[ad_1]
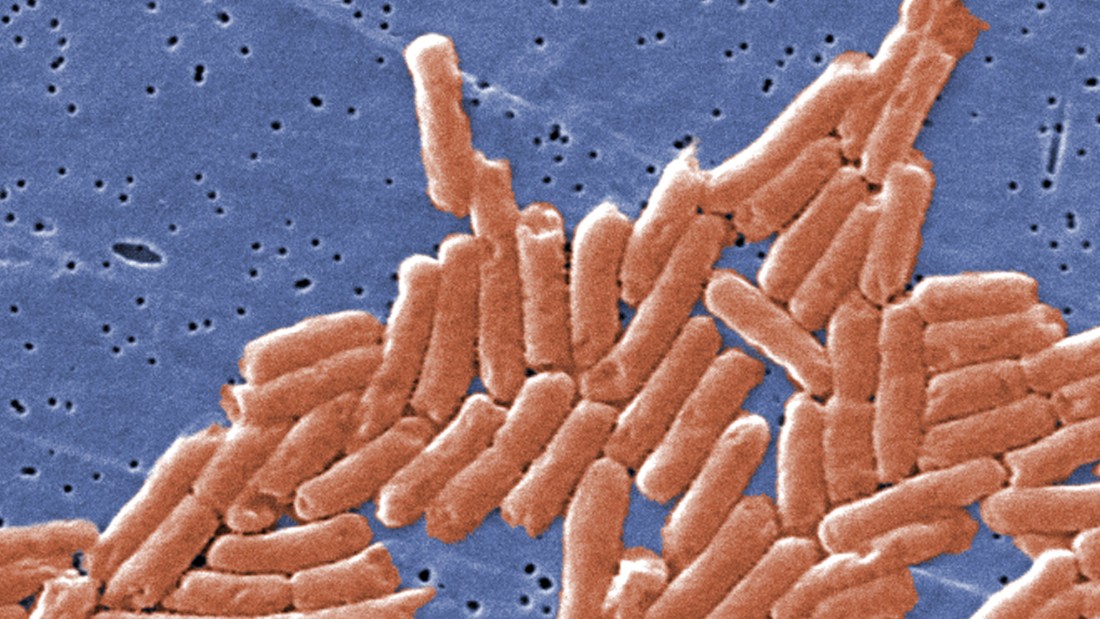
"We continue to see cases arise among patients," said Dr. Ian Plumb, an epidemiologist with the CDC's Department of Enteric Epidemiology and lead author of the report, in an email to CNN.
"The antibiotic resistance profile of this strain is alarming because the main oral antibiotics used to treat patients with this type of Salmonella infection may not work," he said.
Salmonella infections were linked to beef obtained in the United States and soft cheese obtained in Mexico, suggesting that this strain may be present in cattle in both countries, the CDC said. Eighty-nine of the people who contracted the infection had recently returned to Mexico.
"To prevent infection, consumers should avoid consuming soft cheese that can be made with unpasteurized milk.When preparing beef, they must use a thermometer to achieve proper cooking temperatures: 62 ° C (145 degrees Fahrenheit) 3 minutes rest time and 160 degrees Fahrenheit (71.1 Celsius) for ground beef or hamburgers, "according to the new CDC report.
The CDC called the strain "emergent" and clarified that it had not been detected before 2016. The strain did not respond to ciprofloxacin and had "reduced sensitivity" to it. Azithromycin – two antibiotic drugs often prescribed to treat Salmonella infections.
Most Salmonella patients recover without antibiotics, but those with serious infections need antibiotics Resistant infections may be more difficult to treat and patients are more likely to develop serious complications.
The CDC said that avoiding the unnecessary use of antibiotics in cattle, particularly those that are important for the treatment of human infections, could help prevent the spread of this strain of salmonella that is resistant to drugs.
[ad_2]
Source link
