
[ad_1]
This year, 15 million euros were allocated to the treatment of hepatitis C, but only six million euros were spent in six months. At the same time, in Latvia, the "pretreatment" of patients is still in effect – only patients with hepatic impairment due to hepatitis C are more likely to receive advanced drug treatment.
Patients with hepatitis C but the health problems are not serious yet. it is not possible to receive paid treatment for new drugs, so choose to pay for the drug by ordering it outside the European Union and by mail. Patients are not always protected by the choice of a survival strategy because doctors are not obliged to monitor the treatment of these patients. In Latvia, there are also no guidelines to take if the patient orders drugs online. state of play. The Hepatitis Society is alarmed by the slowdown in government budget spending, which could theoretically reduce the amount to be allocated next year and by patients who can not expect that drugs paid by government to be paid and purchased in India
] One-fifth of patients are infected with health care
The number of people with hepatitis C in Latvia is not well known but there are certainly many people in whom hepatitis C has been diagnosed.
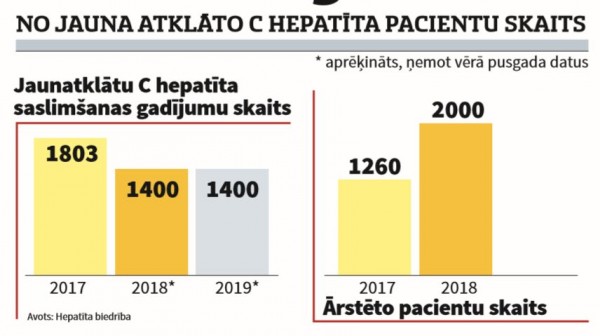
Hepatitis C was detected in 1803 patients, but estimates from the Hepatitis Society show that there will be 1400 patients this year. The number of patients treated last year was 1260, this year it was planned for 2000.
One-third of cases of hepatitis C infection are unknown, but in this case, one-fifth of patients were infected with health services rather than with badual or intravenous contact. "Unfortunately, it can also be infected by medical processes, depending on the storytelling of the patient and the history of the disease, when the incubation period coincides with the treatment," says Velga Ķūse, head of the Center for Disease Control. Infectology of Latvia. Hepatitis C most often occurs without yellowing, which usually refers to hepatitis in humans, so most patients accidentally find it. The doctor reveals that hepatitis C has at least 11 genotypes, and the determination of the genotypes of patients treated at the Center for Infectious Diseases of the Latvian Infectology Center shows that in Latvia, most patients with the first genotype (64%) and the third genotype (32%). The identification of genotypes is important because some drugs are effective for certain types, but currently there are also appropriate medications to treat all types of hepatitis C.
Recalling the history of the treatment of hepatitis, V. Kūse indicates that hepatitis C began its treatment in 1986 with interferon preparations, which we call conventional or conventional interferons, the treatment was long and severe. In contrast, ribavirin appeared in 1998, an antiviral drug that could be added to interferon, but in 2000, pegylated interferon, with which the treatment was long and with side effects. The direct-acting antiviral drugs appeared in 2016 have caused some revolution in the treatment of hepatitis C, since the effectiveness of treatment is 97-99%, shorter treatment times and no side effects
Patients continue to proretise
It was started by identifying priority groups to receive these drugs and, until now, patients with hepatitis C with greater hepatic insufficiency – fibrosis in the third and fourth stages, and from this year – also patients with fibrosis at the second stage.
Hug says that to date, 25 consoles have been withheld, dealing with 1,061 cases of hepatitis C treatment with state funding and 140 cases where patients are paying for them -Same. Most patients (785) received a drug suitable for any genotype of hepatitis C (the so-called pangenotypic) and whose treatment lasts 12 weeks. The doctor confirms that those who choose to pay for themselves are patients with less than zero hepatic impairment, first or second stage, because the state does not prescribe drugs funded by the state for these patients. It is true that at the present time, the treatment paid by the state can also be received by patients with a second phase of fibrosis because of additional funding . After the consensus, the decision of the National Health Service on the granting of treatment must be received – 959 decisions have now been received and treatment started in 767 patients. Treatment completed in 530 patients
Why not treat more patients?
This year, 15 million euros were allocated to the treatment of hepatitis C, with six million euros spent during those six months. Kristaps Kaugurs, leader of the hepatitis society, said: if money is not an obstacle and that funding for the treatment of hepatitis C is significantly more high than the other years, why not treat more patients? Are there bureaucratic obstacles? "Why in this situation, there are no expanded groups of patients eligible for modern treatment for hepatitis C and do we have the hope that patients will receive this treatment in n & # 39; any situation? ", said Kaugurs, 1965, Jana Feldman. that drugs are expensive, so it is important that decisions are made by competent and qualified doctors. "We have resolved the issue that treatment should be available not only in Riga, but also in the hospital areas." The regional hospitals of Daugavpils and Liepaja have shown their willingness to take patients with the disease. " hepatitis C, "explains J. Feldman, stressing that it" was necessary to define priority groups for patients because funding was limited. "The specialist believes that it was and can be done because the Hepatitis C is a chronic disease, and this year the state has already made a step towards providing patients with treatment in patients with stage II liver fibrosis. Hepatologists, Pauls Aldiņš, hospital nurse Straudin, points out that patients who do not appear on the priority list are looking to find an alternative and to buy drugs outside of the European e) we must remove the restrictions and how ready we will be to say that we will treat everyone. "A. Feldman says: you do not need to get behind the wheel." Prorating patients could be reviewed after badyzing data for the current year and reviewing budget options for the year. to come
The Hepatitis Society, meanwhile, complains – wait a long wait for an infectious disease specialist, wait for a consular notice, wait for the response of the National Health Service, and only then can get treatment. .. It may also affect the slowing of money for hepatitis C.
However, the Ministry of Health and the National Health Service are in the opposite view. "Zinta Rugja, chief of the Department of Drug Evaluation at the Department of Drugs and Medical Devices, said that all funds are under control and that they have no problem.The service can decide even if it is not necessary. is necessary even during the The Ministry of Health, meanwhile, ignores cases where the ability of doctors is not enough to accept all patients, patients do not have to wait for the long lines of time. waiting.
How to become infected with hepatitis C? 19
Intravenous Drug Use 10
Sexes 16
Place of Work 3
Of Mother's Baby 3
Other Type 6
Source: Hepatitis Society according to the Center for Prevention and Prevention
Source link