[ad_1]
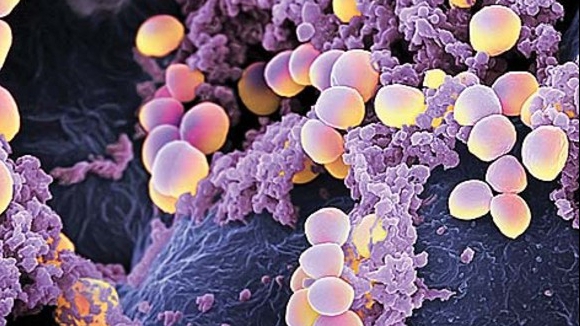
Do you have these symptoms? Great attention! This is STAFILOCOC Golden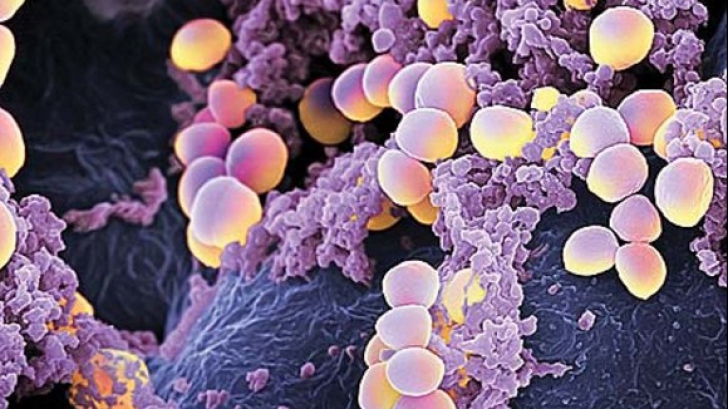
Staphylococcus aureus: MRSA infection is caused by a bacterial strain of antibiotic resistant Staphylococcus aureus.
Staphylococcus aureus is a bacterium that normally appears in the human body; the skin and nasal cavity of man constitute the natural habitat of this bacteria. It is present in about a third of the population.
Staph does not cause infection unless it enters the body through cuts or other types of wounds (eg, burns, tears, open fractures, etc.) and, even in this case, causes localized minor infections. in competent skin).
According to the Center for Disease Control and Prevention, about 2% of the population is a healthy carrier of MRSA.
Staphylococcus aureus: Antibiotic resistance
The main problem posed by MRSA infection is the difficulty of finding appropriate antibiotic treatment due to bacterial resistance to antibiotics used to treat staph infections. MRSA is the result of the use of antibiotics in years where they were not really needed.
For example, antibiotics have been prescribed for colds, flu, and other viral infections that do not respond to these medications. Even when properly used and targeted, antibiotics contribute to bacterial resistance. This is because the antibiotic does not destroy the entire bacterial population and those who survive quickly acquire resistance. New research aims to eradicate bacteria through nanotechnology.
Staphylococcus aureus: symptoms
Staphylococcal infections (including MRSA) usually manifest as a slight red swelling of the skin, such as bark, boils or spider bites. They can easily turn into deep and very painful abscesses requiring drainage surgery.
Most of the time, bacteria can remain attached to the skin, but in some cases they invade the body and can cause serious infections of the joints, bones, wounds, heart valves, lungs and blood.
Staphylococcus aureus: The main risk factors are:
- Entering hospitals – MRSA remains a concern in hospitals because it can infect people who are vulnerable or immunodeficient at any time.
- Long-term life in retirement homes
- Live in congested and crazy spaces;
- Invasive medical devices – by intubation, catheterization, perfusion, there is a risk of creating an entry of MRSA into the body;
- Practice contact sports.
Source link
