[ad_1]
Tesla (TSLA) is working on the development of its autonomous driving system called Autopilot. The system has the potential to be incredibly lucrative because Tesla has the ability to set up a fully autonomous phone lift service, the Tesla Network, but other companies are also working on their own systems. Waymo, a subsidiary of Google (NASDAQ: GOOG) (GOOGL), currently seems at the top of the pack, but Cruise Automation, a grant from General Motors (GM), is close to Tesla. Lyft (LYFT), Uber (UBER) and Didi Chuxing (DIDI), the world's three most established after-sales service providers, are also working on the development of their autonomous vehicles, but are lagging behind their newer ones. competitors. This article will explain which company will probably be the first to offer its service, the profitability of this type of service and what it will mean for Tesla's future financial statements.
Autonomous Development
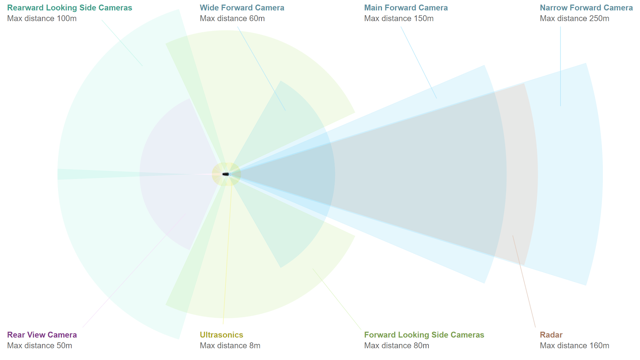
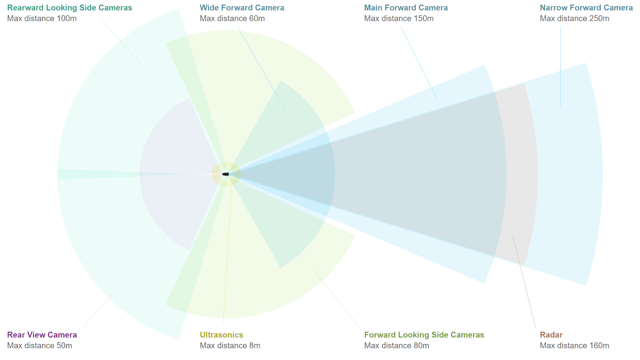
Tesla's current autopilot system is based on eight cameras, twelve ultrasonic sensors, a radar, a powerful computer chip and numerous software packages. The eight cameras provide a complete 360-degree view of the surroundings without a bulky camera configuration mounted on top. The radar measures the distance and speed of objects to come and can see through precipitation, fog, dust and future vehicles. Tesla also created its own computer chip, which according to Musk (17: 20-17: 39) represents a 2000% improvement over the previous chip provided by Tesla to NVIDIA (NVDA). With more processing power, chips will be able to process more data and make decisions faster, making the software more secure and accurate. Whereas Tesla had to fold pixels and reduce frame rates, they are now able to allow cameras and sensors to operate at full power. Elon Musk recently tweeted about the superior processing power of their full-auto computer, indicating that the chip must operate at 5% of its processing load, or "10% with full failover redundancy". Musk went on to say that the previous chip, provided by Nvidia, is currently running at about 80 percent computing load, even with curved pixels and reduced frame rates. The Tesla chips team was led by Peter Bannon, currently vice president of engineering at Tesla, who had nearly eight years of experience at Apple (AAPL) in the development of their A5-A9 computer chips. The new chips are not only more powerful and specialized for the Tesla autopilot, but they cost even less than the previous Nvidia chips.
Source: Tesla
Many manufacturers have chosen to use LiDAR radar with radar, because of the added benefit of being able to generate highly accurate three-dimensional shapes and determine the direction of motion. LiDAR can determine hand gestures or signals, as well as how a person walks, anything the radar alone can not do. The images produced by LiDAR are also much more sophisticated and detailed than those produced by the radar. Waymo relies on LiDAR, as well as Cruise Automation, Lyft, Uber and Didi Chuxing to run their autonomous vehicles.
