[ad_1]

Hackers are actively exploiting today's critical vulnerability on the widely used Oracle WebLogic server to install ransomware without any clicks or other interaction from end-users, Cisco Talos researchers said Tuesday.
According to researchers from the SANS ISC safety training group, vulnerability and functional operating code were made public two weeks ago in the National Vulnerability Database in China. They warned that the vulnerability was the object of an active attack. This vulnerability is easy to exploit and allows attackers to execute code of their choice on cloud servers. Because of their power, bandwidth, and use in high-security cloud environments, these servers are considered valuable targets. The disclosure prompted Oracle to issue an emergency fix on Friday.
Cisco Talos researchers said on Tuesday that CVE-2019-2725, the vulnerability has been indexed, had been active since at least April 21. Starting last Thursday, one day before Oracle corrects the zero-day vulnerability, attackers began using exploits in a campaign to install "Sodinokibi," a new piece of ransomware. In addition to encrypting valuable data on infected computers, the malicious program attempts to destroy shadow backups to prevent targets from simply restoring lost data. Curiously, about eight hours after the infection, the attackers exploited the same vulnerability to install another ransomware software called GandCrab.
No interaction required
"Historically, most types of ransomware have required a form of user interaction, such as a user opening an attachment to an email, clicking a malicious link, or running a malicious program on his device ", Pierre Cadieux, Colin, researcher at Talos Grady, Jaeson Schultz and Matt Valites wrote in the article on Tuesday. "In this case, the attackers simply exploited the Oracle WebLogic vulnerability, forcing the concerned server to download a copy of the ransomware from IP addresses controlled by the attacker. 188.166.74[.]218 and 45.55.211[.]79. "
This vulnerability is easy to exploit because all you need is HTTP access to a vulnerable WebLogic server. Its severity rating according to the Common Vulnerability Rating System is 9.8 out of 10. Attackers send vulnerable servers a POST command containing a PowerShell command that downloads and then executes a malicious file called "radm.exe". In addition to PowerShell, attackers exploit CVE-2019-2725 to use the Certutil command-line utility. Office.exe and untitled.exe are among the other downloaded and executed files.
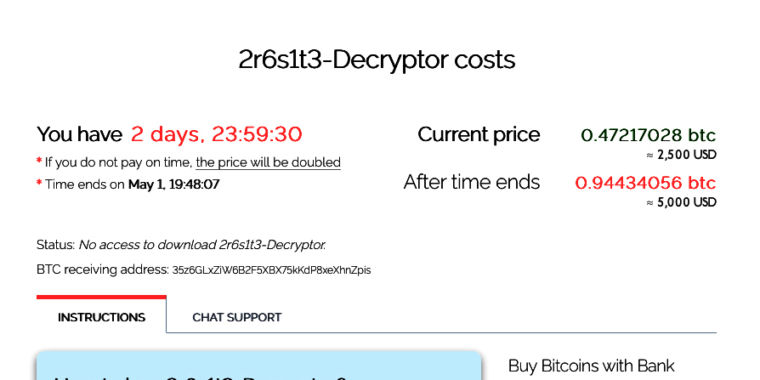
The ransom note illustrated in part above and partly below requires that targets pay $ 2,500 in bitcoins within two days to obtain the decryption key that will unlock the encrypted data. After this deadline, the ransom doubles to $ 5,000. Attackers provide instructions explaining how novices in cryptocurrency can establish a bitcoin wallet and get the digital currency, even going as far as recommending the use of Blockchain.info.

Cisco Talos
The attacks are characterized by the use of a zero day of high severity in software widely used in cloud environments. The combination means that the attacks are likely to continue. Organizations using WebLogic should give top priority to installing Friday's patch.
[ad_2]
Source link