[ad_1]
I'm not sure if you know it, but the launch of Apple Maps has gone bad. After a brutal first impression, a CEO apology, several years of frills with data partnerships and a few glimmers with expected transit directions and improvements in business data, parking and location, Apple Maps is still not there. it must be considered a world class service.
Google Maps needs to be fixed.
Apple is aware of this, so he is rebuilding the maps part of Maps
. This using first – party data collected by iPhones with a privacy methodology first and his own fleet of cars packed with sensors and cameras. The new product will be launched in San Francisco and Bay Area with the upcoming iOS 12 beta and will cover Northern California in the fall.
All versions of iOS will receive updated maps and will be more responsive to road changes and construction, visually richer depending on the specific context in which they are seen, with a ground cover, a foliage, pools, walking trails and more.
This is nothing less than a complete reshuffle of Maps. four years in the making, which is when Apple began to develop its new data collection systems. Eventually, Apple will no longer rely on third party data to provide the basis for its cards, which has been one of its major pitfalls since the beginning.
"Since we introduced this six years ago – we will not be raising all the problems we had when we introduced it – we made a huge investment to put the card up to the mark, "said Eddy Cue, Apple, SVP who now owns Maps, in an interview last week. "When we were started, a lot of that work was on directions and going to a certain place, finding the location and getting directions to that place." We made a huge investment in doing some of the work. Millions of changes, adding millions of locations, updating the map and changing the map more frequently.All these things in the last six years. "
But, says Cue, Apple has to the place to improve the quality of Google Maps, a thing that most users would agree with, even with recent progress. Take that to the next level, "says Cue." We have been working on trying to create what we hope to be the best map application in the world, going to the next step.
In addition to Cue, I spoke this week to Patrice Gautier, vice president of Apple, and to more than a dozen members of the Apple Maps team at its mapping headquarters in California. to rebuild Maps, and to do it in a way that fits the very public position of Apple on the privacy of users.
If, like me, you wonder if Apple thought to build its own maps before launching Maps, the answer is yes. At the time, there was a choice to be made about whether or not she wanted to take cards. As the future of mobile devices became very clear, he knew that mapping would be at the heart of almost every aspect of his devices, from photos to directions to location services provided to apps. Decision taken, Apple took a step forward, building a product that was based on a mosaic of data from partners like TomTom, OpenStreetMap and other geographic data brokers. The result was disappointing
Almost immediately after Apple launched Maps, he realized that he was going to need help and he signed on a bunch of vendors to additional data to fill the gaps of location, base map, point of interest and
That was not enough
"We decided to do it a little more than four years ago. "Where do we want to take maps? What are the things we want to do in Maps?" We realized that, given what we wanted to do and where we wanted to go, we had to do it ourselves, Cue explained to so many functions, success was not related to a single function.The cards had to be perfect for transport, driving and walking, but also as a utility used by applications for location services and other functions.
Cue says that Apple had to have all the data necessary to create a map and control it both from the point of view of quality and privacy

