
[ad_1]
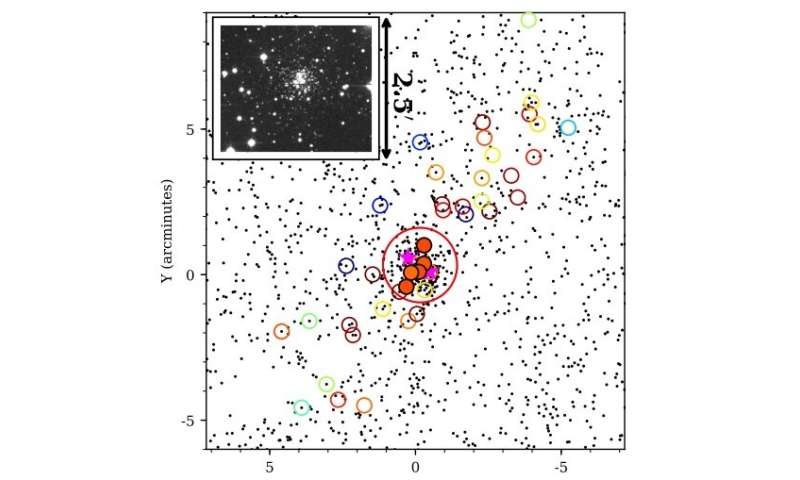
Spatial distribution of the Lae 3 stellar population in the field of view. Credit: Longeard et al., 2019.
Using the Canada – France – Hawaii Telescope (CFHT) and the Keck Observatory, an international group of astronomers conducted a photometric and spectroscopic study of Laevens 3, a satellite globular cluster located in the galaxy of the Milky Way. The search, detailed in an article published September 18 on the arXiv preprint repository, provides information about the properties of this cluster.
Globular cluster (GC) observations in the Milky Way galaxy are of great importance to astronomers because they are among the oldest objects in the universe. Therefore, they are perceived as natural laboratories for the study of stellar evolution processes.
Located some 210,000 light-years away from Earth, Laevens 3 (or Lae 3 for short) is a galactic GC discovered by Benjamin PM Laevens in 2015 using the Pan-STARRS telescope 1. The first observations revealed that it 's been a small group of about 8 billion years, with a half – light radius of about 23 light – years and a relative metallicity low to a level of about -1.9. It is assumed that the system gravitates around the center of the Milky Way in the galactic outer halo.
Observations of satellite systems as weak and distant as Lae 3 could be crucial to better illuminate the formation and evolution of our galaxy of origin. That is why an astronomical team led by Nicolas Longeard of the Strasbourg Observatory in France decided to take a closer look at this cluster.
"We present a photometric and spectroscopic study of the Milky Way satellite Laevens 3. Using MegaCam / CFHT photometry g and i and Keck II / DEIMOS multi-object spectroscopy, we refine the structural and stellar properties of the system", wrote the astronomers. the paper.
The study revealed that Lae 3 is bigger and older than previously thought. The color-magnitude diagram shows that it is about 13 billion years old, while the broadband photometric analysis indicates a half-light ray of about 37 light-years.
The distance to Lae 3 was calculated at about 200 000 light-years and its metallicity was measured at a level of -1.8. The research also revealed that the total brightness of the cluster was about 1,125 solar luminosities, which translated into an absolute magnitude of -2.8 mag.
The study confirmed that Lae 3 had an outer halo orbit with a pericenter of about 133,000 light-years and an apocenter of about 279,000 light-years.
According to the document, all the results suggest that Lae 3 presents the main characteristics of the globular clusters of the external halo of the Milky Way. In addition, the study showed that Lae 3 exhibited signs of mass segregation, confirming the globular nature of this system.
"Overall, Laevens 3 shares the typical properties of the outer halo globular groups of the Milky Way, and we find that this system shows signs of mass segregation, which reinforces our conclusion that Laevens 3 is a globular group." , concluded the researchers.
Djorgovski 2 is a globular group moderately low in metals, reveals a study
Nicolas Longeard, et al. Detailed study of the globular cluster of the Milky Way Laevens 3, arXiv: 1909.08622v1 [astro-ph.GA]: arxiv.org/abs/1909.08622#
© 2019 Science X Network
Quote:
The satellite globular cluster of the Milky Way studied in detail (September 26, 2019)
recovered on September 27, 2019
from https://phys.org/news/2019-09-milky-satellite-globular-cluster.html
This document is subject to copyright. Apart from any fair use for study or private research purposes, no
part may be reproduced without written permission. Content is provided for information only.
[ad_2]
Source link