[ad_1]
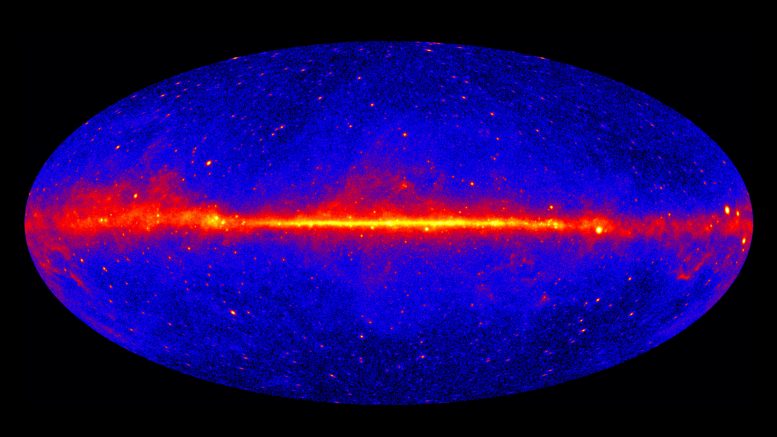
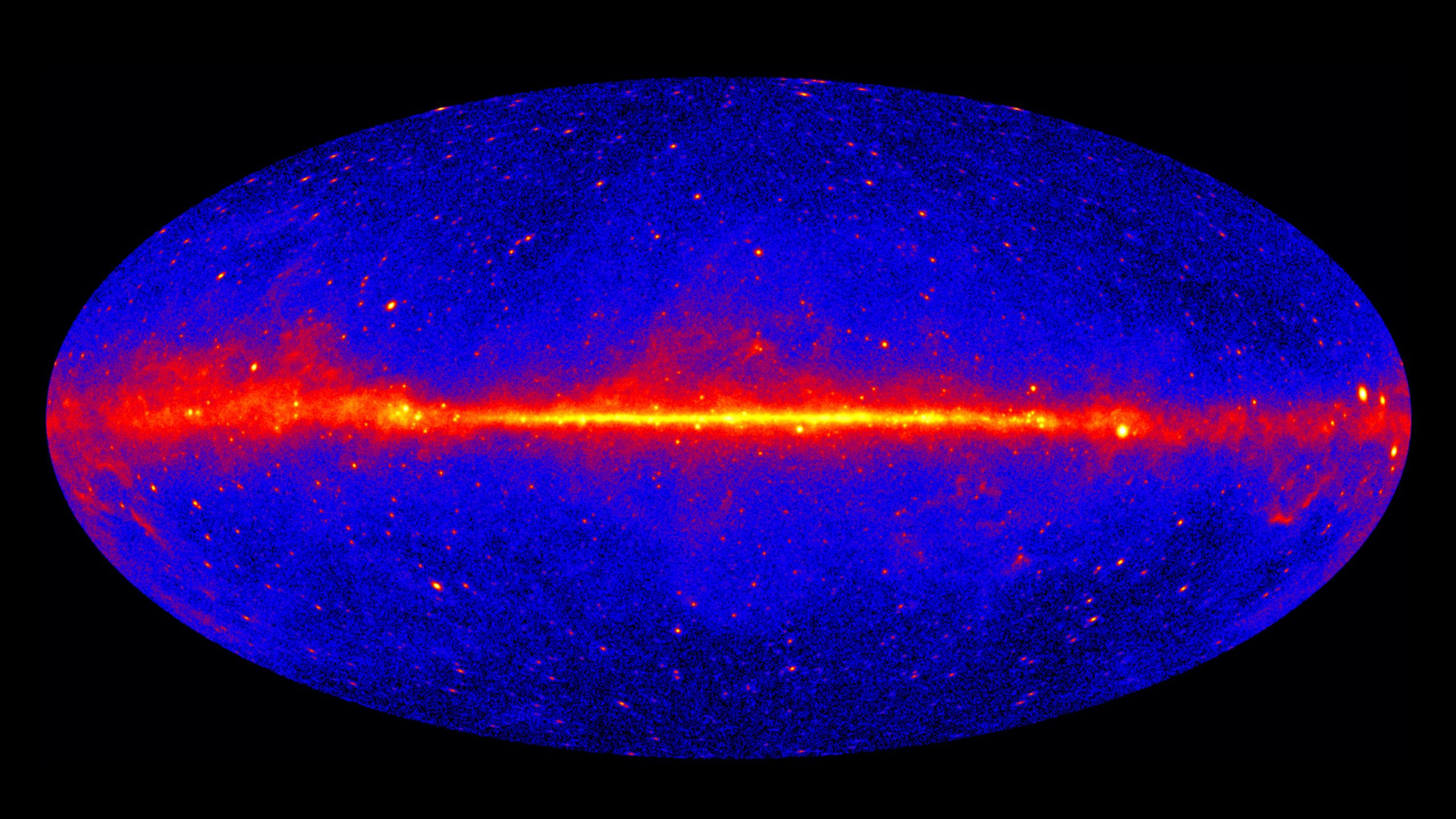
A detailed look at the gamma sky. Credit: NASA / DOE / Fermi LAT collaboration
Star-forming galaxies are responsible for creating gamma rays that until now had not been associated with a known origin.
Star-forming galaxies are responsible for creating gamma rays that until now had not been associated with a known origin, researchers at The Australian National University (ANU) confirmed.
Lead author Dr Matt Roth, from the ANU School of Astronomy and Astrophysics Research, has so far said it was not clear what created the gamma rays – one of the most energetic forms of light in the Universe – which appear in seemingly “empty” patches of light. sky’.
The discovery could offer clues to help astronomers solve other mysteries in the Universe, such as the type of particles that make up dark matter – one of the holy grails of astrophysics.
“It is an important step to finally discover the origins of this gamma ray emission, to solve a mystery of the Universe that astronomers have been trying to decipher since the 1960s,” said Dr Roth.
“There are two obvious sources that produce large amounts of gamma rays seen in the Universe. One when gas falls into supermassive black holes that lie at the center of all galaxies – called the active galactic nucleus (AGN) – and the other associated with star formation in galaxy disks.
“We modeled the gamma ray emission from all galaxies in the Universe and compared our results with predictions from other sources and found that it is the star-forming galaxies that produce the majority of this diffuse gamma radiation. not the AGN process. “
