[ad_1]
It is easy to think that the idea of an "aura" that surrounds us belongs strictly to the plane of esotericism.
A quick search on the Internet gives dozens of tips for "cleans the aura" and "repels negative energies". And this may be the only context in which you have seen the word, usually badociated with emotions and how they can affect your physical and mental well-being.
But, aside from esotericism, science has shown the existence of a "living aura" individual: it is called the human exponent and has nothing to do with spiritual energies.
The term describes this personal cloud of microorganisms, chemical elements and other compounds that actually go with us wherever we are.
The exhibition is the focus of a study conducted by a group of geneticists from Stanford University (California, USA) for five years.
Science already had notions about this concept, the research, published in the scientific journal Cell in mid-October, showed that it is possible to measure "on an individual level" the elements of the 39 environment to which it is exposed. each person.

Michael Snyder – who was behind the study – told BBC World that the most important "is that these measures can make all the difference study and prevent diseases such as l? Asthma and Allergies ", which makes an important contribution to the field of health.
Experience
For their experience, the researchers manufactured a small air-control device and they attached it to the arm of 15 volunteers, who were exposed to different places as the device absorbed samples of their personal orbits and the surrounding environment.
The elements collected by the device (bacteria, fungi, viruses, etc.) gave DNA and RNA sequences forming a unique chemical profile for each volunteer.
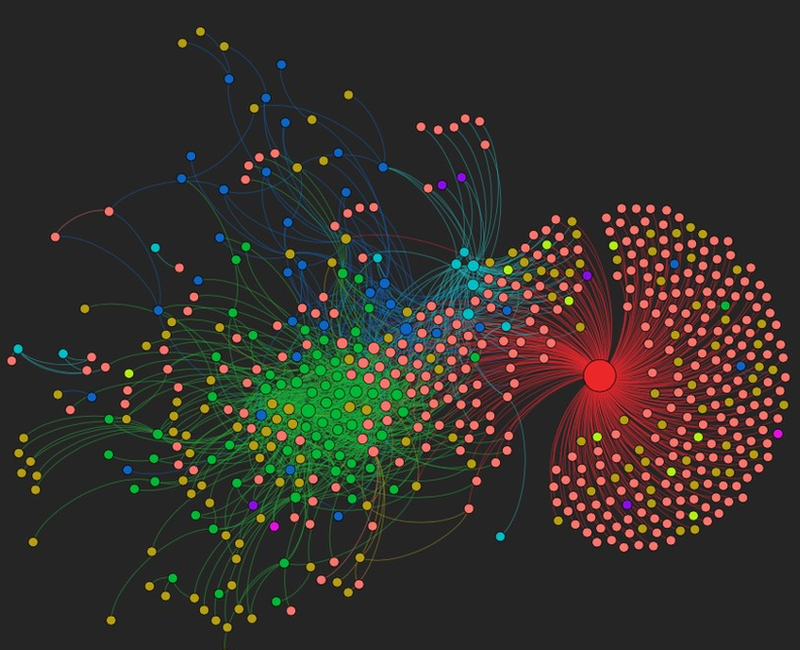
By the end of the study – which included hundreds of thousands of readings – the researchers managed to accumulate a large amount of data on the components of their own exposome.
Snyder himself, who used one of the devices during the study revealed that compounds such as eucalyptus pollen were present in his probably at the origin of an allergy that he had suffered in the past.
Individual Cloud
The human exposure was known before Snyder and his team make known the results of their research is that individuals are certainly exposed to a number of elements present in the world. ;environment.
However, measurements made in this sense only "Therefore, we focus primarily on the PM2.5 particles present in the atmosphere, which result from the and they end up being absorbed into the lungs, "explains Chao Jiang, another of the authors of the study.
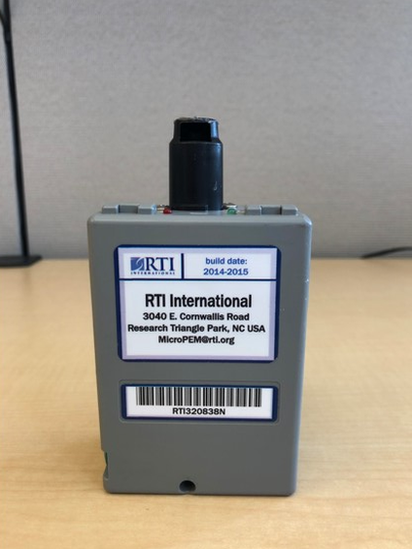

So far, the exposome was also badyzed only at fixed locations in the city, where a device was taking a sample of air.
"We can now follow the elements that all no one is exposed, no matter where they are. Snyder explains:
The volunteers traveled to different areas of San Francisco Bay and it was shown that even when they were in the same place, their exhibits were different. [19659004] This confirms that each individual is surrounded by his own microbial cloud, which continuously collects and expels around them
The authors of the study agree that the greatest contribution of this new information will be: á in the field human health, which is not only determined by genetic factors, but also by environmental factors.
Accessible to all
"Many genetic factors have been studied, but little is known about environmental exposure affects people's health, "said Jiang Jiang.
The scientist thinks that this new thorough knowledge of the human exposometer will be essential the understanding and even prevention of conditions such as cancer, asthma, allergies and some heart and respiratory diseases.
In fact, one of the most important findings of the exhaustive investigation was the presence of insect repellent particles in all samples collected.
"People could suck this compound – which is not he knows how toxic it is for health – as well as diethylene glycol which is highly carcinogenic and has been found everywhere" , Snyder says
He, Jiang and his other companions have not finished, study the "living aura" around us
And to answer the BBC's question about the next steps of research, geneticists draw a plan.
"We want to make a cheaper device so that everyone can map their individual exposures to the environment," says Jiang Jiang.
"Conditions such as asthma and allergies can be better controlled if we are able to understand the reactions of these patients," he says.] In the medium term, the team also plans to implement this technology in the most exposed places environmental contamination, such as hospitals and nurseries.