[ad_1]
A few days before Mars recorded the closest distance to Earth in 15 years, scientists reported spotting an important salt lake under ice in the plain Southern polar of Mars, a water plan that lets hope that there is more water – and perhaps even primitive life – on the Red Planet.
The reservoir has been detected – about 20 kilometers in diameter, shaped as a rounded triangle under the surface of the ice – represents the first and largest stable body of liquid water ever found on Mars, said the report in the journal Science . "The water is there, we have no doubt," said co-author Enrico Flamini, director of the Mars Express mission of the Italian Space Agency . pole when radar signals appear on the left. AP ” width=”1024″ height=”768″/>
This artistic rendering shows the Mars Express Spacecraft probing the south pole of Mars while radar signals appear on the left. AP
Is this new?
Previous research had already found possible signs of intermittent flow of water to the surface of Mars, so how does this discovery offer anything new? sort of water plan that was observed
"Now we are talking about a potential lake that we talked about in 2011 and 2015 are probably transient liquid water to the surface – the key word here being "transient", in that its existence on the surface is temporary. What these guys are talking about is a stable lake body.If that is indeed the case, then the results are huge and could have important implications for our search for habitat environments on Mars, "Lujendra Ojha, a global scientist at Johns Hopkins University in Baltimore, United States, said tech2 .
"Of course, we must be careful right now to make sure that it's actually a lake," Ojha, who is credited with discovering the flow of liquid salt water on the surface of Mars in 2011, quickly added
Read the interview of Lujendra Ojha in 2015 tech2 on his discovery here
Professor Mayank Vahia the Department of Astronomy and Astrophysics of TIFR in Mumbai, although the amount of water observed is quite significant, the reflection of the water plan indicates that it is unlikely that it's pure water. "At this point, we do not even know if it's a piece of mud or if it's water which is salty for the most part, but it's interesting anyway, "he said.
However, the type of water observed will not be easy to study the signs of the life or chemical nature because it is buried deep beneath the Martian surface. "The radio frequency instruments we use now will never talk to you about life – you'll need a physical sample and digging a kilometer on Mars will be far from easy," said Vahia
. As the South Pole is still liquid, given the stiffness of the poles, Ojha explains: "On Mars, you have a lot of exotic salts, you can only have liquid water at the South Pole of Mars if it 's not. water is saturated with exotic salts, such as perchlorates, chlorates and / or sulphates. "
Detection
The discovery was made with the aid of a radar instrument aboard the Mars Express orbiter of of the European Space Agency . Launched in 2003.
This tool, named Mars Advanced Radar for the underground and ionospheric sounding (MARSIS), was designed to detect groundwater by sending radar pulses penetrating into the surface and ice caps. MARSIS "then measures how radio waves propagate and reflect toward the spacecraft," says the study.
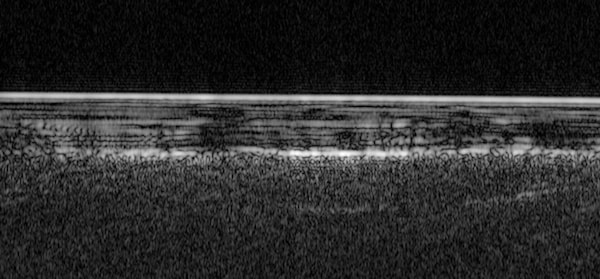
Radar detection of water under the south pole of Mars. Image reproduced courtesy of ESA
A team of researchers led by Roberto Orosei of the National Institute of Astrophysics of Bologna in Italy studied a region called Planum Austral, located in the southern ice cap of Mars, from May 2012 to December 2015. a total of 29 sets of radar samplings showed a "very abrupt change in its associated radar signal", allowing scientists to map the contours of the lake .
"The radar profile of this area is similar to that of the liquid water lakes found beneath the Antarctic and Greenlandic ice sheets on Earth, suggesting that there is a subglacial lake at this location on Mars, " the report says .
The researchers said that they did not know where it was going, but (19659002) Does this indicate life on Mars?
Space agencies are trying to find traces of contemporary water because such discoveries are essential to unlock the mystery. The discovery of this lake adds to the evidence that Mars was once active, at least geologically and chemically, but the question that must be answered now is whether these processes were sufficient. to produce life.This study clearly showed that Mars may have been habitable once .. Frankly, we have absolutely no idea of how life appeared on Earth, but we have our theories, "says Vahia .
Ojha, too, was sure that this discovery could have excited many astrobiologists, "but I have already said, we must be careful before jumping on this.We must exterminate any glimmer of doubt that it is not a lake. "
However, even after this is confirmed and if life forms are actually observed, they are likely to be very primitive life forms such as microbes. In addition, the search for life on Mars is not limited to the search for liquid water: last month the rover Curiosity of NASA discovered organic molecules "hard" in sedimentary rocks three billion years old. surface, as well as seasonal variations in the levels of methane in its atmosphere.

The southern polar cap of Mars as it appeared on the Mars Mars Orbiter camera Global Surveyor (MOC) Reuters
Organic molecules include carbon and hydrogen, and may also contain oxygen, nitrogen and other elements. Life, organic molecules can also be created by non-biological processes, and are not necessarily indicators of life, NASA pointed out. But for scientists, these discoveries are always encouraging.
"With these new discoveries, Mars is telling us to stay the course and continue to look for evidence of life," said Thomas Zurbuchen, a senior NASA official. "I am confident that our ongoing and planned missions will unlock even more breathtaking discoveries on the red planet."
The Challenges of Martian Exploration
Going to Mars is not only very expensive, also extremely difficult. Prior to this discovery, the largest lessons on Mars were learned almost exclusively from data collected by NASA's probes at the Red Planet. "The reason we receive data mainly from NASA is that many countries have spectacularly failed to reach Mars, the Indians were the only ones to do it right the first time," said Vahia
. The Martian surface, can we expect more ambitious space programs towards Mars in the years to come? Maybe those who can possibly drill into its surface and reveal what kind of water and soil exist underneath? Maybe, said Ojha.
"But the way forward with NASA seems to be a sample return mission, there is a mission dedicated to Mars that will sound up to 5 meters deep, but this mission is to to know how much The heat escapes from inside March. "
" Perhaps this is the time for India and China to take the initiative of l & # 39; 39, Martian exploration, "says Ojha

A map of Mars produced from images captured by Mangalyaan. Image courtesy: ISRO
The Mars Orbiter Mission, better known as Mangalyaan is the own Indian space probe in orbit around Mars since September 24, 2014. This is the first mission interplanetary of India. agency to reach Mars, after the Soviet Space Program, NASA, and the European Space Agency. But, until then, has it been useful?
"Our scientific data are not very solid from Mangalyaan: if you ask how much science has resulted, there is not much of it." He explained that Mangalyaan also has a very strong orbit. elliptical, so when it gets closer, it can study the planet properly, but when the probe moves away from its orbit, it can reach 66,000 kilometers from Mars. "In principle, the instruments on Mangalyaan had a specific detector for methane, but I do not know any scientific results of the spacecraft."
With the entries of agencies