
[ad_1]
2018 was apparently the hottest year ever recorded for the world's oceans.
Buzz60
Emissions of carbon dioxide – the greenhouse gas most responsible for global warming – could reach levels never seen since 56 million years in the middle of the next century, scientists warn in a new study Wednesday.
Even if it does not happen in our lifetime, it could very well happen in the lives of our grandchildren or great-grandchildren.
"You and I will not be here in 2159, but there are only four generations left," said Philip Gingerich, author of the study, a paleoclimate researcher at the University of Michigan.
He added that humans now release 10 to 10 times more carbon dioxide into the atmosphere than during a natural warming of the planet, about 56 million years ago.
This era, known to scientists as the Paleocene-Eocene Thermal Maximum (PETM), was the hottest period on earth since the extinction of dinosaurs 66 million years ago. According to the study, during this period, the poles were ice-free and the Arctic was home to palms and crocodiles.
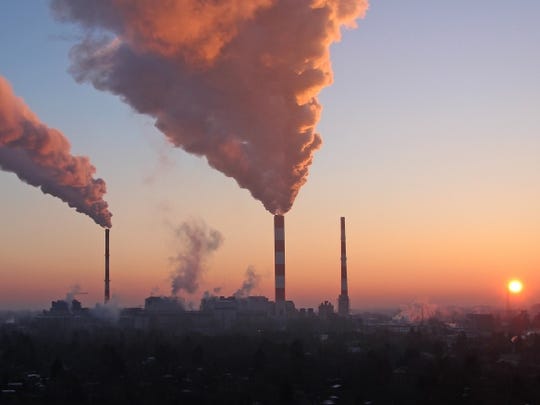

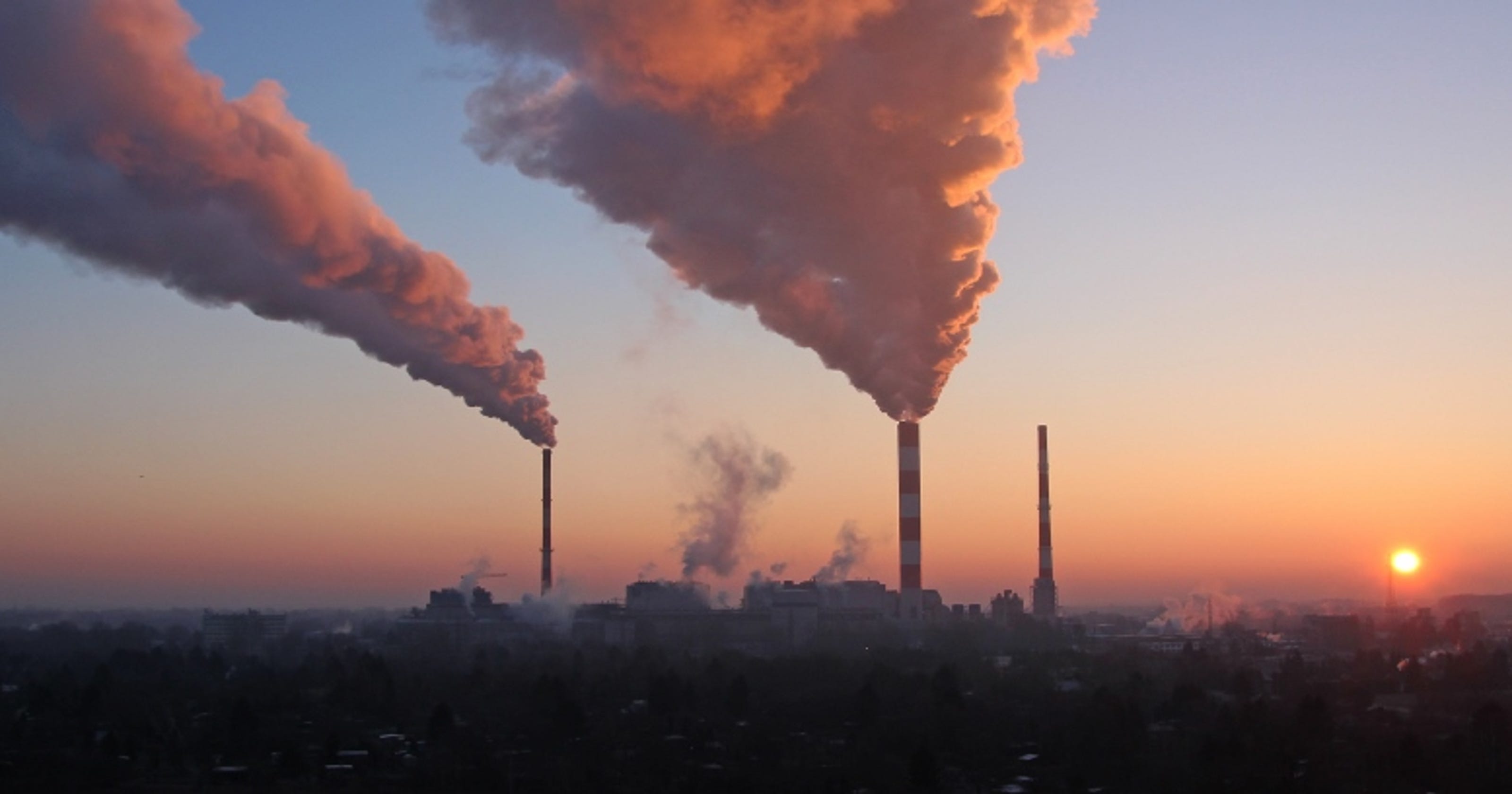
The burning of fossil fuels such as oil, gas and coal releases carbon dioxide and other gases into the atmosphere, causing global warming that can not be explained by natural variability. (Photo11: United Nations)
This heat has caused a major extinction of organisms in the depths of the ocean, which constitute a vital link in the marine food web.
Scientists are unsure of the cause of this increase in carbon dioxide during this period, but we certainly know the cause:
