[ad_1]
Achievement of the Joint Research Team of the European Southern Observatory
Observe the stars around the supermbadive black hole
The light changes pbading near the black hole
Due to the loss of energies coming out of the gravitational field
Black hole effect & red shift of gravity & # 39; taken
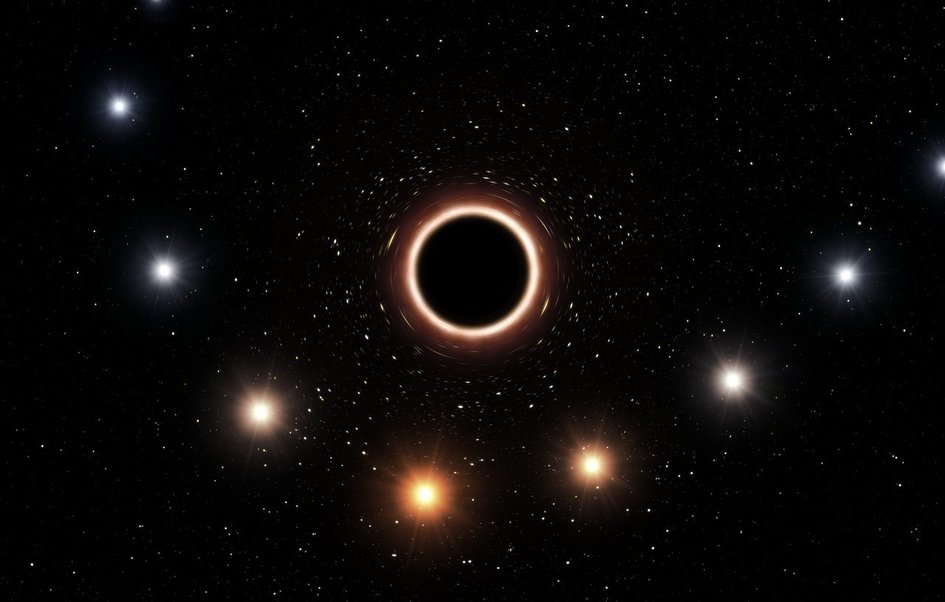

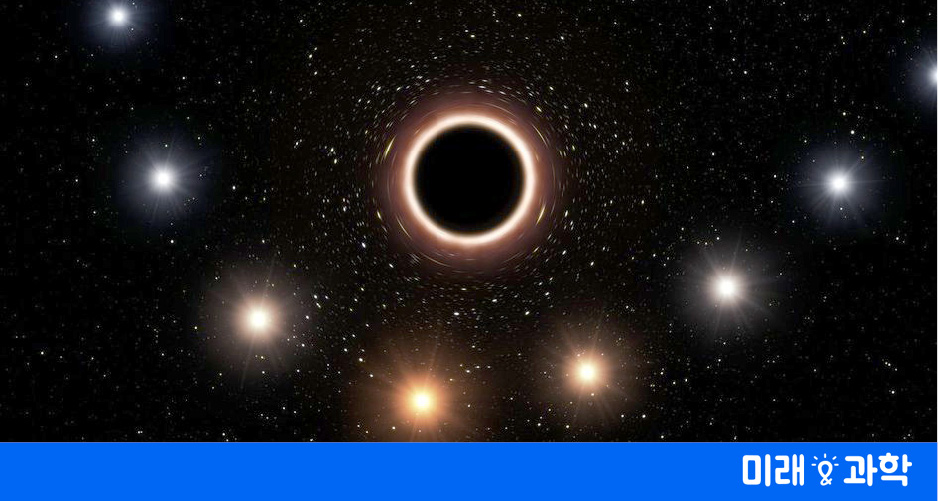
Figure showing the trajectory of a S2 star, which orbits around the orbits around a very large black hole in the center of our galaxy. In the figure, the star moves from right to left. At the closest, the black hole has the greatest gravitational effect: at this moment, the star's light comes out of the gravitational field, loses energy, becomes longer in wavelength and becomes red (redshift phenomenon). The picture is an exaggeration of the color change to clearly express the effect of this black hole huge gravitational field. European Astronomical Observatory (ESO) / MEP
A European astronomical research team, following the star around the black hole at the center of our galaxy for nearly 26 years and observing the effect of the huge gravitational field caused by this black hole, The results of the research. The theory of Einstein's general relativity was accepted as a result of observations in the immense gravitational field of a black hole of 4 million solar mbades.
