
[ad_1]

Austrian study reveals important features of the virus: Analysis of infection clusters and spreading events in Austria laid the groundwork for general information on the properties of transmission between people and the mutation of the virus in patients . Credit: Andreas Bergthaler / CeMM Group
During the COVID-19 pandemic, 57 million people have already been infected worldwide. In the search for vaccines and therapies, a precise understanding of the virus, its mutations and its transmission mechanisms is crucial. A recent study by the research group of lead researcher Andreas Bergthaler at the CeMM Research Center for Molecular Medicine of the Austrian Academy of Sciences, in the famous journal Scientific translational medicine, makes an important contribution. The high quality of the epidemiological data in Austria, as well as the state-of-the-art virus genome sequencing, have supported unprecedented knowledge about the mutational behavior and transmission of the SARS-CoV-2 virus.
The project “Mutational dynamics of SARS-CoV-2 in Austria” was launched by CeMM in close cooperation with the University of Medicine in Vienna at the end of March. Together with the Austrian Agency for Health and Food Safety (AGES) and in cooperation with many universities and hospitals across Austria, scientists are working to get a more accurate picture of the mutations and viral transmissions that occur by sequencing the genome of SARS-CoV-2 virus. Under the guidance of CeMM principal investigators Andreas Bergthaler and Christoph Bock, 750 samples from large SARS-CoV-2 infection clusters in Austria, such as the tourist town of Ischgl and Vienna, were phylogenetically reconstructed. and epidemiologically and their role in the transcontinental spread of the virus has been analyzed. The results also provide important information on the transmission and development of mutations in the SARS-CoV-2 virus.
Mutation analyzes revealed correlations between clusters
Based on epidemiological data, scientists used mutation analyzes to reconstruct a SARS-CoV-2 cluster consisting of 76 cases and to discover a cryptic link between two epidemiological clusters. “This example illustrates how contact tracing and viral mutation analysis together form a strong pillar in the modern pandemic response,” says project leader Andreas Bergthaler. Franz Allerberger, head of the public health division of AGES and co-author of the study, agrees: “Modern viral genome sequencing techniques support epidemiological contact tracing and offer high-resolution information on the pandemic In progress.”
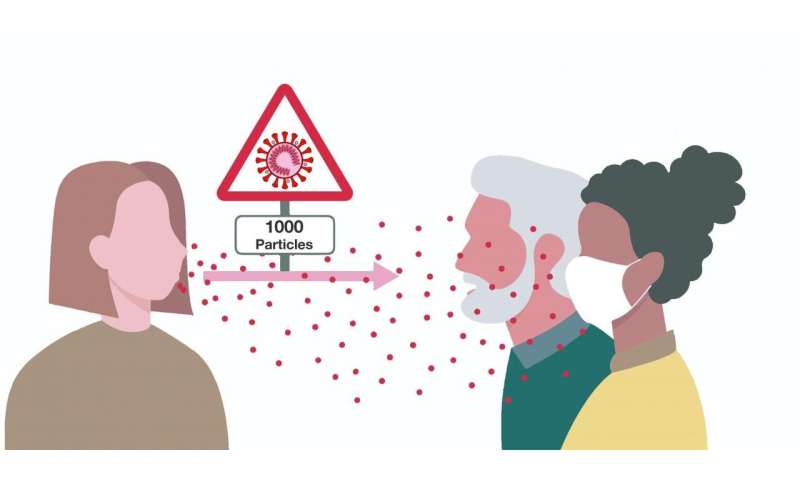
Analysis of epidemiologically validated chains of infections in mass-market events in Austria revealed that a relatively high average dose of 1000 infectious viral particles is transmitted. Credit: CeMM
Researchers observe the development of new mutations
A special feature of the study is that a chain of eight consecutive transmissions was analyzed. “The chain of transmission started with a returnee from Italy. Within 24 days, the SARS-CoV-2 virus spread throughout the greater Vienna area via public and social events in closed rooms,” say the authors of the CeMM study, Alexandra Popa and Jakob-Wendelin Genger. The precise breaking of the chain of transmission has allowed scientists to closely observe the development of a new mutation in SARS-CoV-2. “Thanks to excellent epidemiological data and our extensive virus sequencing data, we were able to track how the SARS-CoV-2 virus mutated in one individual and was then passed on to others,” says Andreas Bergthaler. In addition, scientists observed the mutating behavior of the virus during the disease in 31 patients. This can help in the future to determine whether the treatments influence the mutation characteristics of the virus.
On average, 1000 virus particles are transmitted during an infection
The results of current analyzes also show that on average 1000 infectious viral particles are transmitted from one infected person to another. These values are overall much higher than for other viruses such as HIV or norovirus. Andreas Bergthaler adds: “Yet we have sometimes also found infected people who apparently have come into contact with less virus particles and are still infected. We believe that parameters such as the application of protective measures, the route of transmission or the immune system may play a role here. ”These findings raise important new questions and hypotheses. Reducing the viral load of those infected by a combination of measures such as mouth-to-nose protection, physical distance, and adequate indoor air exchange could play a key role in preventing the spread of the virus and possibly even influence the course of the disease.
The current study, based on data collected during the early phase of the SARS-CoV-2 pandemic in the spring of 2020, provides important information on the fundamental dynamics of SARS-CoV-2 mutations in patients and during transmission events. These results support other ongoing research projects aimed at better understanding and controlling the pandemic.
Follow the latest news on the coronavirus epidemic (COVID-19)
Alexandra Popa et al, “Genomic epidemiology of super-propagation events reveals mutational dynamics and transmission properties of SARS-CoV-2”, Scientific translational medicine on November 23, 2020. DOI: 10.1126 / science.abe2555
Provided by the Austrian Academy of Sciences
Quote: New Study Provides In-Depth Information on Transmission and Mutation Properties of SARS-CoV-2 (November 23, 2020) Retrieved November 24, 2020 from https://medicalxpress.com/news/2020-11-deep-insights -transmission-mutation- properties.html
This document is subject to copyright. Other than fair use for private study or research purposes, no part may be reproduced without written permission. The content is provided for information only.
[ad_2]
Source link