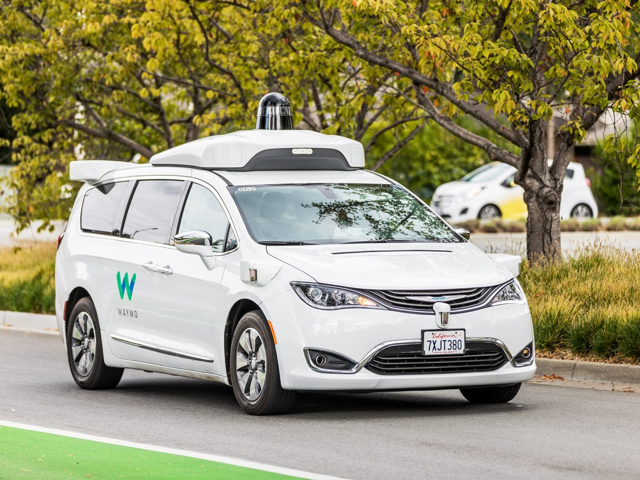
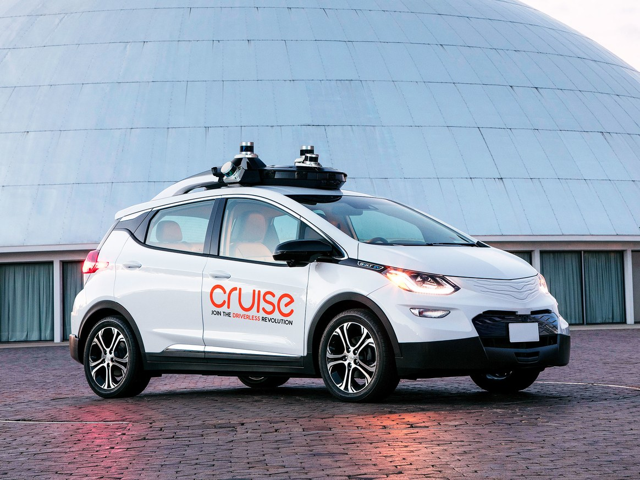
Although LiDAR has many obvious advantages, the system is far from perfect. LiDAR works through a series of mirrors and rotating lasers, a system particularly subject to damage and regular focus. A single small movement of the equipment in a LiDAR system requires repairs, which requires constant diagnostic testing of the LiDAR system. The radar is also more energy-efficient, allowing longer ranges on electric vehicles (EVs) and is less demanding on a car battery. LiDAR systems are also extremely expensive, Waymo has been able to reduce the cost of its high-end LiDAR system by 90%, according to 75,000 USD, the industry standard, according to Waymo CEO John Krafcik. This is good news for Waymo, but not for other autonomous car manufacturers, since Waymo does not plan to sell its system to potential competitors. By avoiding LiDAR, Tesla is able to significantly reduce the cost of its autonomous system. LiDAR is also more sensitive to malicious entries and may cause a vehicle error. As a car manufacturer, Tesla is also concerned about the aesthetics of its cars and LiDAR systems are incredibly bulky. The system also reduces the efficiency of vehicles, making it significantly less aerodynamic. Take note of the images below, all the extra weight on cars comes from the LiDAR system. The major disadvantage of LiDAR is perhaps their inability to navigate precipitation, dust or fog.
Source: Wired (Waymo vehicle)
Source: Wired (Automatic Cruise Vehicle)
LiDAR is not just what distinguishes companies in their autonomous driving projects, even if it's a major difference. I've already talked about the computer chip manufactured by Tesla, but Waymo relies on Intel, as well as Cruise Automation to provide them with their chips. While this is not a big problem, the chips that Tesla manufactures now are more powerful and can reduce the cost of autonomous driving through in-house manufacturing. However, a much bigger difference lies in the way Tesla and Waymo collect their data. Waymo has more than five billion kilometers traveled by its fleet, but all by simulations. Their real-world miles represent only ten million. Ten million represent a significant number of autonomous vehicles, by far the largest, but Tesla has collected the most data, with more than ten billion kilometers of driving data and more than one billion kilometers of autopilot. Later in the article, I will discuss a little more about the importance of this differentiation.
