
[ad_1]
OUT OF THIS WORLD | What's new in space – the biggest news arriving on Earth from space
Scott Sutherland
Meteorologist / Scientific writer
Wednesday, July 4, 2018, 18:53 – A global dust storm still engulfs Mars, and while NASA's venerable Rover Opportunity sleeps, its biggest cousin, Curiosity, is still at work and returns incredible images of its dusty sky.
It's been over a month now that a dust storm has erupted on Mars, starting around the Opportunity robot, then spreading around the planet in the days that followed.
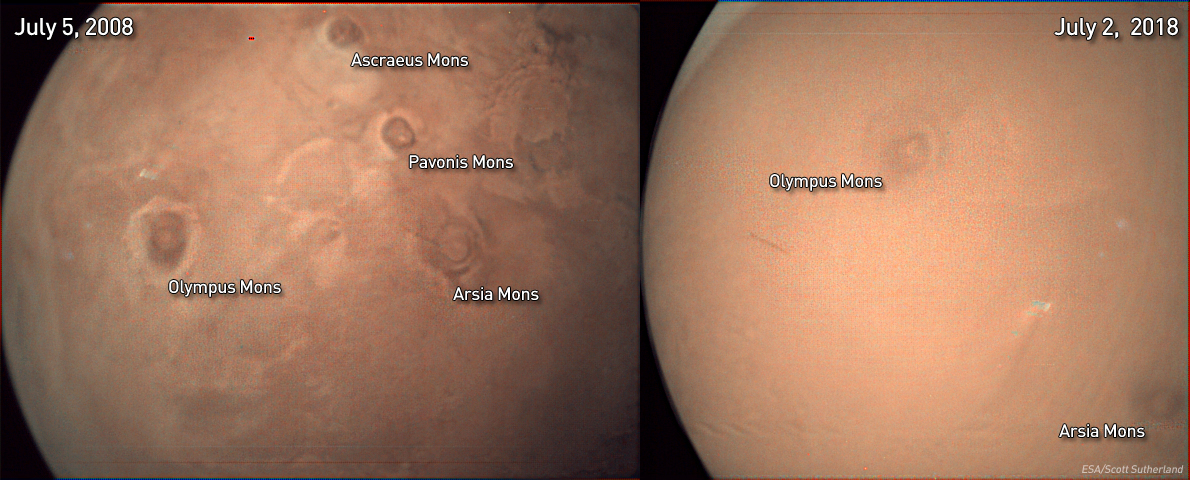
Two images of the Mars Express orbiter from ESA, taken about 10 years apart, of different distances and different angles, but showing the same region of Mars. In July 2008 (left), it was easy to see many Martian surface features, including the four giant volcanic mountains of the planet: the three Tharsis Mountains – Mons Ascraeus, Pavonis Mons and Arsia Mons – and the l & # 39; Olympus Mons alone. In July 2018, there is so much dust in the atmosphere that only the summits of the two largest – Olympus Mons and Arsia Mons – are barely visible. Credit: ESA-European Space Agency / Scott Sutherland
Currently, the NASA team for Opportunity at the Jet Propulsion Laboratory in Pasadena, California, is still waiting, hoping to soon hear from their explorer veteran soon. Since the robot is powered by solar energy, the dust has made it impossible to gather enough energy to maintain communication. He remained silent on June 12
Curiosity the largest nuclear cousin of Opportunity, still operating at near optimal levels, and continues to render images every soil of the storm and its scientific operations.

The Curiosity MastCam images, from May 17 (Sol 2054) to June 29 (Sol 2096), show that the dust is gradually deteriorating in the crater of Gale, causing a total loss of sight of the robot. from the edge of the crater to June 15 (Sol 2082). Only the nearest rocky outcrop and some sand dunes just beyond, remain visible until the end of the month. Source: NASA / JPL-Caltech / MSSS / Scott Sutherland
A Soil & # 39; is a day on Mars, which lasts 24 hours, 39 minutes and 35 seconds. The number of soil is specific to each mission, however. Sol 2082 for Curiosity is the 2082nd ground of this rover on Mars, and corresponds to June 15, 2018 here on Earth. On June 12, 2018, when the rover Opportunity went out, he was the 5112nd ground of his mission.
As we wait, with orbiters and at least one rover recording the progress of this storm, there is really no telling exactly when
Stay tuned for more bets up to date, and to see more images, ground-by-floor, from Curiosity's camera collection, go to the Mars Science Laboratory site of NASA JPL
Source: NASA | ESA – Mars Express
Look below: Curiosity finds a treasure of organic matter from Mars
You too … Like
Source link