[ad_1]
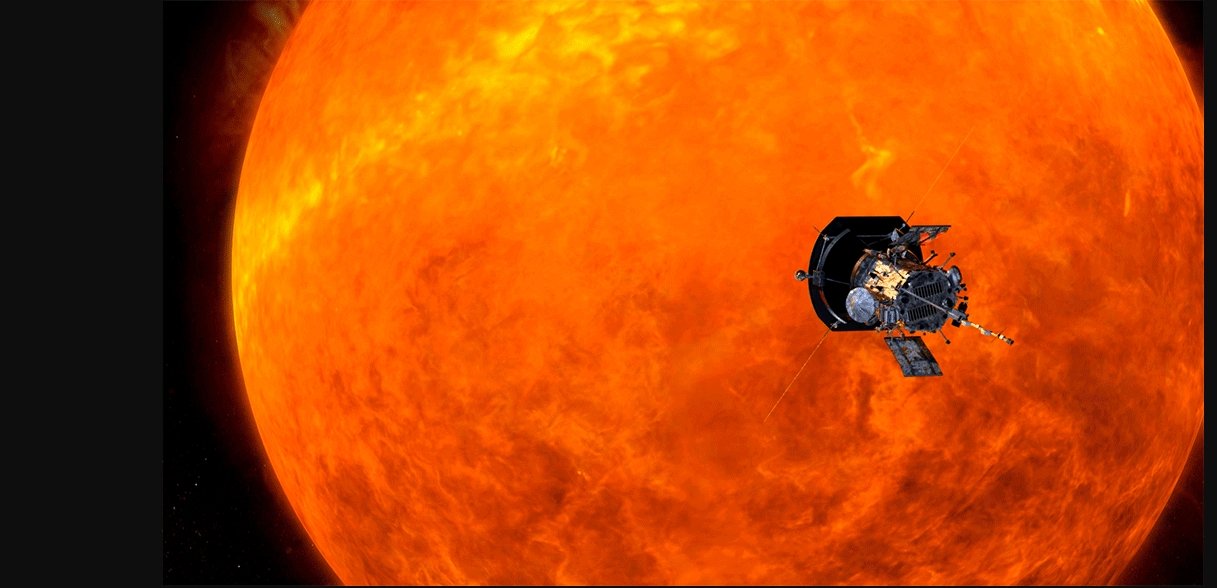
In this part of the solar atmosphere, called the crown, the PSP will conduct unprecedented observations of forces that emit energy, heat and particles to the solar system and well beyond beyond the orbit of Neptune. The inside of the crown is, of course, incredibly hot. The probe circulates in a substance with a temperature above 500 000 ° C and a high intensity light source.
Why the probe does not dissipate?
The Parker Solar Probe probe has been designed to withstand extreme mission conditions. The most important protection is provided by a specially designed heat shield and an autonomous system that protects the mission from intense sunlight but allows the material to "touch" it.
Why the probe does not dissipate
It is necessary to understand the concepts of heat and temperature and their differences. High temperatures do not necessarily mean the warming of another object
The temperature of the cosmos can reach thousands of degrees, although objects can not, at least, become more intense. How can this be? Temperature is the measure of particle velocity, while heat indicates the amount of energy that they transmit. The particles can work very quickly (high temperature), but if the particles are very small, they do not transmit much energy (low heat). Since the space is essentially empty, the probe transfers very few particles.
For example, the temperature of the crown during which the PSP flies is extremely high, but the density of the material that it contains is extremely low. Compare inserting the hand into the oven and inserting into a pot of boiling water (do not try it at home!) – you'll keep your hand baked a lot longer and at a much higher temperature than in water. So the sun's crown is much rarer compared to the surface, so the probe works less hot particles and less heat.
Therefore, although the PSP will fly in space at temperatures of several million degrees, ~ 1400 ° C)
Shield protecting it
Of course, it would be difficult to name a thousand and a half degrees of temperature as summer snow. (For comparison, the volcano triggers a lava of 700-1200 ° C. This heat, the PSP is protected by a thermal shield – a thermal protection system (TPS) 2.4 m in diameter and 115 mm d & Thickness that maintains a comfortable temperature of 30 ° C on the other side of the panel).