The real question is whether Tesla will actually be able to develop a fully autonomous vehicle without using LiDAR. If they are not able to do it, the future of the company is rather bleak and, in my opinion, could probably fail. This is unlikely, however, as Tesla continues to prove the effectiveness of radar, camera and ultrasound systems with its autopilot system. The most damning proof of the reliability of a system without LiDAR is also its success with other companies. No other company uses it as the main sensor, but in poor conditions, LiDAR becomes useless and cars rely on their radar as the primary sensor. If the radar is not safe enough to be used without LiDAR, no business will succeed because precipitation is quite common, as is dust in China. It has been proven that the radar is able to detect objects with sufficient detail for autonomous vehicles and continues to gain safety as the technology evolves. As Tesla continues to develop its standalone software around the radar, they are collecting more data on how to improve their system and create a safe vehicle in all conditions – with radar in the heart.
First on the market
Every developer is looking to become the first federally registered company to offer independent freestanding descent. This section presents the winners. Waymo has already been licensed to operate a fully autonomous fleet in a small area of California, making it technically the first on the market. However, keep in mind that this is only a small area in California where Waymo did most of her testing, which makes her incredibly familiar with the area. Waymo is far enough ahead of all its competitors in terms of driving reliability, requiring only one intervention every 11,018 km in 2018, which doubles its efficiency compared to the previous year. No other company has moved closer, with Cruise Automation ranking second with an intervention every 5,205 miles compared to 1,256 km last year. Tesla has not been included in the survey as they do not test complete self-driving: the autopilot is a driver assistance function. Unfortunately, recent reports claim that Cruise Automation is struggling to determine if an object is moving, causing delays in the program. The exponential growth of the two companies' self-driving capabilities is likely to continue, with data arriving at an accelerated pace and engineers in both programs working to upgrade their hardware and software. I think that by the end of 2020, Cruise Automation will be fully able to drive independently – Waymo is already, although limited by speed and routes.
Musk predicted (7: 48-11: 31) that they would be able to create a fully "functional" autonomous Tesla by the end of 2019 and allow the driver to "fall asleep", the two waiting for regulatory approval. at the end of 2020. Musk's confidence in a complete autonomous vehicle until 2019 was quite high, as he repeated this point three times during the podcast and declared that He was "100% certain". and that it is not "a question mark". Tesla and Musk, in particular, have notoriously missed their deadlines, so why should this forecast have any weight? Elon Musk seems to have learned his lesson about the promise made in the past, mainly with the Hell of Model 3 production. The first 3 models arrived in China earlier than expected and a start date and production more cautions have been announced for the Y model. Tesla has also rolled out some important autopilot upgrades and is continuing its advances with the software. As a result, the likelihood of full autonomy by the end of 2020 seems highly likely, the same year as Cruise Automation and nearly two years after Waymo.
Lyft and Uber are currently the leading US providers of mobile services. Both have established a strong brand in the sector and are also working to create autonomous taxis. However, both are behind their competitors. Uber was progressing well. In March 2018, one of their vehicles struck and killed a pedestrian. Immediately after the accident, all tests were stopped and resumed only in December 2018. However, their tests were reduced to the strict respect of the day, with no precipitation or speeds exceeding 25 mph. . In trying to recover the permission to test their vehicles, Uber cars have repeatedly failed and had a reaction time of 20% slower than a human. Their two cars with which they will resume testing, a dramatic downgrade from the previous 200, will follow these strict guidelines until Uber can obtain the necessary approval to continue testing. As a result, I find it highly unlikely that Uber could even have the full autonomy capability by the end of 2021 and is likely considering a date closer to 2023 or 2024 for fully autonomous capabilities, even before regulatory approval.
