[ad_1]
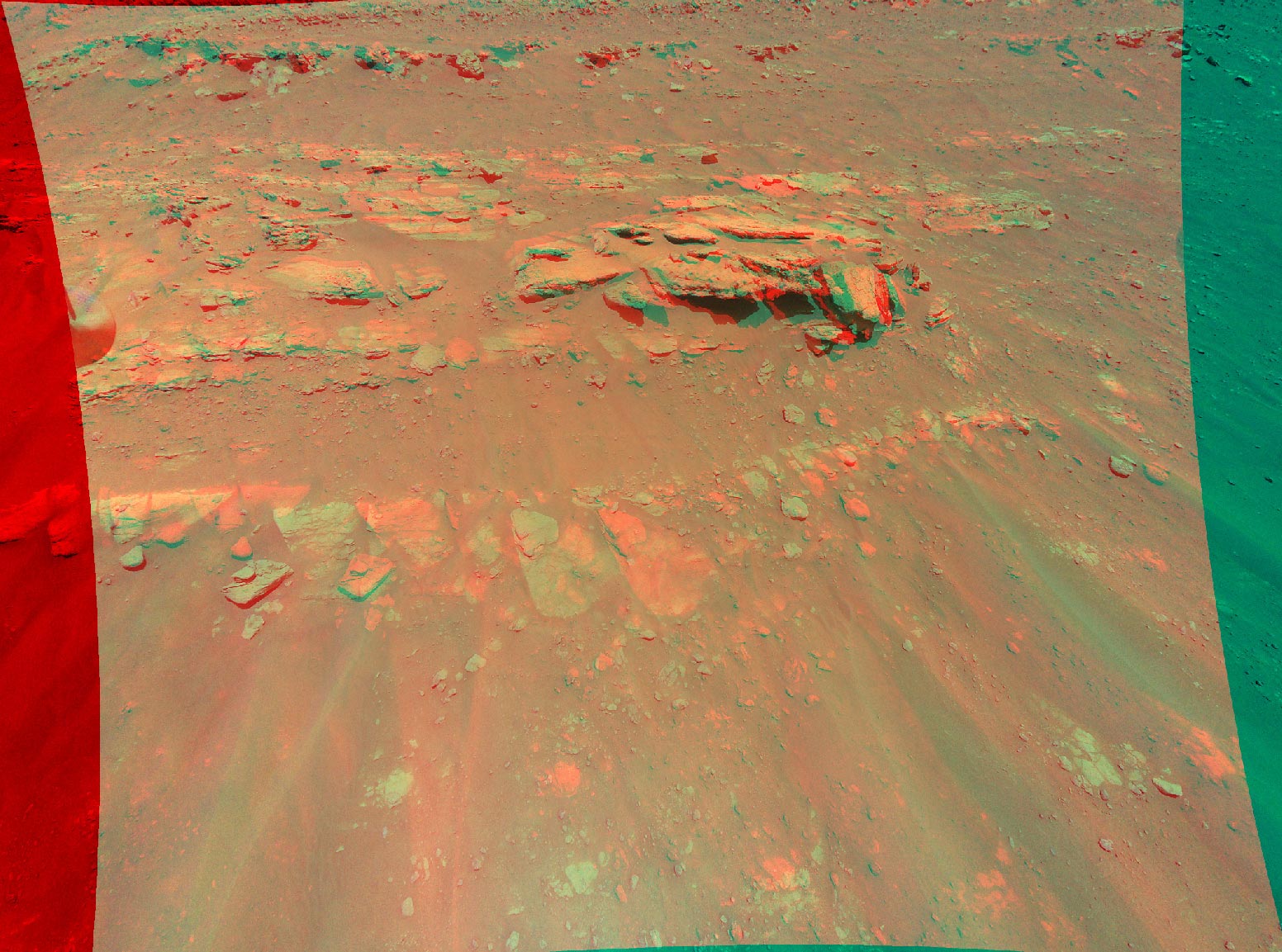
This 3D view of a rocky mound called “Faillefeu” was created from data collected by NASA’s Ingenuity Mars Helicopter during its 13th flight to Mars on September 4, 2021. Credit: NASA / JPL-Caltech
The rotorcraft captures shades of rock outcrop during aerial reconnaissance.