TPS was created at the Johns Hopkins Applied Physics Laboratory, and was developed by Carbon-Carbon Advanced Technologies, using carbon composite foam between two carbon panels. This light insulation on the side facing the sun is covered with white ceramic paints, to reflect more warmth. Tested at 1650 ° C, the TPS will increase the heat transmitted by the sun and will protect virtually all instruments.
Vayamatis
But not all Solar Parker Probe instruments are hiding behind TPS. The Solar Probe Cup of the SPS heat shield will be one of two unshielded instruments. This instrument is what is called a Faraday ship, a sensor to determine the strength and direction of ions and electrons in a solar wind. Because the intensity of the solar atmosphere was extremely high, it was necessary to create unique technologies that ensure the survival of electronics, but also accurate data.
The vessel is made of titanium, zirconium and molybdenum alloys (melt temperature 2349 ° C). The electric field of the Solar Probe Cup is tungsten, the metal having the highest melting point (3422 ° C). Typically, in these chips, grid lines are burned in lasers – but because of the high melting temperatures, they had to acidify them in this case.
Another challenge was the electrical installation – most of the heat dissipated. The team solved this problem by producing roped sticks with sapphire crystal tubes, while the wire itself was made of niobium.
In order to test the resistance of the instrument, the researchers had to replicate the heat of the sun in the laboratory. To do this, they used a particle accelerator and specially designed for high temperature IMAX projectors. The projectors repeated the heat of the sun, and the particle accelerator pulled the radiation from the ship to make sure the device captures the particles precisely even under such conditions. And to clarify if the Solar Probe Cup would support such a hostile environment, Odeillo Solar Furnace was used – where 10000 custom mirrors were concentrated in one spot
The Solar Probe Cup test withstood and the longer it was in the environment test, the more it was clear. results provided. "We believe that the radiation has eliminated all potential pollutants," said the SWEAP instrument at the University of Michigan Ann Arbor. Researcher Justin Casper. "Essentially, he's purified."
Save the cold probe
The heat of the safety of the PSP and some technologies of more. Energy-efficient photovoltaic panels can overheat without protection. Whenever we approach the Sun, the elements slide in the shadow of the heat shield, so that the intense light of the sun only lights up a small segment .
But so close to the Sun, you need more protection. The cooling system of the elements is incredibly simple: a heated capacity to protect the freezer against freezing during the flight, two radiators, aluminum panels for a larger cooling surface and a circulation pump. The power of the cooling system would be sufficient for a medium sized salon, and it will maintain the operating temperature of the device and instruments in the solar heat.
The system refrigerator will be 3.7 liters of deionized water. Although full of chemical refrigeration can be very small compared to water and operate at a temperature between 10 ° C and 125 ° C. To prevent water from boiling, it will have a pressure in the system which will drain the boiling point above 125 ° C.
Another problem with the probe is communication. Most of the trip to the PSP will have to think: the probe's signal will last more than 15 minutes, so if something goes wrong, it may be too late to fix a bug
. Sun Path Several sides of the smartphone's size sensors are attached to the probe along the shadow of the heat shield. Anyone who has recorded sunlight notifies the central computer and the sensor can adjust its position so that the sensors and other instruments remain safe. All this must be done without human intervention, so the central computer software has been programmed and carefully checked that all necessary adjustments can be made on the flight.
After launch, the PSP probe will determine the sun's position, move it to the heat shield, and continue its journey for three months, shielding the heat from the sun and the emptiness of space.
The probe on our star will turn 24 times. Whenever he approaches, he will take samples of the solar wind, study the sun's crown, and present the images of our star near him – he will be able to stand his cold mind all the time with various innovative technologies [19659025]! Function (f, b, e, v, n, t, s) {if (f.fbq) returns; n = f.fbq = function () {n.callMethod? n.callMethod.apply (n, argument): n.queue.push (argument)}; if (! f._fbq) f._fbq = n; n.push = n; n.loaded =! 0; n.version = 2.0 & # 39 ;; n.queue = []; t = b.createElement (e); t .async =! 0; t.defer =! 0; t.src = v; s = b.getElementsByTagName (e) [0]; s.parentNode.insertBefore (t, s)} (window, document, script, // connect.facebook.net/en_US/fbevents.js');fbq(& # 39; init, # 1720142964883079 & # 39;); fbq ("track", "Pageview");
[ad_2]
Source link