Lyft is ahead of Uber, but not with his own vehicles. Lyft uses 20 Aptiv autonomous vehicles (APTV) 75 in Las Vegas to transport passengers to and from their destinations. An employee at the front takes notes and is ready to step in. Thanks to its partner, Aptiv, Lyft could be ready to acquire full autonomy by the end of 2020 or the beginning of 2021. Thanks to its own development, Lyft is very late on its partnership project with other companies such as Aptiv. , to ensure his autonomous driving. In July 2017, Lyft announced that it plans to create autonomous vehicles, almost ten years after the creation of Waymo. Although the team around Lyft's autonomous driving is growing rapidly, with acquisitions and the hiring of new employees, they started a lot after their competition, placing them in the race for autonomous vehicles. As a result, I anticipate that Lyft will be able to achieve full autonomy by the end of 2023. Their growth is fast and successful; The acquisition of Blue Vision Labs is also a considerable benefit for the rapid development of autonomous vehicles. Didi Chuxing will probably be successful by the middle of 2020 with the ability to run an autonomous vehicle. Their general manager, Cheng Wei, believes that their capabilities for full autonomy will be ready by mid-2019, although the prediction seems a little optimistic based on their current approvals and capabilities.
The biggest hurdle these companies will face is getting regulatory approval, an idea I've already referred to. At the moment, Waymo is probably the first company to be able to create a fully autonomous vehicle, but that does not mean that it will be the first to be allowed to use it. Currently, Tesla appears to be best placed to advocate for a federally approved autonomous vehicle. As stated previously, the conditions under which LiDAR does not work, especially precipitation, are quite common, which means that radar is often the main source of data for a stand-alone vehicle. This gives an advantage to Tesla's approval, which has built its entire autonomous vehicle software around the radar and has therefore spent more time developing its radar applications and capabilities. As a result, the safety of their vehicle will not decrease with the weather conditions. Since they have been working on the development of their autopilot equipment with radar as the main sensor, they have spent the most time creating a secure radar system, a factor that may appeal to government regulators.
The vast amount of real Tesla data includes data that no other company has or is able to obtain. This includes navigating smoke from California wildfires and roadblocks, hurricanes on the southeast coast, and blizzards to the north. To navigate in each of the above conditions, LiDAR would fail and autonomous vehicles would have to rely on their radar. Tesla is also the only car manufacturer to offer its vehicles with the ability to collect detailed driving data. Thus, although General Motors has more vehicles on the road, none, with the exception of those driven by Cruise Automation, collects data and can not contribute to the development of standalone software. Cruise Automation made only 450,000 miles in 2018, following the absence of miles the previous year, and did not issue an official statement on the number of miles of its simulations recorded. The kilometers traveled by Uber and Lyft with their 750,000 and 1.4 million pilots, respectively, have not yet been documented as those of Tesla. Musk estimated (16: 11-16: 23) that Tesla owns 99% of all real-world data, an unparalleled advance. Even without autopilot engaged, Tesla uses his cars to teach his software to drive; Whenever a Tesla vehicle crosses an intersection, it explains to the software how to do it. Tesla cars are taught by people who drive as usual, a benefit that other companies can not get. Tesla's autopilot kilometers will also increase exponentially, as shown in an MIT research paper, proving the capabilities of the system. With the unparalleled amount of data with the autopilot used, Musk thinks it will be much easier to prove to regulators the vast improvement in safety provided by the autopilot. Musk explained (20: 08-2018) that it was undoubtedly dangerous to drive without an autopilot and that they would be able to show this information to the regulators. Waymo was allowed to test his fleet in his small suburb of California because they knew the area well – they had the most real data in the area. In addition to the amount of data from the real world, there is no difference between Mountain Area and Mountain View, thus demonstrating the importance of real-world data for obtaining approval. regulatory. Even after Tesla's first fatal accident with Autopilot, Musk agreed with Cathie Wood (20: 23-20: 38), the podcast host and general manager of Ark Invest, that the regulators had defended Tesla and blamed the pilot and not the autopilot system. However, according to Musk (13: 30-14: 37), interventions on the autopilot also teach the system by allowing Tesla to solve the problems that may have caused the intervention and further enhance the realism of his autonomous driving.
