
[ad_1]
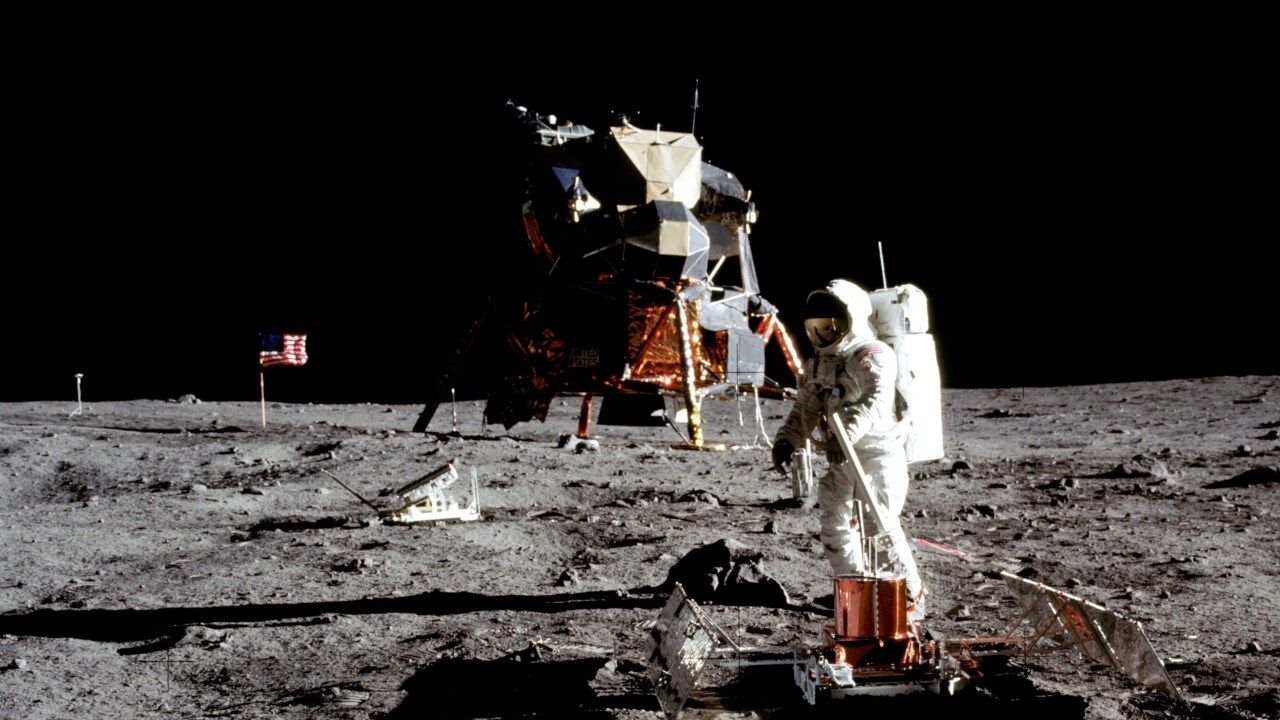
Here is one of the most famous images of history, clicked by the first man on the moon.
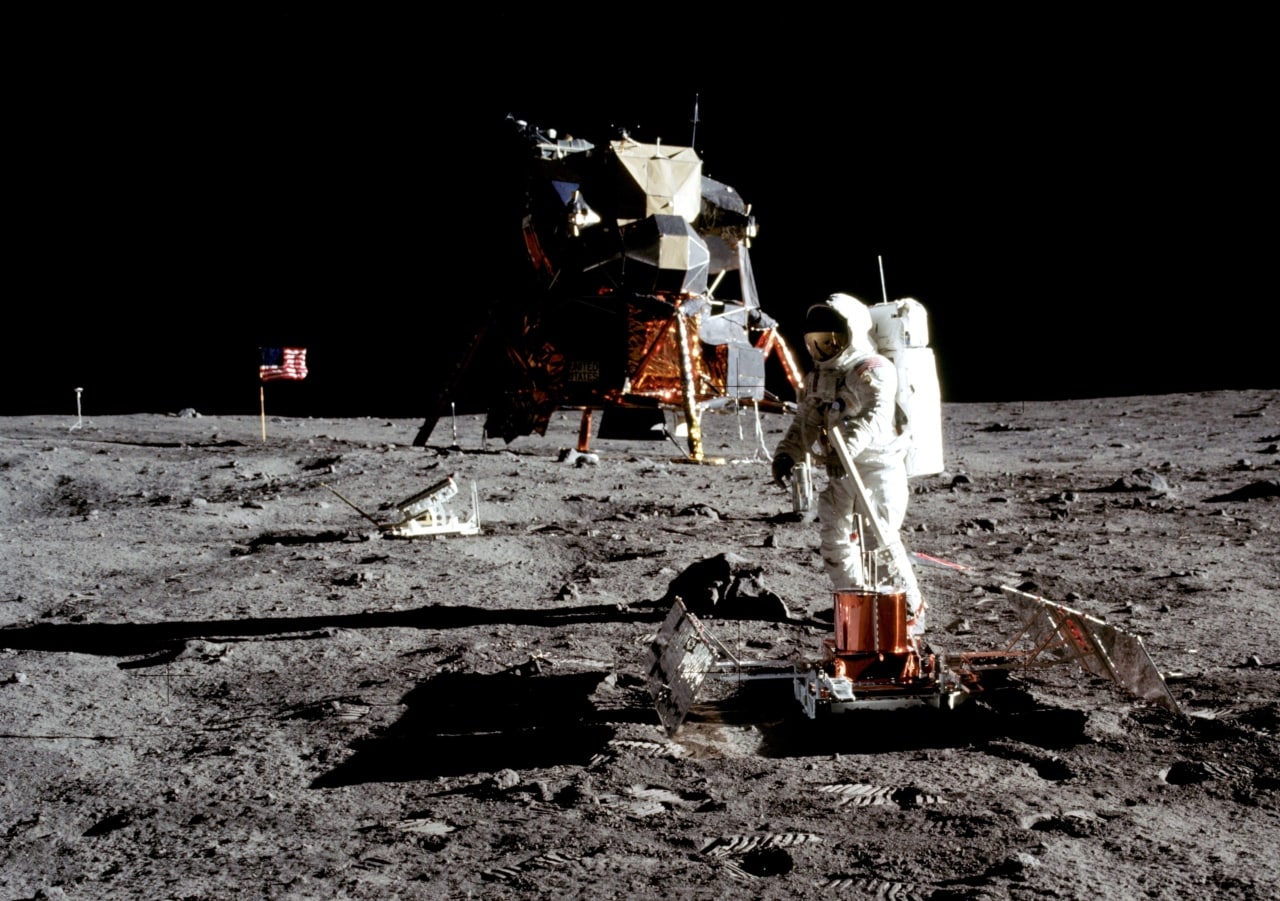
Neil Armstrong captures the astronaut of D & C Apollo 11, Buzz Aldrin, working on the deployed package of pbadive seismic experiment on July 20, 1969. Image courtesy: NASA
