[ad_1]
The National Administration of Aeronautics and Space of the United States (NASA, by its acronym in English) released Tuesday new images of the planet Ceres.
The spacecraft Dawn currently in orbit around the dwarf planet Ceres reached a new record in its surface voyage at a distance of only 35 kilometers, an opportunity in which not only got important data, but also captured unusual images.
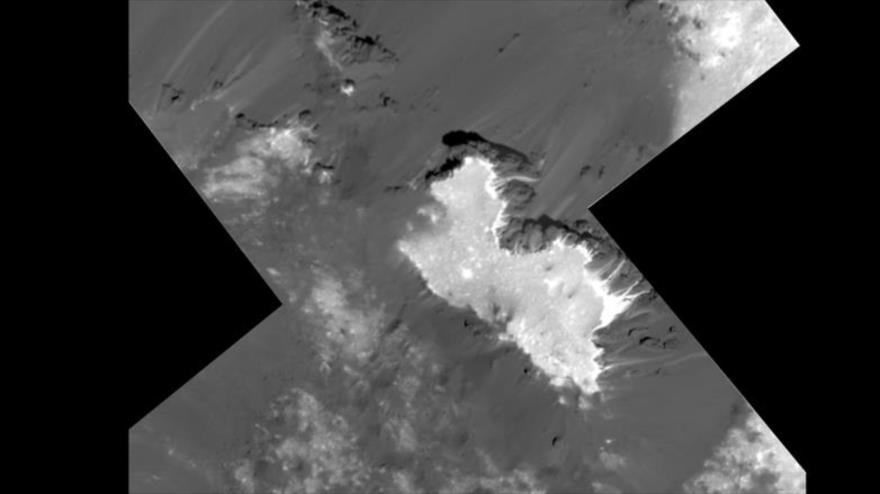
Some have been shown by the US Space Agency and they may be seeing the Occator crater, famous among astronomers for its shiny deposits.
Until now, the Dawn spacecraft had remained in orbit 385 kilometers from the surface of Ceres, located in the asteroid belt between Mars and Jupiter. This rocky body only reaches an approximate diameter of 945 kilometers, but it remains one of the largest solar system objects of its kind.
The obtaining of these images (from the planet Ceres) was one of the biggest challenges for the extraordinary dawn expedition. The results are even better than we expected, "says Chief Engineer Marc Rayman of the Reaction Propulsion Laboratory at the US National Aeronautics and Space Administration (NASA). .
According to NASA, these near-surface voyages "revealed unprecedented details in the relationship between light and dark materials in the Vinalia Faculae region." Previously, the probe had already detected deposits of sodium carbonate, a common material on Earth.
"The obtaining of these images was one of the greatest challenges of the extraordinary Dawn expedition. The results are even better than we expected, "says Marc Rayman, chief engineer of the NASA Jet Propulsion Laboratory mission
hgn / mla / alg / mkh
[ad_2]
Source link