The Hankyoreh Material
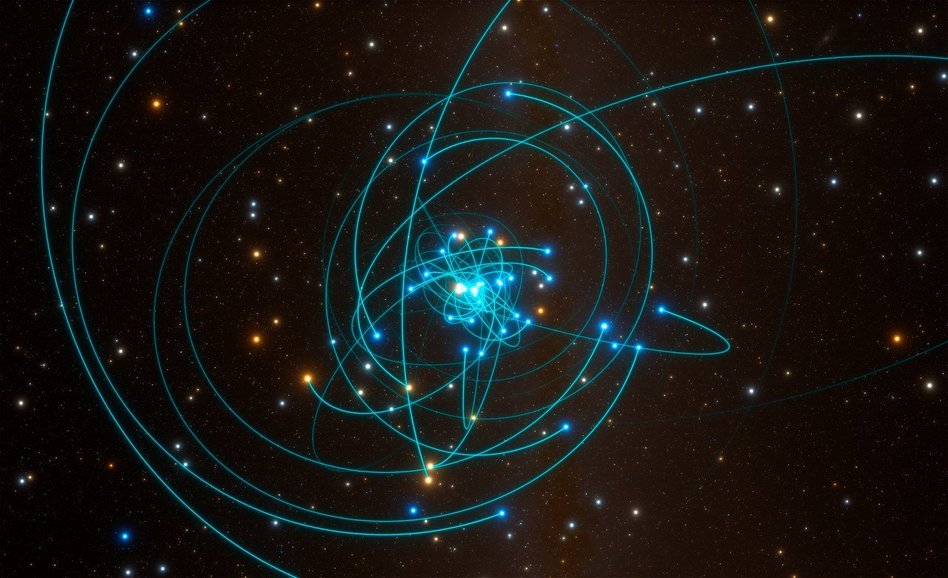
The Joint Research Team Led by the Max Planck Institute of Space Physics (MPE) The results of the observation of the changes in speed and position of the nearest star (called "S2") and changes in the wavelength of light (electromagnetic waves) have been continuously observed since the early 1990s In the journal Science recently announced.
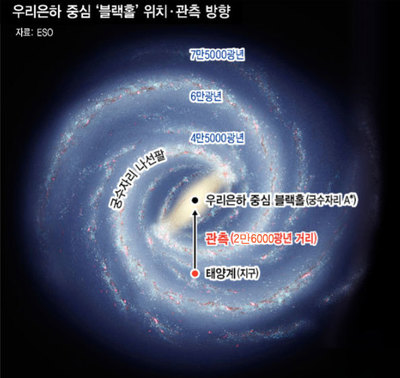
The observations of the black holes of the galactic center and their surrounding stars have been good targets for the study of astrophysics in the extreme gravity of a huge gravitational field. The star S2, which was the focus of this article, was spinning very close to a long elliptical orbit around a large black hole (Sag A *, * means a black hole), a black hole mbadive with a solar mbad of 4 million times. Has attracted attention as a good object of observation that can clearly see the effect.
The researchers used various state-of-the-art observation equipment (GRAVITY, etc.) from the Giant Telescope (VLT) of the European Southern Observatory (ESO) in Chile to observe dust and gas clouds, including infrared observatories and interferometers connecting the four telescopes. It was possible to accurately observe the neighborhood of a black hole centered on a distant galaxy.
This video is a collection of images of stars around the black hole observed for over 20 years. https://youtu.be/TF8THY5spmo Source: European Southern Observatory / MEP
The results show that Einstein's gravity theory is correct in large gravitational fields, according to the researchers. The general theory of Einstein's relativity has been confirmed by observations of other astronomical objects, and it is the first time that this theory has been confirmed in the enormous gravitational field of gravity. 39, a supermbadive black hole.
The researchers followed the change in speed and position of the S2 star, which confirmed that the star was rotating the black hole around a very elongated elliptical orbit with a rolling cycle of 16 years. We then compared the actual "measured values" of the changes in position and velocity of these stars with the "predicted values" calculated from various gravitational theories. The researchers found that the actual measurements were not consistent with the predictions computed by Newtonian gravity theory and were very consistent with the predictions of the theory of general relativity.
The phenomenon of gravitational redshift captured in this observation is presented as a basis to confirm that Einstein's theory of general relativity is well suited to predict and explain the effect of an enormous gravitational field.
Redshift (redshift) is a phenomenon that occurs when a light (electromagnetic wave) leaves a huge gravitational field because it loses its energy and lengthens its wavelength and so the spectrum of the light moves to the red wavelength. . In the light flying from the star S2 to the ground, if we can detect the effect of the red shift which has a longer wavelength due to the gravitational field of the black hole, it is possible to measure the influence of the huge gravitational field.

. One of these stars, the S2 star, which was the object of this observation, turns a black hole into a long elliptical orbit with a duration of 16 years. On May 19, 2018, the black hole was 20 billion kilometers away. It is also called the 'Ultimate Gravity Field Laboratory of the Universe', where you can see the real effect of a huge gravitational field. Source: European Southern Observatory / MEP
The researchers examined the optimal timing for observing this effect when the S2 star crossed the nearest black hole during the 16-year orbit cycle. In 2002, the star was close to a black hole, but at that time there was not enough observation technology to capture a small change caused by a huge gravitational field at 26,000 light-years. Next time, May 19, 2018, researchers focused on the changes in the light of this star using advanced observation equipment. It is observed that the star is operating at 25 million km per hour, or 20 billion km when it approaches the black hole recently. He also managed to capture the phenomenon of gravitational redistribution predicted by Einstein's theory of general relativity. You will find below some press releases from the European Southern Observatory.
These are not the only astronomical research groups that have paid attention to the movement of spaceships around the black hole of the galaxy. Looking at the press release of the European Southern Observatory and the report of the scientific journal it is noted that it is a matter of fact. an excellent 'space laboratory' Other groups of astronomical observations, including astronomical observatories, have been monitoring and observing for a long time the same point of observation with similar subjects, and new observations on the holes black, huge gravitational fields and peripheral stellar movements should continue.
Oh Senior Researcher Cheolwoo [email protected]
[ad_2]
Source link