The burning of fossil fuels such as coal, oil and gas releases greenhouse gases such as carbon dioxide and methane into the atmosphere and oceans of the Earth. This extra carbon has caused temperatures to rise over the past one hundred and fifty years, which can not be explained by natural factors, scientists said.
"The carbon emission rates that are occurring today are truly unprecedented," he said. Gabriel Bowen, geophysicist from the University of Utah.
The increase in gases such as carbon dioxide, methane and nitrous oxide is fueling climate change and making "the planet more dangerous and inhospitable for future generations," said the Meteorological Organization. World.
More: Carbon dioxide emissions in the Earth's atmosphere reach record levels
Experts said that to reduce or reduce carbon emissions and the abnormal warming of the planet, citizens, governments and businesses must reduce the consumption of fossil fuels and adopt renewable and carbon-free energies.
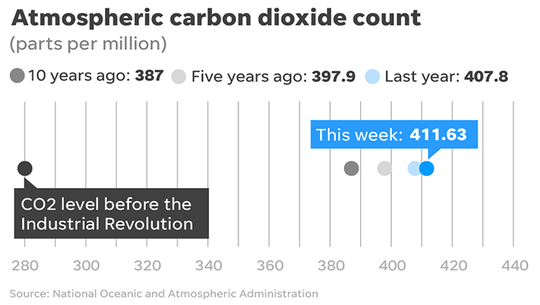
Levels of atmospheric carbon dioxide as of 14 February 2018 (Photo11: Graph of George Petras / USA TODAY & # 39; HUI)
"It will not only be 100 years, it will take a long time for carbon dioxide to reappear in the earth's crust," he said. Larisa DeSantis, paleontologist at the University of Vanderbilt. "This is not a short – term event – we are really engaging in thousands of years of a warmer world if we do not act quickly.
The study was published in Paleoceanography and Paleoclimatology, a journal of the American Geophysical Union.
Read or share this story: https://www.usatoday.com/story/news/nation/2019/02/21/global-warming-earth-could-could-see-carbon-dioxide-levels-not-seen- 56- m-years / 2930902002 /
[ad_2]
Source link