Nasaingenuity March The helicopter provided a 3D view of a rock-covered mound on its 13th flight on September 4. The plan for this reconnaissance mission in the “South Seítah” region of the Jezero de Mars crater was to capture images of this geological target – nicknamed “Faillefeu”. (after a medieval abbey in the French Alps) by the agency’s Perseverance rover team – and get the color images at an altitude lower than ever before: 26 feet (8 meters).

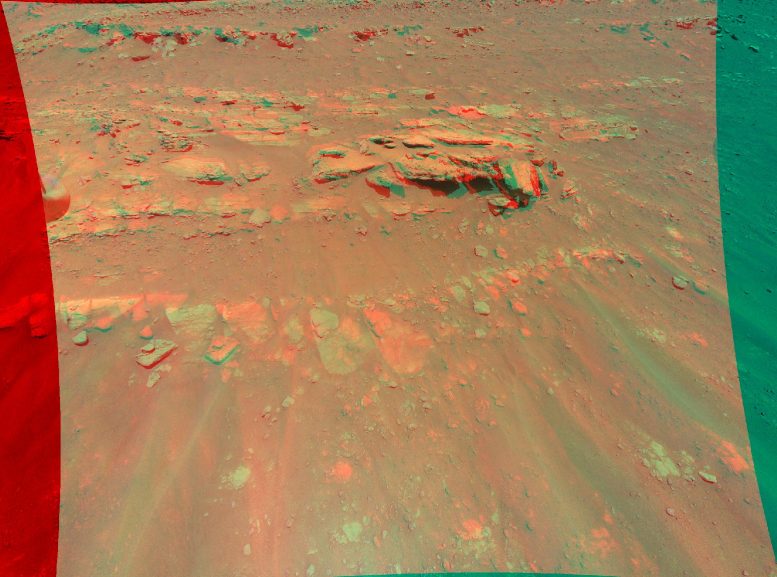
This image of an area that the Mars Perseverance rover team calls “Faillefeu” was captured by NASA’s Ingenuity Mars helicopter during its 13th flight to Mars on September 4, 2021. Credit: NASA / JPL-Caltech
About 33 feet (10 meters) wide, the mound is visible just north of the center of the image, with a few large boulders casting shadows. Stretching across the top of the image is part of “Artuby,” a ridge line over half a mile (900 meters) large. At the bottom of the image, and vertically to the middle, are some of the many ripples of sand that inhabit South Seítah.
Best viewed with red-blue glasses, this stereo or 3D view (also known as an anaglyph) was created by combining data from two images taken 16 feet (5 meters) from each other by the onboard color camera from Ingenuity.
Learn more about ingenuity
The Ingenuity Mars helicopter was built by JPL, which also manages the operations demonstration activity during its extended mission for NASA Headquarters. It is supported by the Science, Aeronautical Research and Space Technology mission directions of NASA. NASA’s Ames Research Center in Silicon Valley, California and NASA’s Langley Research Center in Hampton, Virginia, provided significant flight performance analysis and technical support during the development of Ingenuity. AeroVironment Inc., Qualcomm and SolAero also provided design assistance and major components of the vehicle. Lockheed Martin Space designed and manufactured the Mars Helicopter Delivery System.
Learn more about perseverance
A key focus of Perseverance’s mission to Mars is astrobiology, including looking for signs of ancient microbial life. The rover will characterize the planet’s past geology and climate, pave the way for human exploration of the Red Planet, and be the first mission to collect and cache Martian rock and regolith.
Subsequent NASA missions, in cooperation with ESA, would send spacecraft to Mars to collect these sealed surface samples and return them to Earth for further analysis.
The Mars 2020 Perseverance mission is part of NASA’s approach to exploring the Moon to Mars, which includes Artemis missions to the Moon that will help prepare for human exploration of the Red Planet.
JPL, which is managed for NASA by Caltech in Pasadena, Calif., Built and manages the operations of the Perseverance rover.
[ad_2]
Source link