So, even though Waymo will have got the ability to drive independently almost two full years before Tesla, he will probably get regulatory approval only a year before Tesla. In the middle of 2021, Waymo will get his approval for full autonomy in the United States, while Tesla will likely receive it by the middle of 2022. Waymo will also have the disadvantage of being the first company to seek approval for an autonomous vehicle. hail the fleets, which means that they will be forced to shoulder the burden of legal battles and chart the way for others to get regulatory approval. Cruise Automation might not receive regulatory approval until the middle of 2023 because of its lack of actual data. Uber may not be approved until 2027, because of his low number of real-world miles and his track record of hitting and killing a pedestrian. They will probably have to prove that their company has solved this problem and must meet more stringent standards than other companies. Lyft, with Aptiv, will probably get approval at the same time as Cruise Automation, in mid-2023 and with the approval of their own fleet in early 2026. Didi Chuxing will likely receive regulatory approval early in the year. 2024, partly because of hostility between China and America and concerns about security around companies like Huawei (SHE: 002502).
China will also make a significant contribution to the growing market for strike tourism as their monstrous cities continue to grow. China also suffers from heavy pollution in many of its major cities and, although smog is dangerous as a pollutant, it will also prevent LiDAR, especially on the darkest days. As a result, Tesla could more easily obtain regulatory approval in China due to further development of the radar as the main sensor of the vehicle. Tesla also has good relations with the government, having received a lot of support for the recent construction of Gigafactory and becoming the first foreign car manufacturer to be allowed to produce in China without a local partner. Musk also said that he expected China to be at the same level as the United States in terms of automation regulation while they strive to stay ahead of the technological world and find their regulators very reasonable. On the other hand, Google has a rather weak relationship with China, to the point that Google Maps and Google Play are both blocked in the country. This is a problem for the company, which will probably depend on its own mapping software and, in general, Google's software is generally not well received in the country. As a result, Google may be forced to first win a legal battle for its cards and then focus on its approval. It will take a lot of time for society, much longer than in America, if it is completed. As a result, China may not certify Waymo before the end of the year 2023 at best, while Tesla could receive approval by the end of 2022. I expect Didi to Chuxing is the first to get approval in China in early 2022. Uber, Lyft and Cruise Automation will likely experience a similar schedule to that of America, though pushed back from six months to a year. In Europe, I do not think a company has an innate advantage for approval, although Musk seems to think (11: 57-12: 15) that obtaining regulatory approval could be a little more difficult, because "Europe is a bit conservative in this area". Regarding. "Therefore, each company will likely see a delay of one and a half to two years from its first national approval.
If the obvious benefit of becoming the first supplier in the market is to be able to realize revenue and profits faster, it also helps to strengthen brand recognition and future market dominance. The sooner a company will be able to penetrate a market, the greater will be its success in this market, as the Uber and Lyft concept has shown in the stimulus market. While Uber controls 69.2% of the American hiking market, Lyft controls only 28.4%, according to Second Measure. Uber began operations in March 2009, while Lyft opened in June 2012, three years later. These three years have resulted in a fairly large dispersion of the market share, which proves the importance of rapidly adopting the market. The only real threat to Tesla and other companies to radically change their development schedule is a fatal accident, similar to Uber's. However, for all the companies involved, this is rather unlikely because of the strict guidelines for the release of an autonomous vehicle and their continued success.
