
[ad_1]
Under what circumstances can an asteroid be called an "asteroid"? When is a binary pair. It turns out that an "asteroid" discovered last year is not really an asteroid, but two objects that are in orbit with respect to one another. other. This particular duo, called 2017 YE5, belongs to an exceptional class of objects close to the Earth.

The interstellar asteroid Oumuamua has its own natural propulsion system
Its passage in the Solar System was very short, but its elongated shape like that of a cigar and of its …
Read more
The 2017 YE5 object was identified by astronomers from the Oukaïmeden Observatory of Morocco last December. There was no knowledge of the object, in addition to that it existed. In June, the object approached Earth – it will no longer be in such a close position for another 170 years – and researchers have been able to analyze it closely. What first looked like an asteroid turned out to be two objects in orbit, rotating between them: a binary asteroid.
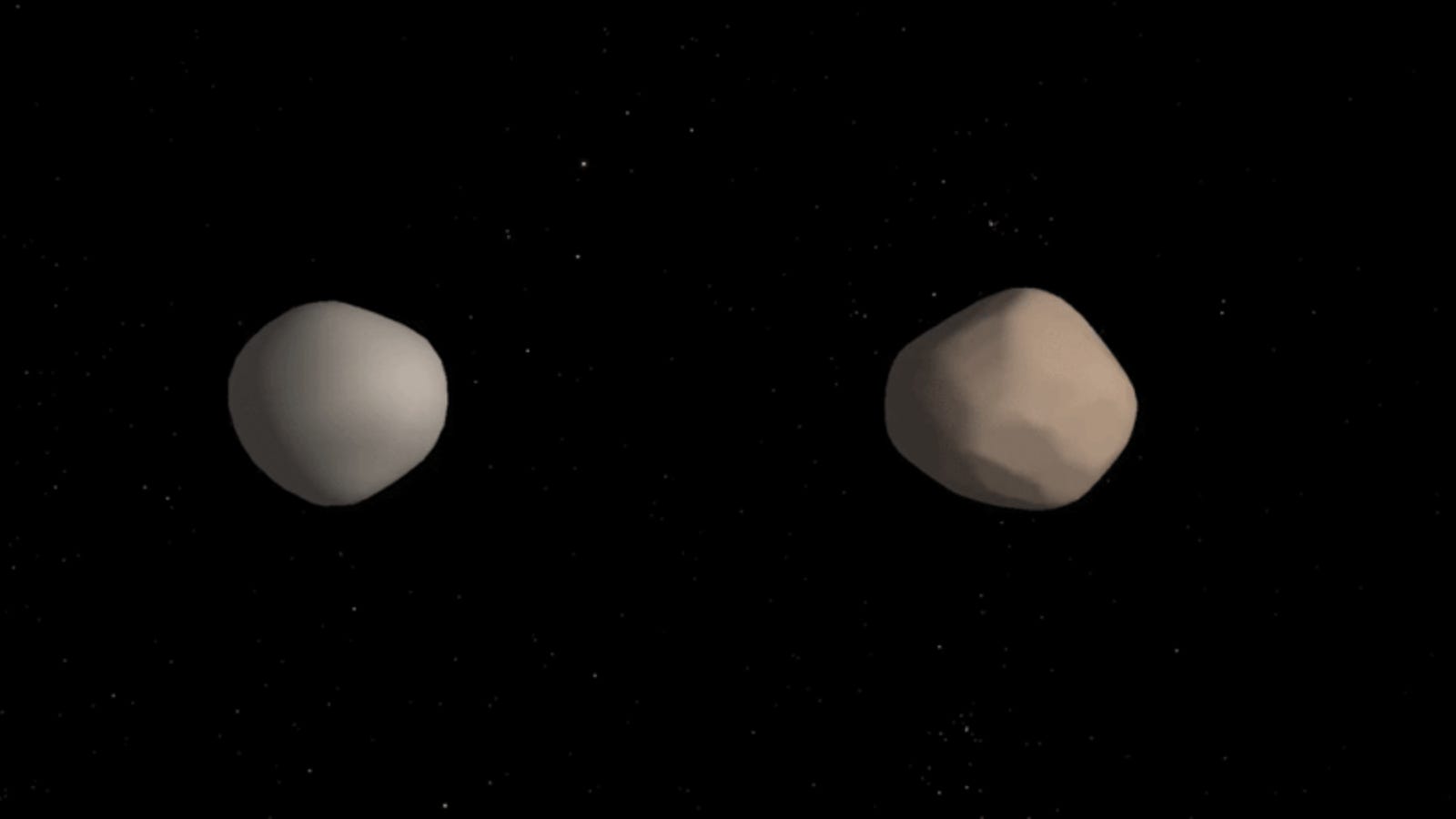
Normally we would say that this is not a big deal. About 15% of all known asteroids with a diameter greater than 200 meters are binary. But 2017 YE5 is special because it is a binary asteroid with an "equal mass", which means that both objects have approximately the same mass. Most binaries are composed of an uneven pair, where one asteroid is significantly larger than the other. Astronomers have documented thousands of asteroids in the solar system, but only four binaries with an equal mass. The latest observations offer the most detailed pictures ever made of this exceptionally rare phenomenon.
2017 YE5 was 6 million kilometers from the Earth, or 16 times the distance between the Earth and the Moon, on June 21st. Using a bistatic radar – a technique in which the transmitter and receiver are placed in separate locations – astronomers from the NASA Solar System Goldstone Solar Radar (GSSR) in California scanned the object and found only in reality A pair of asteroids had been discovered instead of one. Observations were confirmed by astronomers at the Green Bank Observatory in the state of West Virginia.
The observations show that the two asteroids are rotating towards each other once every 20 to 24 hours or so. In addition, asteroids are larger than expected. The losses are very dark, with a color similar to that of coal, which complicates the process of making visual observations. The radar images revealed its real size: each asteroid is about 900 meters long. That said, their reflectivity patterns were radically different, suggesting that objects, although of similar size and mass, have different densities or compositions. That means it's a duet, yes, but not identical twins.
A new study warns us that we are not ready to detect a meteor like Tunguska's
for bad asteroids. The media loves to publish …
Read more
As we have mentioned, binary asteroids are common in the solar system. Interestingly, we sometimes see their "signature" on Earth with double impact craters, which means that the asteroids managed to stay together when they learned the atmosphere of our planet and hit the surface. It is estimated that these craters account for about 3% of all craters impacting Earth. Unfortunately, it also means that if we detect an asteroid related to our planet, there is a 15% chance that it has a companion. [NASA]
Source link