
[ad_1]
Only a few decades ago, we knew nine planets in the universe. Later, they became eight when Pluto was demolished on the dwarf planet.
But today we know about 4,000 planets and all but eight are part of solar systems other than ours. They call themselves exoplanets.
Out of nearly 4,000 exoplanets we know of today, no less than 2,600 have been discovered thanks to Nasap 's Kepler Space Telescope, which was permanently decommissioned after nine years of operation. activity.
More planets than stars
The Kepler Space Telescope owes its name to the German astronomer and mathematician Johannes Kepler (1571-1630), who has formulated several groundbreaking theories of planetary motion.
And the fact is that today we know a lot, thanks to Kepler's telescope, that there will probably be many more planets in the universe than solar floors, that is, stars.
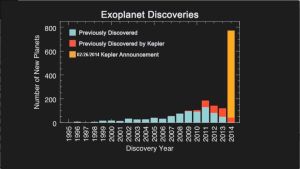
The discovery of the planet took place after the Plantselescope data began circulating.
Histogram of exoplanets detected over the years.
We also know that nearly half of the stars around us may have small, earth-shaped planets surrounding them.
"Thirty-five years ago, when the Kepler project got under way, we had no idea of other planets besides the nine planets contained in our own solar system." We now know that there is planets everywhere, says William Borucki, one of the forces behind the project.
Earth-like planets
The chapel telescope's explicit mission has been to search for earth-like planets, that is, small, earth-shaped stone planets, in the size class ranging from half of the Earth's size. land mass at twice the size of the Earth.
The artist's vision of an "earthquake".
The planet Kepler-186f
Image: NASA Ames / SETI Institute / JPL-Caltech
Of course, planets that travel at such a distance from the star are neither too hot nor too cold for the water to be in liquid form.
In other words, planets likely to take life.
Kepler observed nearly 100,000 stars in the heavily congested area surrounding the Swan and Lyran constellations.
Kepler's operation is called the transit method. It is to observe small changes in the brightness of a star. When a planet passes in front of its sun, it produces a small "eclipse".
The transit method illustrated.
The transit method illustrated.
The larger the eclipse, the greater the planet that provokes it: the principle is behind all that.
A space telescope is needed
But the change in brightness of the star caused by this type of passage of the planet is very small, about 100 parts per million or so, and usually lasts between 1 and 16 hours.
For this reason, a space telescope is explicitly required for this type of observations.
The telescopes connected to the ground are forced to look through the earth's atmosphere and, as we know from the "Blink a little star", the stars do not even shine when they see them from the ground: they "blink" because of the movements of the air in the atmosphere.
VLT Observatory in Paranal, Chile.
ESO Telescope (VLT) in Paranal, Chile.
Image: ESO
On the other hand, in the airy space, the star lights are absolutely stable and "blinkless". Except that, as said, one of the star planets passes between the star and the earth.
And since you've already seen the planet, you can wait for it to pass next time and then calculate the size of its orbit.
From the orbital size and shape, you can then roughly calculate the typical temperature of the planet. When you know it, you can also decide whether the planet is habitable or not.
Silence but do not go away
The Kepler probe is now closed and will continue to circulate around the sun, in the wake of the Earth, more or less forever.
But just because Kepler turned a blind eye, the researchers will stay busy for years to tweak all the data collected by the telescope.
And in addition: The successor of the Chapel Telescope, the TESS Space Telescope, was fired from Cape Canaveral in April of this year.
The TESS spacecraft is prepared for shooting.
Space telescope TESS.
Image: Nasa
TESS will observe more than 200,000 of the brightest stars near the Earth over a two-year period. Thus, all planetary hunters do not have to despair.
The news of the newly discovered worlds will therefore be dense even in the years to come.
Source link