ANU researchers were able to identify what created these mysterious gamma rays after gaining a better understanding of how cosmic rays – particles that travel at speeds very close to the speed of light – move through gas between the stars. Cosmic rays are important because they create large amounts of gamma ray emission in star-forming galaxies when they collide with interstellar gas.
“It is an important step to finally discover the origins of this gamma ray emission. “- Dr Matt Roth
Data Nasa‘s The Hubble Space Telescope and the Fermi Gamma-Ray Space Telescope was a key resource used to uncover the unknown origins of gamma rays. The researchers analyzed information about many galaxies such as their star formation rates, total masses, physical size, and distances from Earth.
“Our model can also be used to make predictions about radio emissions – electromagnetic radiation that has a frequency similar to that of a car radio – from star-forming galaxies, which could help researchers better understand the structure. internal galaxies, ”said Dr. Roth. noted.
“We are currently looking to produce gamma ray sky maps that can be used to inform future gamma ray observations from next generation telescopes. This includes the Cherenkov Telescope Network, in which Australia is involved.
“This new technology will hopefully allow us to see many more star-forming galaxies in gamma rays than we can detect with current gamma-ray telescopes.”
Reference: “The diffuse -ray background is dominant by star-forming galaxies” by Matt A. Roth, Mark R. Krumholz, Roland M. Crocker and Silvia Celli, September 15, 2021, Nature.
DOI: 10.1038 / s41586-021-03802-x
This research, published in Nature, features authors from Australia and Italy. The ARC Center of Excellence for 3D Astrophysics of the Sky (ASTRO 3D) was also involved.
[ad_2]
Source link