The next image of the planet Jupiter is a contemporary legend clicked by the NASA. Juno.
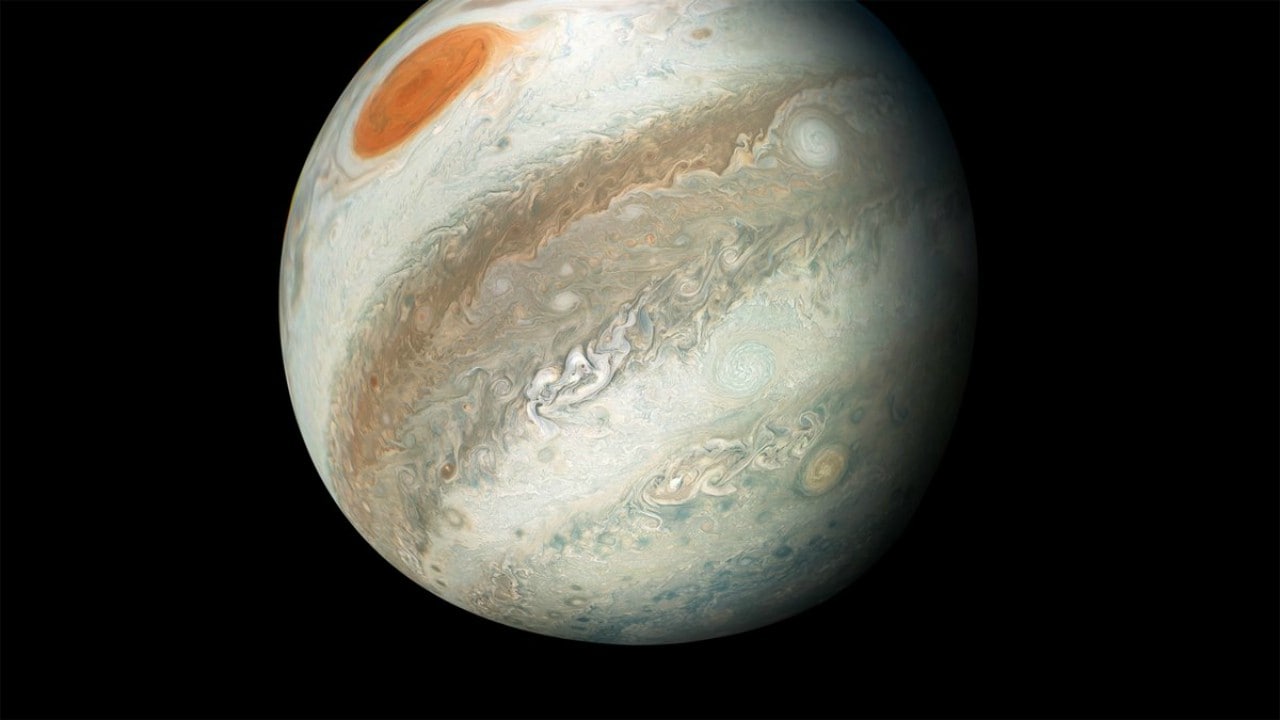

In this May 2018 image, the extraordinary view of Jupiter from the south shows the great red spot as if it were in the northern territory. Image courtesy of NASA
This one comes from the only laboratory that humans have built in space.
