[ad_1]

The entire planet of Mars is going through a mbadive sandstorm that has been raging for weeks. The Opportunity rover is caught in the middle of the storm, does not get enough light and has been put into low power sleep mode. It may never wake up again, but scientists say there is a good chance this storm will occur. The rest of Mars' instruments, including the Curiosity rover, are operational, allowing a personal look at Mars weather.
There are currently a number of missions performing instruments on and around the Red Planet. who are in the perfect place and time to study Mars. Global dust storms like this one are not common, and according to a Space.com report, they only appear once in eight years
The Young Opportunity Colleague Rover, Curiosity, is busy studying the Martian atmosphere. For the size and distribution of dust particles, NASA notes using a variety of embedded instruments.
The Curiosity meteorological data collection could shed light on how storms can affect the "atmospheric tides" on Mars. These are atmospheric pressure waves that travel in the air of the planet, notes the report.
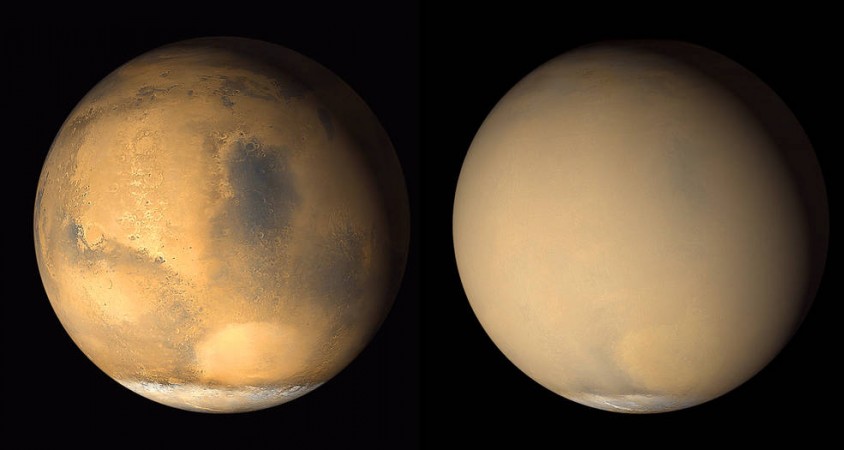 Two 2001 images from the Mars Orbiter camera on NASA's Mars Global Surveyor orbiter show a dramatic change in the appearance of the planet NASA / JPL-Caltech / MSSS
Two 2001 images from the Mars Orbiter camera on NASA's Mars Global Surveyor orbiter show a dramatic change in the appearance of the planet NASA / JPL-Caltech / MSSS
Curatorial project scientist Ashwin Vasavada of NASA's Jet Propulsion Laboratory (JPL) spoke of the impact of the dust storm in the south. consulting team is acquiring a new sample of rock, but we also use instruments to study the evolution of the dust storm. "
In addition to the reports of Curiosity field, At present, the space agency has three different orbiters who study the storm quite intensively: the storm itself, noted the report, started small in May and, at the June 20, covered the entire planet.] Thermal imaging emission The system (THEMIS) on Ma NASA's Odyssey monitors surface and atmospheric temperatures as well as the amount of dust in the air of the planet.
This dust storm is one of the biggest weather events that Mars scientists have been able to get closer to. According to a THEMIS team member, Michael Smith, "Another example of a dust storm really helps us understand what's going on."
NASA's Mars Reconnaissance Orbiter (MRO), is also busy at work since he spotted the storm at the end of May, notes the report. The MRO uses its instruments to track the effects of the storm on the atmospheric temperatures of Mars. On how the storm became stronger and stronger until it took the whole planet, the scientists explain that the storm is self-reinforcing. NASA explained that when the dust in the upper parts of the atmosphere absorbs solar energy and that it gets hot, it can change the wind patterns, possibly raising more dust from the surface .
Source link