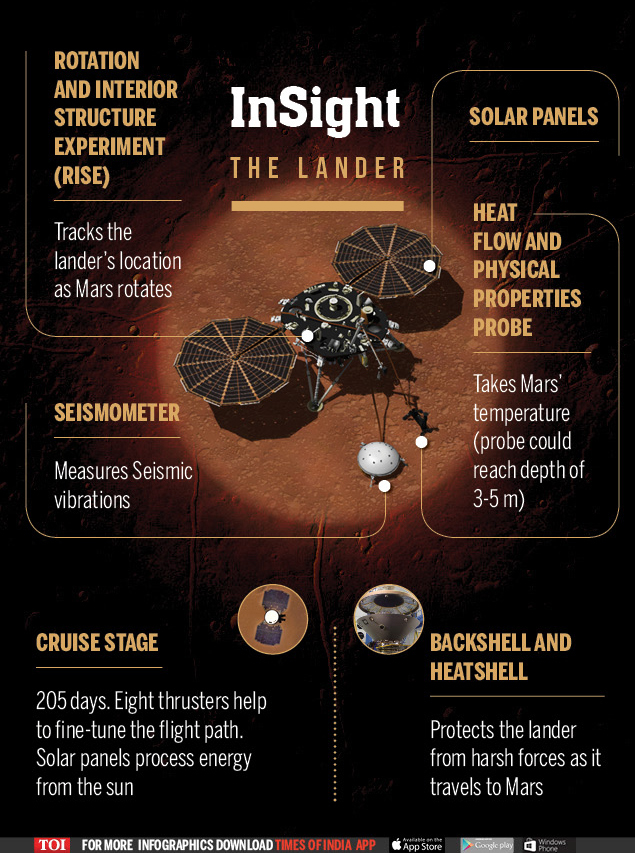
Wearing instruments that detect planetary heat and seismic rumblings that have only ever been measured on the Earth, the stationary undercarriage interferes with the thin Martian atmosphere at a speed of 19,300 km / h.

His 77-mile descent was then slowed down by atmospheric friction, a giant parachute and retro rockets, causing the three-legged spacecraft to land a smooth landing 6:30 minutes later. InSight has been immobilized as planned in the middle of a vast bare plain called Elysium Planitia, near the planet's equator.
InSight will spend 24 months – about a Martian year – taking seismic and temperature measurements to unlock mysteries about the formation of Mars and, by extension, about the origins of the Earth and other rocky planets of the internal solar system.
Our @NASAInSight spacecraft blocked the #MarsLanding! His new home is Elysium Planitia, a still flat area and … https://t.co/PrgkLOBjTF
– NASA (@NASA) 1543262172000
The fixed probe is programmed for a 16-minute break for that dust literally settles around its landing site, before disc – shaped solar panels unfold like wings to provide energy to the spacecraft.
A few minutes after the landing, the JPL controllers received a fuzzy picture of the new probe environment on Martian soil.
InSight – its name is the abbreviation for Inner Exploration Intelligence using seismic surveys, geodesy and heat transport – is the 21st Mars mission launched by the United States, which dates back to overflights of Mariner in the 1960s. Nearly two dozen other missions on Mars were sent by other countries.
[ad_2]
Source link