[ad_1]
An important article from the Mayo Clinic is the important role played by physicians, hospitals and community members in raising awareness, advice and guidance on the proper use of drugs and reducing their development. Resistance to antibiotics.
Drug resistance
Bacteria become resistant to the drug when they change to protect themselves from drug interactions.
Any bacterium that survives antibiotic treatment can multiply and transfer antibiotic resistance properties. In addition, some bacteria can transfer their drug resistance properties to other bacteria, as if they were pbading a cheat sheet to help others succeed and survive.
The development of bacteria to resist the drug is a natural and predictable reality. However, the method of use of the drug influences the speed with which the drug's resistance and its extent.
overuse
Excessive use of antibiotics, especially during absorption, even in the absence of adequate treatment, promotes bacterial resistance to antibiotics.
Antibiotics are treated with bacterial and non-viral infections. For example, antibiotics are an appropriate treatment for contractile sore throat caused by Streptococcus bacteria. However, they do not constitute the most appropriate treatment for sore throats resulting from a viral infection.
If you take antibiotics and have a viral infection, antibiotics will continue to attack your body's bacteria, which are useful or at least non-pathogenic bacteria in this case. This inappropriate treatment can improve the antibiotic resistance properties of harmful bacteria that can be transmitted to other bacteria.
– Common viral infections that are not useful for the treatment of the following antibiotics:
Ⅶ Cold
Ⅶ flu
Ⅶ Bronchitis
Most cases of cough
Most sore throat
Ⅶ Some ear infections
Ⅶ Some sinus infections
Flu intestinal flu (gastroenteritis)
Several factors probably contribute to the excessive use of antibiotics. When penicillin and other antibiotics were used for the first time, they were considered fantastic drugs, acting quickly with relatively few side effects. He seemed to treat all common diseases.
Although awareness of antibiotic resistance has increased in recent years, overuse continues to occur for several reasons, including:
Doctor The doctor may prescribe antibiotics before receiving the test results determining the actual cause of the infection.
People who want to quickly relieve symptoms, regardless of the cause of the disease, can put pressure on the doctor to prescribe antibiotics.
People can take antibiotics sold abroad or online after the diagnosis of the disease.
Ⅶ People can take antibiotics left by previous prescriptions.
Problems not in accordance with the instructions:
Contraindications to antibiotics may also contribute to antibiotic resistance.
The instructions of the antibiotic indicate how much grain should be consumed and how often. The prescription is made so that you know exactly how many medications you need to complete the treatment.
It is tempting to stop taking antibiotics when you feel better. But all the treatment is necessary to kill the pathogenic bacteria. Discontinuation may require further monitoring and promote the spread of antibiotic resistance properties between harmful bacteria.
Antibody resistance
For years, the discovery of new antibiotics has surpbaded the development of antibiotic resistance. However, in recent years, the pace of drug resistance has contributed to worsening health problems.
In the United States, according to the 2013 report of the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC), at least 2 million people a year (severe infection or bacteria resistant to antibiotics or intended for the treatment of infection). At least 23,000 people die each year from antibiotic-resistant bacteria.
This increase in drug-resistant infections results in:
Ⅶ more serious diseases or disabilities
More deaths than pre-treatable diseases
Duration of the recovery period
Ⅶ reserve the hospital longer or longer
Increase the number of visits to the doctor
Treatments Less effective or more effective treatments
Treatments more expensive treatments
Antibiotic management
The proper use of antibiotics – often called antibiotics – can help maintain the effectiveness of existing antibiotics, increase their effectiveness and protect people from antibiotic-resistant infections.
Many hospitals and medical institutions have implemented new guidelines for diagnosis and treatment to ensure effective treatment of bacterial infections and reduce the inappropriate use of antibiotics. The public also plays a role in the management of antibiotics.
