[ad_1]
Sediments collected by an international team of researchers, including those from a stalagmite cave at Meghalaya, helped define the smallest climatic event in the history of the Earth.
Agricultural Societies That Developed in Several Regions After the End of The Last Ice Age was hit hard by the 200-year-old weather event that resulted in the collapse of civilizations and human migrations in Egypt , Greece, Syria, Palestine, Mesopotamia, the Indus Valley and the Yangtze Valley.
<! –
->
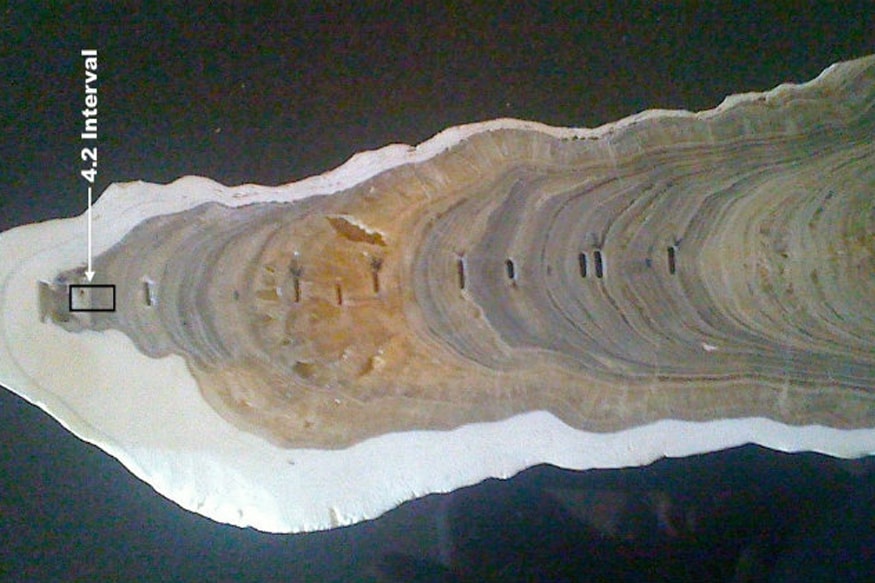
Evidence of the 4200-year-old weather event has been found on all seven continents.
The age of the Upper Holocene meghalayan was ratified as the most recent unit of the geological time scale after many years of research. Two other ages: the Middle-Holocene Holocene age and the age of the Holocene-early Greenland with defined beginnings during the climatic events that occurred respectively about 8300 and 11 700 years ago were also approved. The three ages include the Holocene epoch, which represents the time elapsed since the end of the last ice age.
The meghalayan age is unique among the many geological time scale intervals in that its onset coincides with a global cultural event produced by a global climate event, said Stanley Finney, professor at the University of California. State University of Long Beach in the United States. General of the International Union of Geological Sciences (UISG) in France.
The International Stratigraphy Commission, responsible for standardization of the geological time scale, approved the definition of the beginning of the youngest unit of the geological time scale according to the date of this event
. The Geological Time Scale units are based on sedimentary strata that have accumulated over time and contain sediment types within them. fossils and chemical isotopes that record the pbadage of time and the physical and biological events that produced them.
The three new ages of the Holocene epoch are represented by a wealth of sediments accumulated all over the world on the seabed, on the lake. the bottoms, in the form of glacial ice, and in the form of layers of calcite in the stalactites and stalagmites.
Sedimentary strata intervals on which ages are based The lower boundary of the Greenlandic and NorthGrippian stages is defined at specific levels in Greenland ice cores. The lower limit of the Meghalayan stadium is set at a specific level in a stalagmite of a cave in northeastern India
Ice cores and stalagmite are now identified as international geostandards and have been placed in protected archives accessible for further study.
The decision to define these new stages of the Holocene series and thus the three new corresponding ages of the Holocene epoch allows for an update of the international chronostratigraphic chart, which represents the calendar of complete geological history of the earth.
See also
[ad_2]
Source link