
[ad_1]
Just minutes before SpaceX began feeding Falcon Heavy for its commercial debut, NASA announced that the company had won a contract for its Double Asteroid Redirection Test (DART) mission, which will be launched by Falcon 9 for a small fee. $ 69 million.
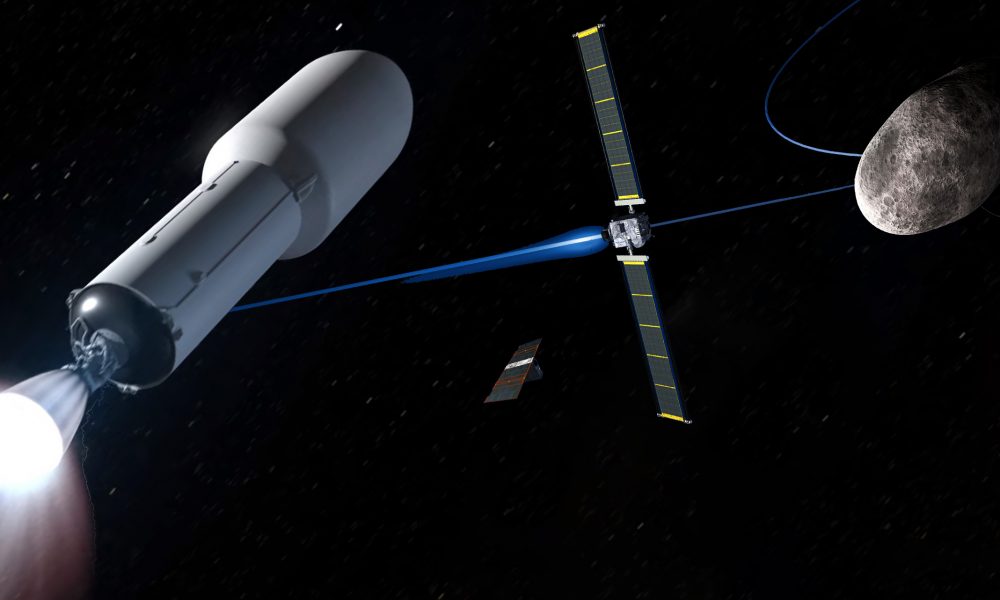
Designed to cost less than $ 250 million in total, the DART mission will aim to be as light and fast as possible, using a dedicated Falcon 9 to send the spacecraft ~ 600 kg (~ 1300 lb) and his Italian companion Cubesat at about 11 million dollars. kilometer (~ 7M mi) to the binary asteroid Didymos. The ultimate goal of DART is to effectively prove the technologies and physics that could be used in the future to defend the Earth against asteroids known for their collision course.
If all goes as planned during the DART design and hardware integration milestones, Falcon 9 could launch the satellite to the Didymos asteroid system in June 2021 for an arrival in October 2022. " arrival "would imply an impact of the DART on Didymos-B – the smallest pair at 163 m (535 ft) wide – at a relative speed greater than 6 km / s (3.7 mi / s). Nicknamed Didymoon, Didymos-B effectively orbits Didymos-A. At this speed, the 600 kg probe will create an impact with an equivalent explosive force of nearly two and a half years. tons TNT, whose goal is to determine how much impact kinetic energy can alter the orbit of a small body around the main asteroid.
According to estimates by the spacecraft mission managers, Didymoon's orbit should be shifted by approximately 1%, measured by the time required to orbit Didymos-A, from ~ 11.9 hours to approximately 11.8 hours. This is a small change, but which should – in theory – be easily measurable by telescopes on Earth, despite the fact that Didymoon's mass is estimated to be about 3.5 million metric tons (7.6 billion pounds), about seven million times. heavier than DART. In short, NASA will functionally bomb an asteroid moon to see if humans could use kinetic impactors to gently "screw up", threatening space objects out of the offending trajectory, or even decades away. advanced.
Despite the inherently destructive and single-use nature of the DART impactor state, current projects happily include an Italian cube known as LICIACube. The small passenger will deploy two days before the impact to fully exploit the scientific value of the disappearance of DART with high quality photos of the event and its consequences. LICIACube will travel at the same speed and therefore will not be able to enter orbit around the asteroid system, but a mission of the European Space Agency (ESA), known as Hera, plans to do so at mid-2020 to better characterize Didymos and the crater (hopefully) made by DART.
In addition to the mission itself, DART serves as a technology demonstration platform for NASA. This will be the first space use of the NEXT-C ion thruster built by NASA and

Go to orbit
For NASA's SpaceX launch contract, the agency will pay only $ 69 million, just 10% more than the $ 62 million minimum price expected for Falcon 9. It is safe to assume that the timing of the awarding the contract – a few days after the brutal suppression of an official protest by ULA of a $ 150 million contract to NASA – might not be taken seriously.
Weighing in at just under 1300 lb (600 kg) wet, DART may be launching additional co-workers on the Falcon 9, although a precedent was set by the NASA 360 TESS and the
Check Teslarati newsletters for quick updates, on-the-ground perspectives and a unique insight into SpaceX rocket launch and recovery processes
[ad_2]
Source link