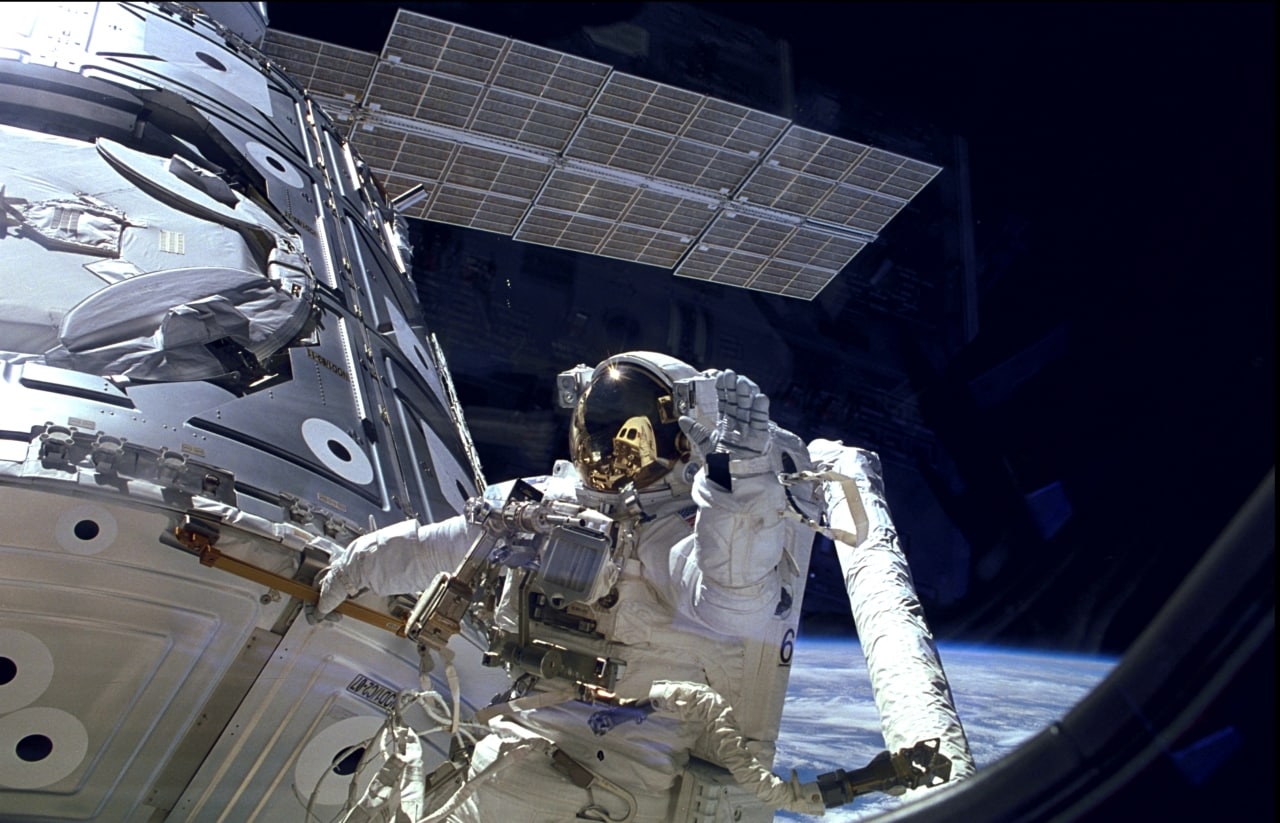

Astronaut James Newman is making waves at an exit into space outside the International Space Station. Image reproduced with the kind permission of NASA
Finally, the Earth seen from the moon
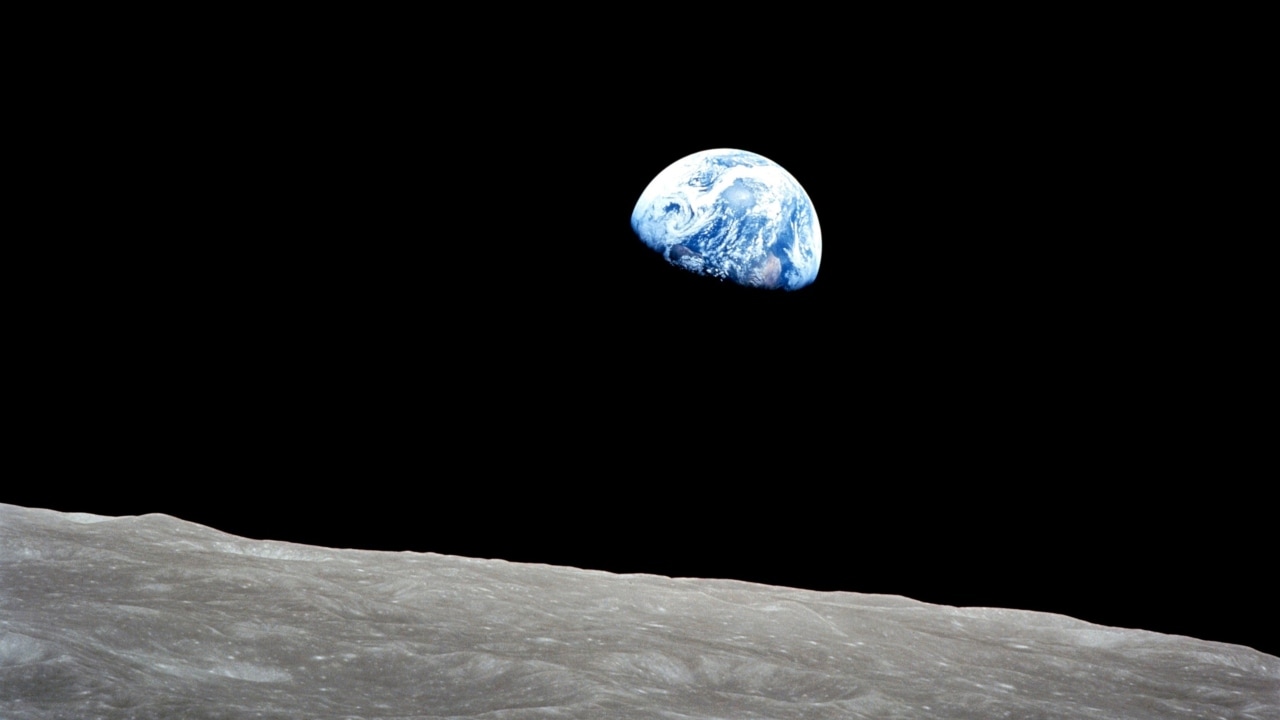

Contrasted against the lunar surface marked by the crater, the Earth is seen rising above the moon in this image of December 24, 1968. Image courtesy: NASA
These are four of the most famous images ever clicked in space. But do you notice that they are missing something?
The only thing common to all is the lack of stars in the background. Given the density of the heavens observed from the Earth on a clear night, this absence of stars in the background has led several conspiracy theorists to question the legitimacy of these images – and sometimes even Historical events like the lunar landing
So do the governments of the world conspire against us to hide the fact that no one has ever gone into space? Because without an atmosphere in the space to block the view of the stars, why do not we see Vincent van Gogh-esque images when astronomers click on images of celestial objects?
The answer has to do more with photography While in space, astronomers can indeed see stars – and perhaps only stars when they look away from the Sun. But these stars are extremely dark compared to the light reflected by the subject of the image (which is the Earth in the case of the last image and Buzz Aldrin in the case of the first). To capture this bright subject, the camera needs to adapt to very short exposure and fast shutter speeds – settings that do not capture dark stars as well.
Without atmosphere, light from the Sun makes a planet (or the International Space Station in the third image) at least as bright as the sunlight we receive on Earth during a clear afternoon. This forces the space cameras to be tuned to the settings we would use on a bright midday here on Earth. And this leaves no chance for the faint stars of distant galaxies to appear on these images
However, unlike their cameras, astronomers can see both stars and a planet in the foreground at the same time when they look at their spaceships. This is because the human eye is much more sensitive to light than a photographic film or a sensor.
