[ad_1]
In what could be the second major discovery in less than a year, Astrosat, the first multi-length space observatory of the Indian Space Organization (ISRO ), captured an image of a cluster of special galaxies. The Galaxy cluster is located more than 800 million light years away. Remarkably, Astrosat also discovered a weak dwarf galaxy – Wolf-Lundmark-Melotte (WLM) – which is located three million light-years from Earth.
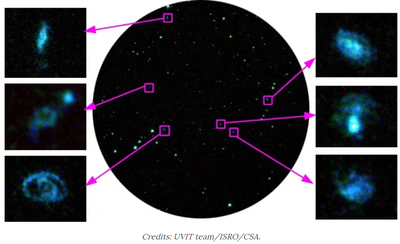
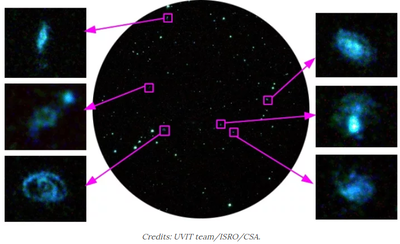
The cluster of galaxies named Abell 2256 is made up of three clusters of galaxies that are all merging with each other. Scientists are of the opinion that this will eventually form one mbadive group in the future. These three fusion groups have more than 500 galaxies and almost 100 times larger and more than 1500 times mbadive compared to our own galaxy of the Milky Way.
The Indian Space Research Organization posted the details on its website Astrosat Far Picture of the Month (APOM) to date. ISRO says that the fusion of the three clusters of galaxies has produced a rich diversity of structures that have been imaged in radio wave lengths by all radio telescopes in the world.
Astronomers have zoomed in on six of these galaxies to capture ultraviolet images, although the cluster contains galaxies spread over a large area. To capture the images of these galaxies, astronomers have used the Ultraviolet Imaging Telescope (UVIT), one of the five instruments embedded on Astrosat.
Astronomers explain that clusters of galaxies slowly transform into lenticular and elliptical galaxies. Spiral galaxies, like our own Milky Way, are more blue in color and form stars all the time. However, elliptical and lenticular galaxies are redder and contain mostly old stars. Abell 2256 is one of those clusters of galaxies where astronomers believe that many galaxies cross this metamorphosis.
Astrosat is the first space observatory dedicated to multiple wavelengths in India. It was launched on a PSLV-XL on September 28, 2015. With the success of this satellite, ISRO has proposed to launch AstroSat-2 as a return for Astrosat as its lifespan approaches. of five years old
[ad_2]
Source link