[ad_1]
By Gabriel Olawale
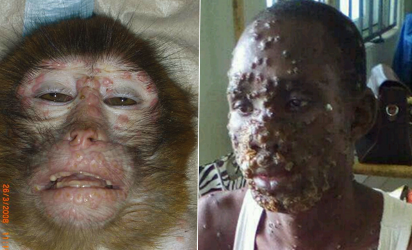
The Nigerian Disease Control Center, NCDC, is investigating reports that two patients suspected of being infected with the Monkeypox virus in the United Kingdom were recently in Nigeria.

NCDC Chief Executive Dr. Chikwe Ihekweazu said in a statement that the Center was working with public health agencies in the UK to investigate the incident.
According to Ihekweazu, "NCDC is aware of two confirmed cases of Monkeypox in the United Kingdom, in the United Kingdom, in patients who have recently traveled to Nigeria.
"After the recent report of the two cases in the UK, NCDC worked with the UK public health agency – Public Health England, PHE, the public health departments of the affected states and other partners in Nigeria – to investigate these cases.
He added that NCDC also worked closely with the country's states to strengthen monkeypox surveillance, detection and case response.
His words: "A technical working group, coordinated by the NCDC and composed of partners from the Federal Ministry of Agriculture and Rural Development, the World Health Organization, WHO, UNICEF, US Centers for Disease Control to ensure coordination.
"In addition, the NCDC recently met with stakeholders, including surveillance officers and case management physicians from all affected states, to review the actions taken to date and develop to strengthen the country's response.
"We reassure Nigerians that NCDC has the ability to effectively diagnose and respond to Monkeypox cases. The National Reference Laboratory in Abuja has the ability to test Monkeypox cases with a quick turnaround time.
"Therefore, we encourage any health worker who suspects a case of Monkeypox to contact their state epidemiological team to take appropriate action."
In September 2017, Nigeria experienced a large and prolonged outbreak of monkeypox, and sporadic cases have since continued to be reported.
Monkeypox is usually self-limiting, which means that patients tend to recover within a few weeks.
However, supportive care and condition management are needed and most importantly successful. Control measures include the isolation of suspected or confirmed cases, strict adherence to universal precautions, especially frequent washing of hands with soap and water and the use of personal protective equipment.
Related
[ad_2]
Source link