Market potential
With the arrival of all the new competition in the running market, the question of whether there is enough room for everyone is worrying. A report by Goldman Sachs predicts that the global market will reach $ 285 billion by 2030; after 2018, the market was valued at $ 59.6 billion. Rapid market growth creates room for incoming competitors wishing to control a significant portion of the market. Although Uber, Didi Chuxing and Lyft are well established players, this does not guarantee them a prosperous future. Autonomous fleets will allow lower prices for trips that can not be compared to those who do not use an autonomous fleet. Autonomous fleets will also be safer than current fleets, which could be of interest to consumers. This forces companies to succeed in their own businesses or lose market share. The independent running market is a completely different market than the traditional running market, and those who can come first will be able to reap the rewards of their success.
At present, Uber controls about 45% of the world market of outflows and Didi Chuxing represents about 35% of the world market (calculations of the author with the data provided by statista). Between them, they have essentially captured the current redemption market in their respective regions, Uber in America and Europe and Didi Chuxing in China. However, emerging competitors in the running market, with their autonomous vehicles, are seeking to take a large part of the existing market. First, while the market is expected to almost five times reach what it is currently by 2030, many new customers need to be split between the major new players. Due to the timing of each company's regulatory approval, size, brand recognition, region, and cost, each company will have more or less success entering the new market. Uber, Didi Chuxing and Lyft will only see their market share decrease due to the rapid growth of competition and the expansion of the market as a whole.
Lyft currently holds 7% of the global market share (author's calculations with data provided by statista), but their position could fall around 5% by 2030. It's important to note that even though their share of As the market shrinks, Lyft will maintain revenue growth as the market also grows. Lyft will market its autonomous vehicles a little later on the market, which will greatly contribute to the decrease of its market share. As mentioned earlier, time is running out for the release of autonomous fleets. Uber should see a drastic reduction in its market share of about 6%. With the very late deployment of their autonomous vehicles, the only thing that will keep Uber at 6% will be the recognition of their brand and their current reach. Be that as it may, this drastic reduction in their market share will result in lower revenues compared to the current situation, even if the market grows. The main driving forces of their considerably reduced market share will be their inability to compete with prices, as autonomous vehicles may charge less for a journey, distrust of their autonomous system and their release is becoming more and more difficult. more delayed.
Didi Chuxing will be able to maintain a high market share of about 27%, while maintaining growth in sales until 2030. Didi Chuxing will maintain a strong hold in the Chinese market with timely publication of their autonomous vehicles and the support of their governments. Didi Chuxing will not feel much pressure from Western competitors entering the market, which will allow them to easily retain their first place in China. Although they are trying to enter the Western market, I do not think they will be very successful because the most popular American brands will likely be the first choice of American consumers. Waymo is expected to be very successful in America, which is beginning to offer its services to the public. As the first to offer its standalone relay service, Waymo will receive a lot of attention and customers eager to see the product by themselves. Waymo is also a grant from Google, a well-known brand in America, that will further contribute to its success in America. For this reason, the retention of their customers should remain high after their national beginnings and should be able to continue to increase their customer base. Even though they will see great success in America, the increased competition will give them a 22% global market share.
Tesla should also experience rapid success because of the attention that the company will receive as soon as its Tesla network is released. As for the reasons for which it will have received regulatory approval before Waymo in China, Tesla's reputation in China is rather positive. It will cut some of Didi Chuxing's customers and boost its global market share to 29%. Although Didi Chuxing is still the dominant company in China, Tesla will still be able to conquer a smaller but significant part of the Chinese market. When calling for third quarter results, Elon Musk described a service, the Tesla Network, similar to Uber, Lyft, and Airbnb (AIRB). Consumers will be able to carpool, as they can share a home via Airbnb, and Tesla owners can register their vehicles so that they are called to serve as driving vehicles, just as they can with Uber and Lyft. En termes de portée mondiale, Tesla sera la société la plus dominante de toutes, même si Didi Chuxing s'empare de la majorité en Chine. General Motors sera le moins réussi des nouveaux fournisseurs de services de relais, ne représentant que 9% du marché. Leur profil bas sur la scène de l'auto-conduite créera moins de visibilité pour eux, et leur publication moins rapide réduira également la portée de leurs clients.
