
[ad_1]
As soon as the typhoon "Pirpurun" ends, another typhoon is emerging in the northwestern Pacific and the typhoon "Pirpurun" is expected to disappear from the sea about 470 km southwest of Sapporo. . Today, at 12 o'clock About 200 km around the south-east of Guam In the sea, spiral clouds, the seeds of typhoons, develop. The center of the vorticity cloud is 11.5 degrees north latitude and 146.4 degrees west. In the southwestern Pacific Northwest, tropical low pressure (TD, tropical depression) is developing.
Today, at 12 o'clock today, the central low pressure of the tropical low pressure section is 1004 hPa (pascal hecto), with a wind speed of 15 m per second blowing from the center and an instant wind of 23 m per second (Source: Meteorological Agency of Japan). The Japanese Meteorological Agency estimates that this tropical low pressure portion will reach a central high pressure of about 1,000 hPa by midnight tomorrow, and a violent wind of 18 m altitude near the center. Typically, the typhoon is clbadified when the maximum wind speed of the tropical low pressure section exceeds 17 m per second. If it is clbadified as a typhoon, it will have a name. The name of the typhoon after "Pirpurun" is & # 39; Maria & # 39 ;. Therefore, it is highly likely that the Typhoon & # 39; Maria & # 39; will rise from tomorrow to the day.
The most important thing is to know where the typhoon Maria will be heading. It is not easy to accurately predict the course of an early typhoon, as the expected course of Typhoon "Pirpurun" went from the north to the west coast to go north to the region of Kyushu.
It is virtually impossible to accurately predict the course of a typhoon more than five days and a week before a day or two, especially if the typhoon is in a low latitude region, the factors that affect them are very diverse. First and foremost, basically, you must know exactly what the typhoon is.
The second is to provide accurate information on the environment that affects the typhoon, and how the typhoon is currently strong, how large it is, what the structure looks like, must have. When a typical is in low latitude, it is an information on a wind of breeze. At low latitudes below 30 degrees latitude, typhoons tend to move westward by the east wind. If a typhoon is above mid-latitudes above 30 degrees of latitude, it is mainly affected by the westerlies and not by the westerlies. The west wind tends to bring the typhoon to the east. Typical examples are the location of shoals and mid-latitude water jets.
North Pacific pressure is also highly dependent on the typhoon's trajectory, but it is also important to note that the high pressure of the North Pacific also depends heavily on the direction of the typhoon. This has a great influence. The high pressure of the North Pacific corresponds to a huge wall compared to a typhoon. Thus, in general, typhoons tend to move along the North Pacific Highway without pushing or pulling up the North Pacific. Therefore, it is necessary to know exactly where the current position of the North Pacific high pressure is, and whether the high pressure of the North Pacific will develop or contract in the future. This is an important variable at which point the waters of the region should move.
From the typhoon information itself to the knowledge of various information on the environment that may affect the typhoon, it is necessary to accurately predict the course as far as possible. Can be predicted. In particular, you should know all this information about a week or ten days earlier, rather than a day or two, so that you can predict the expected evolution of the typhoon more precisely a week to ten days more early. However, there is virtually no way to know all this information accurately a week to ten days earlier.
Of course, it is not possible to say if the seed of typhoon Maria, which has not yet developed like a typhoon, will affect the Korean peninsula, or if it will go to China or will go in Japan. / W), as long as a week, ten days and a month. A single day, ten days or more, not a day or two, can guarantee accuracy. For example, Levi Cowan, a tropical weather expert, reports on the Internet (Tropical Tidbits, https://www.tropicaltidbits.com/), which provides information on tropical cyclones, the expected evolution of Mary varies from south of China east of Japan (see figure below). There are no official data, but there are cases in which it is expected that North Korea will go north on different roads. Of course, the data on tropical flourishes do not show all the possible paths provided. 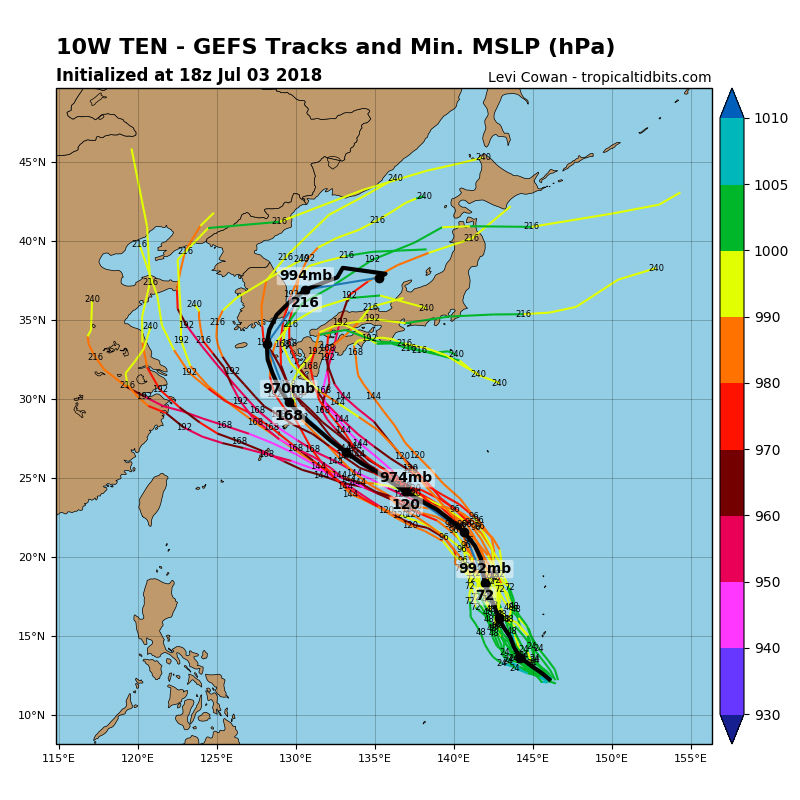 It's not easy to predict the exact course at the moment, but one thing is clear: Maria typhoon, It will be much stronger than the Pirpurun. The typhoon & # 39; Maria & # 39; is generated from the low latitude near the equator in relation to "Pirpurun", and is more likely to develop as a strong typhoon after pbading the warm sea for a long time. In particular, it is not possible to completely eliminate the possibility of coming into the peninsula among the various possibilities, so it is necessary to look closely at the typhoon "Maria & # 39; until more accurate data is available. Of course, it is obvious that we must always prepare for typhoons.
It's not easy to predict the exact course at the moment, but one thing is clear: Maria typhoon, It will be much stronger than the Pirpurun. The typhoon & # 39; Maria & # 39; is generated from the low latitude near the equator in relation to "Pirpurun", and is more likely to develop as a strong typhoon after pbading the warm sea for a long time. In particular, it is not possible to completely eliminate the possibility of coming into the peninsula among the various possibilities, so it is necessary to look closely at the typhoon "Maria & # 39; until more accurate data is available. Of course, it is obvious that we must always prepare for typhoons.
[ad_2]
Source link