
[ad_1]
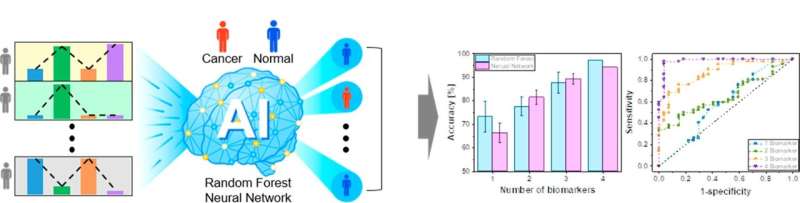
The set of detection signals collected for each patient was then analyzed using ML to screen the patient for PCa. Seventy-six urine samples were measured three times, generating 912 biomarker signals or 228 sets of detection signals. We used RF and NN algorithms to analyze multi-marker signals. Both algorithms provided increased precision and the size of the AUROC increased as the number of biomarkers increased. Credit: Korea Institute of Science and Technology (KIST)
Prostate cancer is one of the most common cancers in men. Patients are determined to have prostate cancer primarily based on PSA, a cancer factor in the blood. However, since the diagnostic accuracy is as low as 30%, a considerable number of patients undergo further invasive biopsy and therefore suffer from the resulting side effects, such as bleeding and pain.
The Korea Institute of Science and Technology (KIST) announced that the collaborative research team led by Dr Kwan Hyi Lee of the Biomaterials Research Center and Professor In Gab Jeong of Asan Medical Center has developed a technique to diagnose prostate cancer from urine in just 20 minutes with almost 100% accuracy. The research team developed this technique by introducing a method of intelligent analysis of AI in an ultrasensitive biosensor based on an electrical signal.
As a non-invasive method, a diagnostic test using urine is convenient for patients and does not require invasive biopsy, thereby diagnosing cancer without side effects. However, since the concentration of cancer factors is low in urine, urine-based biosensors are only used to classify risk groups rather than for precise diagnosis so far.
Dr Lee’s team at KIST worked on developing a technique for diagnosing the disease from urine with an ultrasensitive biosensor based on an electrical signal. An approach using a single cancer factor associated with a cancer diagnosis was limited to increase the diagnostic accuracy to over 90%. However, to overcome this limitation, the team simultaneously used different types of cancer factors instead of using just one to improve diagnostic accuracy in innovative ways.
The team has developed an ultra-sensitive solid-state sensor system capable of simultaneously measuring traces of four selected cancer factors in urine to diagnose prostate cancer. They trained the AI using the correlation between the four cancer factors, which were obtained from the developed sensor. The trained AI algorithm was then used to identify people with prostate cancer by analyzing complex patterns of the detected signals. Diagnosis of prostate cancer using AI analysis successfully detected 76 urine samples with almost 100% accuracy.
“For patients who need surgery and / or treatment, cancer will be diagnosed with high accuracy using urine to minimize biopsies and unnecessary treatments, which can dramatically reduce medical costs and fatigue. medical staff, ”said Prof Jeong from Asan Medical Center. “This research has developed a smart biosensor that can quickly diagnose prostate cancer with nearly 100 percent accuracy just through a urine test, and it can be used later in the accurate diagnosis of other cancers via a urine test, “said Dr Lee of KIST. .
Stop smoking, your bladder will thank you
Hojun Kim et al, Precision Non-invasive Prostate Cancer Screening Using Urinary Multi-Marker Sensor and Artificial Intelligence Analysis, ACS Nano (2020). DOI: 10.1021 / acsnano.0c06946
Provided by the National Research Council of Science & Technology
Quote: Cancer can be accurately diagnosed using a urine test with artificial intelligence (2021, January 21) retrieved January 21, 2021 from https://phys.org/news/2021-01-cancer- precually-urine-artificial-intelligence.html
This document is subject to copyright. Apart from any fair use for study or private research, no part may be reproduced without written permission. The content is provided for information only.
[ad_2]
Source link