[ad_1]
From VOA Learning English, here's the Health & Lifestyle report.
Some diseases receive a lot of attention in the media. Viruses such as Ebola, HIV and influenza are just a few examples.
However, none of them is the number one killer of infectious diseases in the world.
Scientists say that TB, or TB, is the most lethal infectious disease. The World Health Organization reports that in 2017, 10 million people became infected with TB and 1.6 million people died of the disease.
The United Nations General Assembly hopes to draw attention to this problem by organizing its first high-level meeting on tuberculosis. The meeting will be held on Wednesday, 26 September at United Nations Headquarters in New York.
One of the goals of the talks is to expand efforts to end the disease and help those affected.
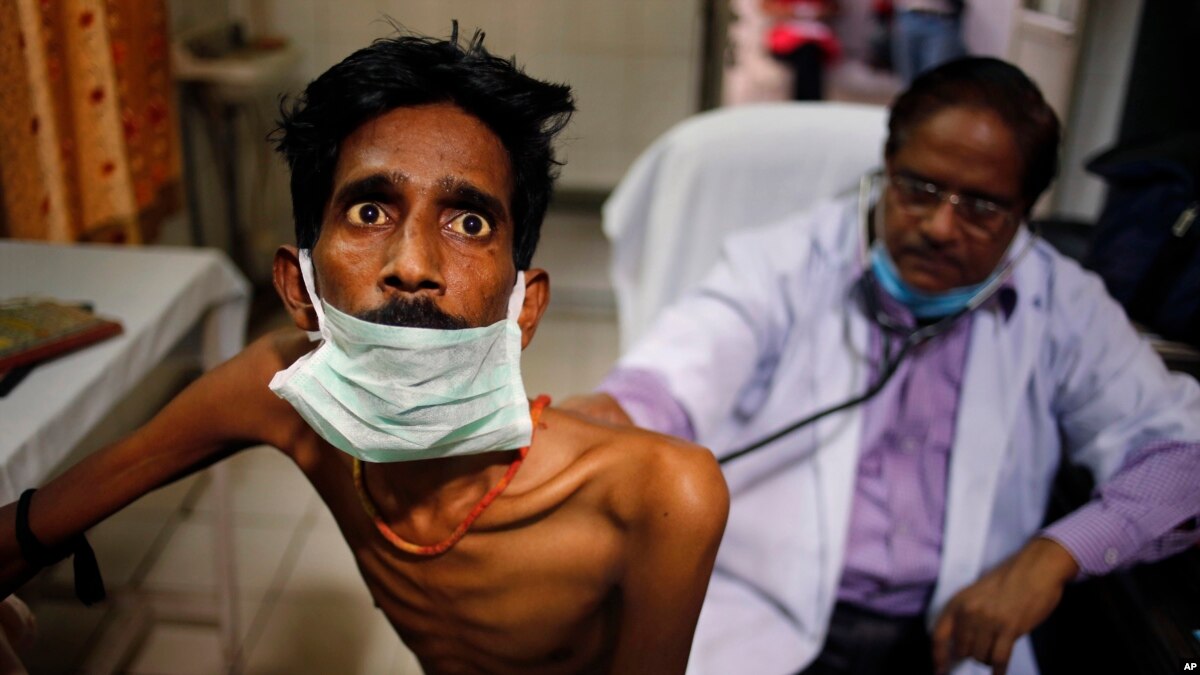
One of those people living with TB is Stella Malgas (South Africa), 54 years old. Life has not been easy for her. She takes nine pills a day for her condition, much less than the 27 she took every day. She is unemployed, has multidrug-resistant TB, and has HIV, the virus that causes AIDS.
She says that people she knows, even loved ones, stay at a distance.
Tuberculosis may not attract the same kind of attention as other diseases. However, health experts warn that we should not ignore TB.
Hank Tomlinson leads the Division of HIV and Tuberculosis in the US Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC). He says that TB is a major health threat.
"It's the No. 1 infectious disease killer. And it kills more people now annually than HIV. There are approximately 1.7 million deaths each year due to tuberculosis. And it's a threat everywhere because of the way it spreads and the ease with which it spreads. "
Tuberculosis is a bacterial disease that spreads in the air. The people most affected are those who live and work closely with others in small spaces and those with weak natural defenses to fight diseases.
Health experts at the CDC say that about 2 billion people are infected with TB worldwide. Rebecca Martin is Director of the CDC's Center for Global Health. She says that preventive treatment is the most important, especially for those with the latent or inactive form of TB.
"Have them follow a treatment that is less expensive, a shorter course, and the adherence is much higher, we can stop moving to active TB, resulting in a spread of TB. "
The CDC website explains the difference between latent and active forms of the disease. He says, "People with latent TB infection do not feel sick and have no symptoms. They are infected with M. tuberculosis, but do not have tuberculosis. People with latent TB infection are not infectious and can not pass the infection to other people. "
To treat the disease, doctors can advise patients to take medication. But if patients do not complete their treatment, drug resistance may develop. As Hank Tomlinson notes, this makes the treatment of TB even more difficult.
"These are variants severe tuberculosis. They do not work with common treatment with four drugs. They are resistant to one or more of these drugs and they require a different treatment, more difficult treatment course for a patient. "
Scientists and health officials hope the US high-level meeting will strengthen the fight against tuberculosis and possibly save millions of lives.
And that's the Health & Lifestyle report.
I am Anna Matteo.
Jill Craig reported this story for VOA News. Anna Matteo adapted her report for Learning English. Additional information from the World Health Organization and the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. George Grow was the publisher.
____________________________________________________________
Quiz
____________________________________________________________
Words in this story
pill – not. a usually medicinal or dietary preparation in a small rounded mass to be swallowed whole
annually – adv. once a year: every year
expensive – adj. cost a lot of money
adherence – not. doing what is required by
symptom – not. a change in the body or mind that indicates that an illness is present
variant – not. strains of a disease
difficult – adj. test one's abilities, endurance, etc .:
Source link