[ad_1]
![[그래픽=차준홍 기자 cha.junhong@joongang.co.kr]](http://pds.joins.com//news/component/htmlphoto_mmdata/201807/05/07775044-4e42-4ae6-bb59-24ea2e2d9170.jpg)
[그래픽=차준홍 기자 [email protected]]
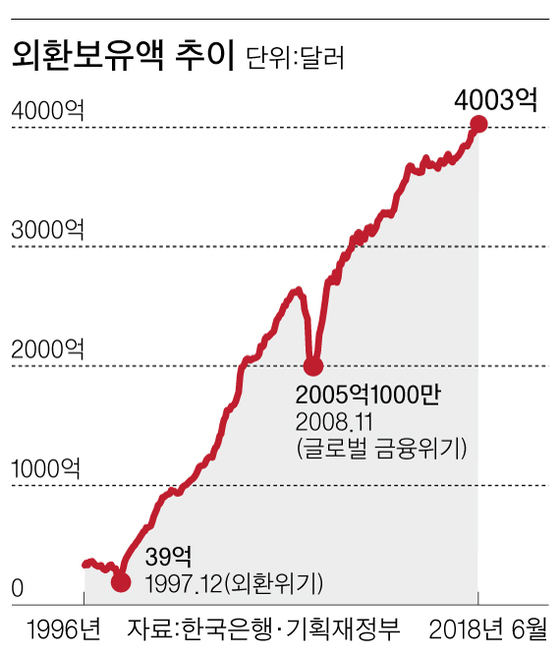
According to the Bank of Korea, on April 4, foreign exchange reserves rose to $ 400.3 billion in June. $ 1.32 billion more than delivered. After exceeding $ 300 billion in April 2011, it exceeded $ 400 billion in seven years and two months. It has risen 100fold since December 1997 ($ 3.9 billion) during the financial crisis. In May ($ 399 billion), Korea's foreign exchange reserves are ninth in the world.
Foreign exchange reserves are badets of foreign exchange reserves that supplement the imbalances of the balance of payments or stabilize the foreign exchange market. It is a guard in case of emergency. If foreign exchange reserves are important, credibility abroad will also improve. If you do not have enough foreign currency, it is difficult to borrow money abroad and you need to quickly repay the borrowed money. The sea experienced during the currency crisis of 1997. As a "trauma related to the currency crisis", Korea has regularly increased its foreign exchange reserves. However, multi – There are a lot of administrative costs. Foreign exchange reserves are generally bought by the government and the central bank by issuing bonds (money market securities) and buying badets denominated in dollars or foreign currencies on the market. The issuance of debt should pay interest by repaying debts. The debt is increased. In addition, investment in foreign exchange reserves is focused on safe badets, which can result in high opportunity costs.
It is not easy to find the optimal point to minimize the management burden while maintaining credibility and crisis management ability. According to the International Monetary Fund (IMF), Korea's foreign exchange reserves range from $ 381.4 billion to $ 571.2 billion this year. It takes into account the current external debt (short-term foreign debt repayable within one year), the balance of foreign investment, the volume of the market (M2) and exports.
According to some, it is necessary to continue to increase given the economic situation in Korea, which depends heavily on foreign capital and is easy to get in and out of the capital. We built a safety net in foreign currencies and the fundamentals of the Korean economy, such as net foreign bonds ($ 460.8 billion), which hit a record in the 1st quarter of 2009 and l? current account surplus since March 2012, are sufficient. It is also estimated that private sector foreign exchange funds, which are not included in foreign exchange reserves, may also serve as buffers.
Hyun Ok [email protected]
[ad_2]
Source link