Bien que la part de marché de General Motors puisse être inférieure à celle de Waymo ou de Didi Chuxing, elle sera en mesure de générer plus de revenus avec sa conduite autonome que l'une ou l'autre des sociétés. Tesla et General Motors sont également des constructeurs automobiles. Ils vendront leurs véhicules autonomes aux consommateurs et les utiliseront également pour leurs services de transport. Pour Tesla, qui a récemment annoncé que toutes les nouvelles Tesla seront vendues avec le pilote automatique en tant que fonction standard, le marché des véhicules autonomes est encore plus important. Un rapport IHS prédit que les véhicules autonomes vendront 33 millions d'unités par an en 2040, soit 26% du marché total. L’adoption de véhicules autonomes devrait être motivée par les États-Unis, tandis que l’Europe et la Chine sont à la traîne, ce qui joue à nouveau contre l’avantage de Tesla et de General Motors, deux sociétés américaines. Cependant, la Chine devrait passer à la fois en Amérique et en Europe, les véhicules autonomes devenant de plus en plus courants, en raison de la taille même du pays. Avec leur Shanghai Gigafactory, Tesla sera en mesure de produire en Chine; General Motors sera en mesure de produire localement avec ses quatre usines chinoises. Tesla peut également limiter le coût de la conduite autonome à moins de 5 000 dollars pour ses consommateurs, soit moins que le coût du système révolutionnaire LiDAR bon marché de Waymo, et Cruise Automation utilise cinq capteurs LiDAR distincts. Le coût du système lui-même est probablement inférieur à 3 000 dollars, car tout le matériel nécessaire au système est inclus dans tous les véhicules Tesla pour moins de 3 000 dollars. Cela forcera le coût d’une voiture entièrement autonome de General Motors à être beaucoup plus élevé que ce à quoi Tesla fournit la leur. En gardant leur autonomie bon marché, nettement moins chère que General Motors, Tesla sera en mesure d’atteindre une clientèle beaucoup plus vaste. Tesla sera également en mesure de garder leurs véhicules élégants en évitant le LiDAR, un facteur qui pourrait également plaire à de nombreux acheteurs potentiels. De plus, avec la possibilité unique pour les propriétaires de Tesla de gagner de l'argent grâce au réseau Tesla, la demande devrait encore augmenter. Les deux sociétés, en particulier Tesla, auront une forte demande pour leurs véhicules autonomes en tant que deux principaux fabricants d’automobiles fabriquant des véhicules autonomes.
Même si l'approbation réglementaire ou le développement autonome de Tesla a pris beaucoup de retard et qu'elle ne sera approuvée aux États-Unis qu'au milieu de 2025 et en Chine jusqu'en 2026, je pense que leur part de marché en 2030 devrait être de 12%. Leur capacité à concurrencer en Chine renforcera un peu leur part du marché mondial, mais leur taille globale sera leur meilleure arme. Waymo travaille actuellement à l’extension de sa flotte de 600 000 à 80 000 personnes. Cela leur donnerait de loin la plus grande flotte de tout fournisseur de conduite autonome, à l'exception de Tesla. Tesla a déjà une flotte de plus de 500 000 personnes, a livré plus de 90 000 voitures au quatrième trimestre de 2018 et environ 60 000 au premier trimestre de 2019, le nombre inférieur de livraisons étant attribué au nombre plus élevé de véhicules en transit, Tesla commençant à pénétrer de nouveaux Modèle 3. D'ici 2030, il y aura des millions de véhicules Tesla dans le monde à mesure que de nouveaux véhicules seront introduits et les taux de production continueront de s'améliorer. Tandis que d'autres sociétés auront besoin de mobiliser beaucoup de capitaux pour démarrer leur flotte autonome, Tesla ne sera pas contrainte par des capitaux alors qu'elle démarrera son réseau et développera rapidement sa flotte autonome. La taille de la flotte de Tesla est un facteur clé de leur part de marché de 29%, mais permettra à la marque de rester pertinente en cas de déploiement autonome très retardé.
