[ad_1]
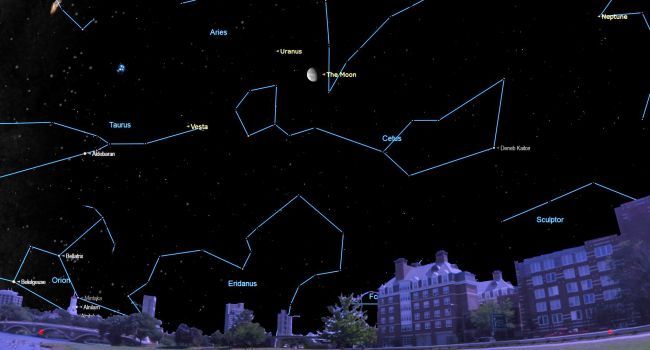
Today (August 21), just before dawn, the waning gibbous moon will be sitting bright in the southern sky near the icy and blue-green planet Uranus.
This planet will be weak, but observers will be able to spot it at the naked eye just under 5 degrees above (north celestial) star Xi Ceti, located in the constellation Cetus. Skywatchers may find the moon, which will be larger than the third quarter-circle moon but smaller than the full moon, located at 6.5 degrees in the lower right (southwest-celestial) portion of the moon. Uranus.
The waning gibbous moon follows Moon of sturgeon of August. The name of this full moon, which appears in the almanac of the old farmer, comes from settlers and tribes of Algonquian language North America, the sturgeons coming from Europe and the Americas.
Related: Launch Calendar in 2019 Space: Sky Events, Missions and More

Image of the Hubble Space Telescope of Uranus.
(Image credit: NASA / MSFC)
Unfortunately for observers wishing to spot our distant blue and far distant planetary neighbor, Uranus is hard to spot even on a dark, clear night. With the bright moon still big enough in the sky, observers might want to grab a pair of binoculars or (more likely) a telescope to actually see the planet, according to earthsky.org.
The moon and Uranus will be visible at night, tonight and tomorrow (August 22), but they will be low in the night sky and will be easier to spot in the hours before dawn, EarthSky said.
Tonight and towards the end of August and early September, observers will also be able to spot Pegasus' main square, a constellation that, unsurprisingly, is a big square. This constellation is an excellent tool for observing the sky because, in addition to being an easy-to-identify form, it points to Messier 31, or the Andromeda galaxy, in the night sky.
To find the Andromeda galaxy, start by "locate the main square of Pegasus in your eastern sky". Earthsky said. "But instead of thinking of the Big Square as a square, think of it as a baseball diamond, now imagine the farthest star on the left – Alpheratz – as the star of the third. A traced line of the first Alpheratz points in the general direction of the Andromeda galaxy. "
Follow Chelsea Gohd on Twitter @chelsea_gohd. Follow us on twitter @Spacedotcom and on Facebook.
[ad_2]
Source link