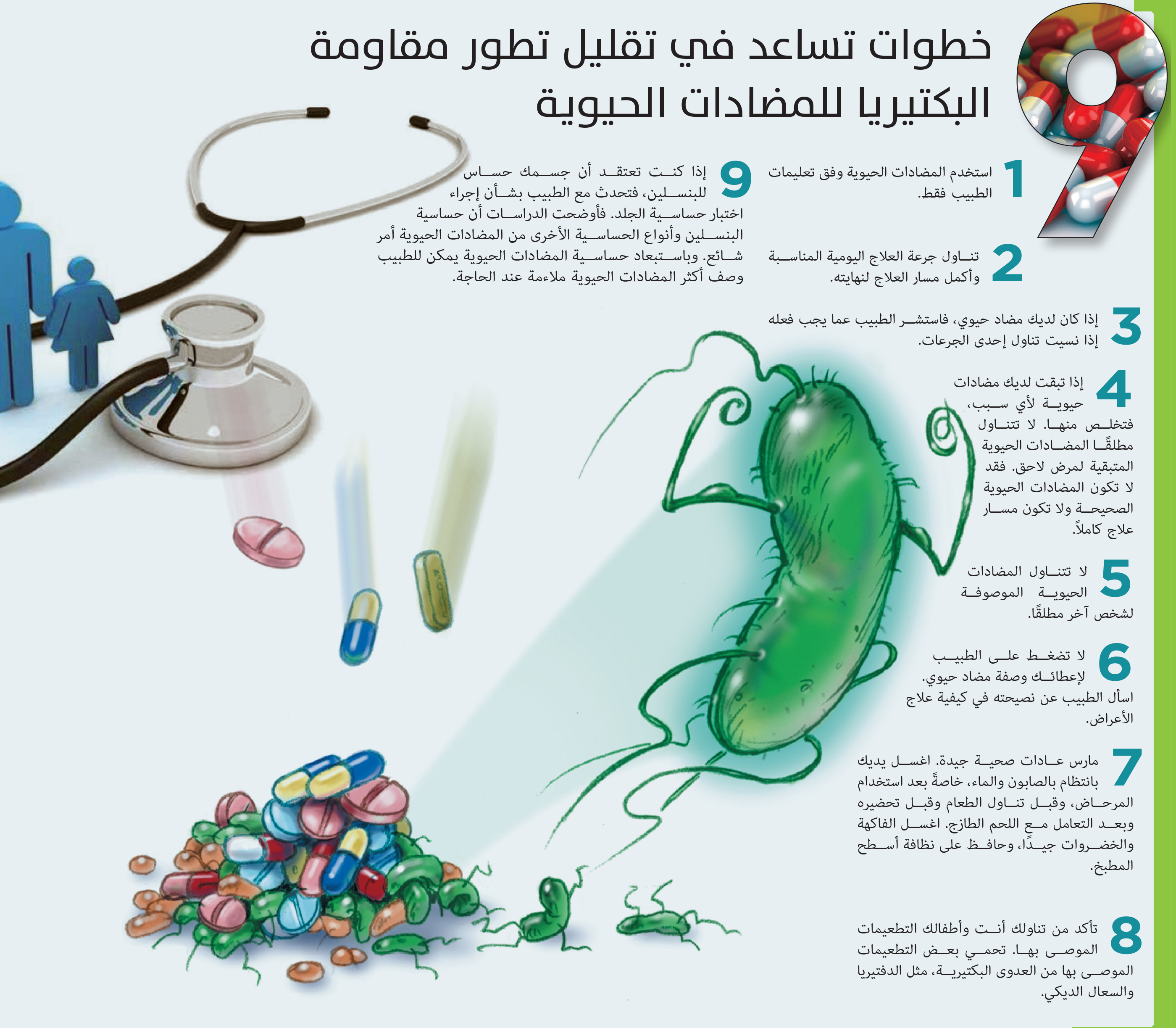
Steps to help reduce the development of bacterial resistance to antibiotics
1 Use antibiotics as directed by your doctor.
2. Take the appropriate daily dose of treatment and end the treatment accordingly.
3 If you have an antibiotic, talk to your doctor about what to do if you miss a dose.
If you have antibiotics for any reason, eliminate them. Never take the remaining antibiotics for later illness. They may not be the right antibiotics and are not a complete treatment.
5 Do not take any antibiotics prescribed to another person.
Do not push your doctor to give you a prescription for antibiotics. Ask your doctor for advice on treating the symptoms.
March 7, good health habits. Wash your hands regularly with soap and water, especially after using the bathroom, before eating, before preparing and after handling fresh meat. Wash fruits and vegetables well and keep kitchen surfaces clean.
Make sure you and your children have the recommended vaccines. Some recommended vaccinations protect against bacterial infections, such as diphtheria and whooping cough.
If you think your body is sensitive to penicillin, talk to your doctor about the skin sensitivity test. Studies have shown that the sensitivity of penicillin and other allergies to antibiotics is common. By excluding antibiotic susceptibility, your doctor may prescribe the most appropriate antibiotics when needed.
According to a recent medical study. Half of the antibiotics are described as undiagnosed for infection
After years of warnings about antibiotic abuse, a new medical study found the problem was far from over. The researchers found that of the more than 500,000 antibiotic prescriptions badyzed, nearly half of which had been described without a diagnosis of infection, about 20% of the antibiotics were administered by telephone without consulting a doctor.
Concern
"It's unclear how much of these recipes are really inappropriate," said Jeffrey Linder, head of research at the Fenberg School of Medicine at Northwestern University in Chicago. He explained that his team had reviewed patient records and that a "bad coding" could be part of the problem, referring to the system used by doctors to record the diagnosis. However, the results are disturbing.
The researchers have suggested that some doctors still prescribe antibiotics easily – perhaps in part because they badume that patients are willing to treat them. But this anti-inflammatory use is the driving force behind the spread of antibiotic-resistant infections.
L & # 39; s effectiveness
The researchers added that antibiotics are only effective against bacterial infections – not against normal colds or other diseases caused by viruses. When patients use antibiotics unnecessarily, they expose bacteria to drugs and give them the ability to mutate and become resistant. For years, public health experts have warned doctors and patients against the use of random antibiotics.
For this study, the research team examined approximately 510,000 prescriptions of antibiotics distributed in 514 clinics in two years: doctors, nurses, paramedics and specialties such as gastrointestinal diseases and skin conditions.
Š Š Š ¨ ..
ØÙÙŠŠØØØ ±
Š Š ƒƒ † †
Interest Pine
Øج "" +
What is App
Source link