This effect of the disappearance of stars in the background in the photographs of space can also be demonstrated on Earth. On a full moon night, the number of visible stars in the sky is much lower than during a new moon night – and that is because dark stars are faded by the sunlight reflected by the moon. The same reason applies to images of sports events held at night, and images of bright night markets in cities around the world.
However, this does not mean that stars can not be captured by cameras in space. We have telescopes like the Hubble Telescope stationed in space for the sole purpose of capturing star systems and galaxies in our universe. In conclusion, here is an image captured by the Hubble to demonstrate exactly this:
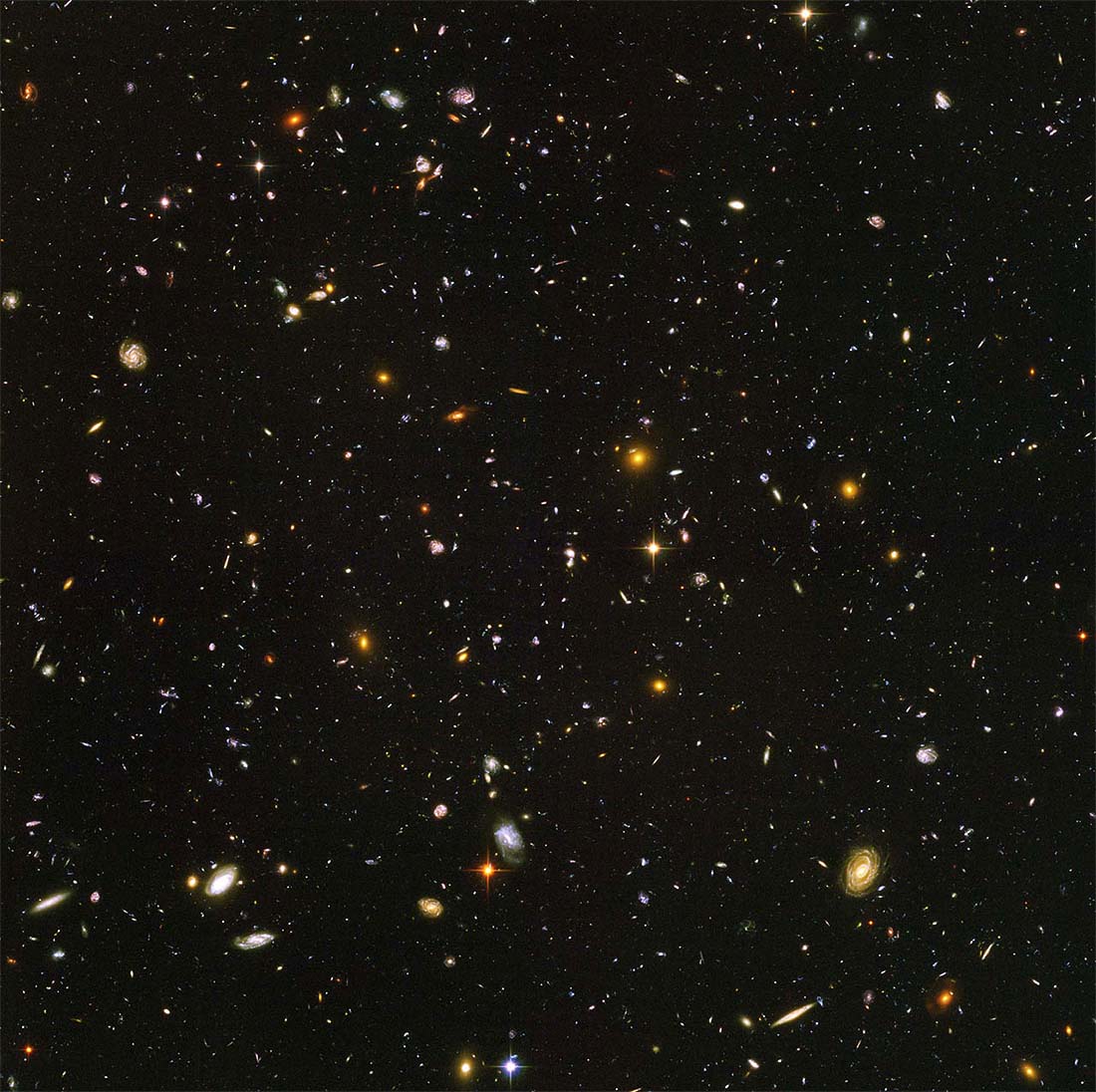

The "Hubble Ultra Deep Field" shows the galaxies furthest away from Earth. Image courtesy of NASA
[ad_2]
Source link