Évaluation résultante
Les marges seront l’apport le plus important pour toutes les entreprises autonomes de tourisme de descente. Selon l'entreprise, les pilotes Uber génèrent actuellement entre 75% et 80% des revenus générés par un lecteur. En éliminant un chauffeur, les entreprises seront en mesure d'éliminer le coût le plus élevé des marchandises vendues pour un service de téléphonie traditionnelle et fonctionneront avec des marges incroyablement élevées. Tesla et General Motors auront également l'avantage supplémentaire de réduire les coûts d'entretien de leurs véhicules, les véhicules électriques ne nécessitent pas d'essence ou de nombreuses mises au point requises pour les moteurs à combustion interne, bien que Cruise Automation devra exécuter des tests de diagnostic LiDAR périodiques. et mises au point. Tesla et General Motors auront également l’avantage supplémentaire de fabriquer leurs propres véhicules, ce qui réduira davantage leur coût des marchandises vendues.
Tesla sera en mesure de générer encore plus de profits avec ses véhicules après les avoir déjà vendus. Ceci est rendu possible par le réseau Tesla, le service de transport en porte-à-porte sera assuré par des véhicules déjà vendus aux consommateurs. C’est peut-être le plus grand avantage du réseau Tesla mais, couplé au fait que Tesla ne nécessitera aucune augmentation de la capacité de CapEx à créer sa flotte autonome, le réseau Tesla devient encore plus rentable. Since the cars used in their ride-hailing service will be the vehicles of Tesla customers, Tesla itself is operating with almost no COGS. Musk said, on the Q3 earnings call, that Tesla will likely take 30% of revenue generated by the cars registered on their Tesla Network. Tesla did say, however, that they will supplement the Tesla Network with some vehicles that had previously been available for lessening, though the vast majority will still be made up by customers' cars. With a market share of 29% and 30% of revenue from the Tesla Network, Tesla will generate an annual EBITDA of $24.795 billion in 2030; even on the delayed timeline margins of 12%, Tesla will be bringing an annual EBITDA of $10.26 billion in 2030 (author calculations with above Goldman Sachs report).
Many investors are currently worried about a serious demand shortage of the Model 3, especially after the Model Y was recently unveiled. Regardless of whether or not a demand shortage is currently an issue for Tesla and its Model 3, the ability to sell their vehicles as fully autonomous will be a large boost for Tesla and its future profitability. Tesla's only constraint for selling their vehicles after they reach full autonomy will be their current production capability projections – about one and a half million vehicles in 2021 and three million in 2023 (as stated on the Ark Invest podcast). The current average Model 3 buy price is $59,300, though this is not an accurate representation of the future because the $35,000 variant was not yet available for sale. Because of this, the average buy price will likely be around $40,000 with margins of 25% (as targeted by Tesla); the Model Y will likely see an average buy price of $45,000 (proportionate to Model 3) with a similar margin. While Model S will average around $92,000 and Model X will average around $96,000, with around 35% margins (margins will improve with battery tech and production improvements). Applying current delivery ratios and one million cars produced annually, this would create an EBITDA of $12.375 billion annually (author calculations with above information).
Ark Invest initiated their famous bull price target of $4,000 per share in the next five years in late August of last year through an open letter to Elon Musk. While I do not share the same extreme bullish prediction, I do believe in a large upside for Tesla's future valuation. A portion Tesla's current value is supported by the prospect of Tesla's advancements as a tech company, self-driving included, which will detract from some of the upside, but nonetheless, Tesla should see strong growth moving forward. As an automotive company with demand and profitability concerns, the arrival of full self-driving will help alleviate these concerns with the Tesla Network and the appeal of an autonomous vehicle.
Disclosure: I / we have / we have no position in the actions mentioned, and we do not intend to initiate a position within the next 72 hours. I have written this article myself and it expresses my own opinions. I do not receive compensation for this (other than Seeking Alpha). I do not have any business relationship with a company whose actions are mentioned in this article.
[ad_2]
Source link