There is also the question of corrections, Updates and changes that go into a long validation loop to be updated when dealing with external partners. The Maps team should be able to correct roads, trails and other update functions in a few days or less, not in months. Not to mention the potential competitive advantages that it could derive from building and updating traffic data from hundreds of millions of iPhones, rather than relying on partner data.
Cue reports the proliferation of devices under iOS, now over a billion
"We had the impression that the switch to devices – the construction of a map nowadays as we did traditionally, as we did it – could dramatically improve things, and improve them in different ways, "he says. "It's more accurate – two are able to update the map faster based on the data and things we see, rather than driving again or getting information when the customer tells us said proactively, and if we could actually see it before all these things? "
I'm asking about the speed of updates to Maps, and if this new map philosophy means faster changes for maps users
"The truth is that are [updated more] and even today," says Cue. "We will do it even more with our new maps, [with] the ability to change the map in real time and often. We do this everyday today. This extends us to allow us to do it through everything on the map. Today, some things take longer to change.
"For example, a road network takes a lot longer to change now, and in the new map infrastructure we can change that pretty quickly, and if a new road opens, we can immediately see that and do that. change very, very quickly around it.It's much, much faster to make changes in the new map environment. "
So a new effort was created to start generating its own base maps, the lowest block of any really good mapping system. After that, Apple would begin to superimpose data on living places, high-resolution satellite imagery and all-new high-resolution image data collected from its railcars until it was overhead. it is considered a first class mapping product. There is really only one big company on Earth that has a complete stack of maps from scratch: Google .
Apple knew that he had to be the other. Enter the vans.
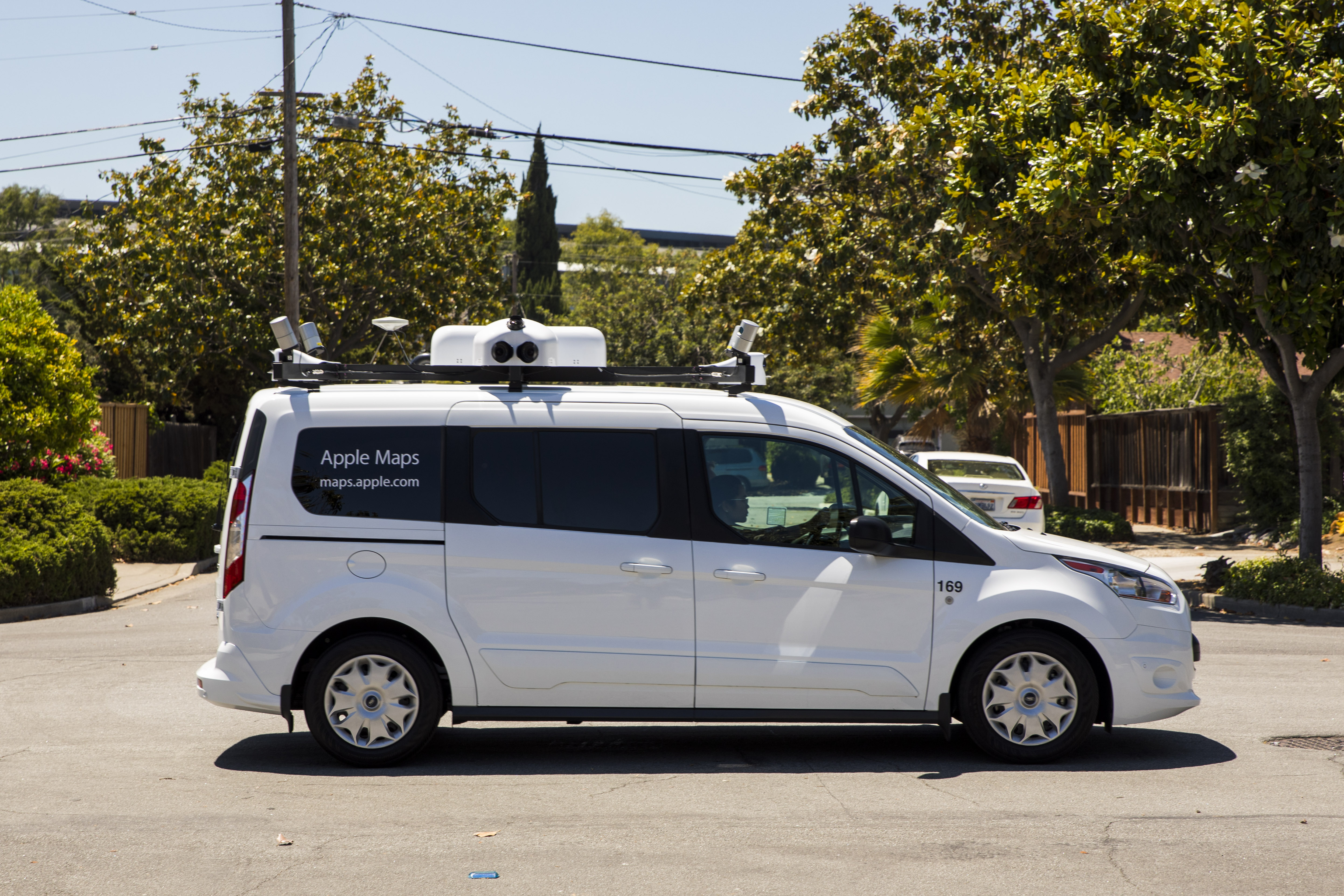

Apple Pickup Trucks Spotted
Although the overall project started earlier, Apple's first efforts to build the best Product Maps were the pickup trucks that started appearing on the road in 2015 with "Apple Cards" signs on the side Covered with sensors and cameras, these vans have appeared in various cities and sparked frantic discussions and speculation.
The new Apple Maps will be the first time the data collected by these vans are used to build
Some people have pointed out that Apple's platforms seem more robust than the simple GPS + Cameras settings on other mapping vehicles – even going as far as to say that they look more like something that could be used.
Apple does not comment on autonomous vehicles, There is a reason why the paintings seem more advanced: they are
Earlier this week, I made a ride in one of the vans. route to collect the kind of data that would go into the construction of the new maps. Here's what's in it.

In addition to a reinforced GPS installation on the roof, four LiDAR tables mounted at the corners and eight cameras filming high-resolution images overlapping, there is also the measuring tool Standard physics attached to a rear wheel that allows accurate tracking of distance and image capture. At the back, there is a surprising lack of bulky equipment. Instead, it's a simple Mac Pro bolted to the ground, attached to a range of SSD drives for storage. A single USB cable routes to the dashboard where the mapping capture software runs on an iPad.
During the mapping, a driver … drives while an operator is on the route, ensuring that a coverage area has been assigned is fully piloted, as well as image capture monitoring. Each disc captures thousands of images as well as a complete point cloud (a 3D map of space defined by points representing surfaces) and GPS data. Later, I was able to see the raw data presented in 3D and this is absolutely like the quality of the data you would need to start driving autonomous vehicles.
More information on why Apple needs this level of data later
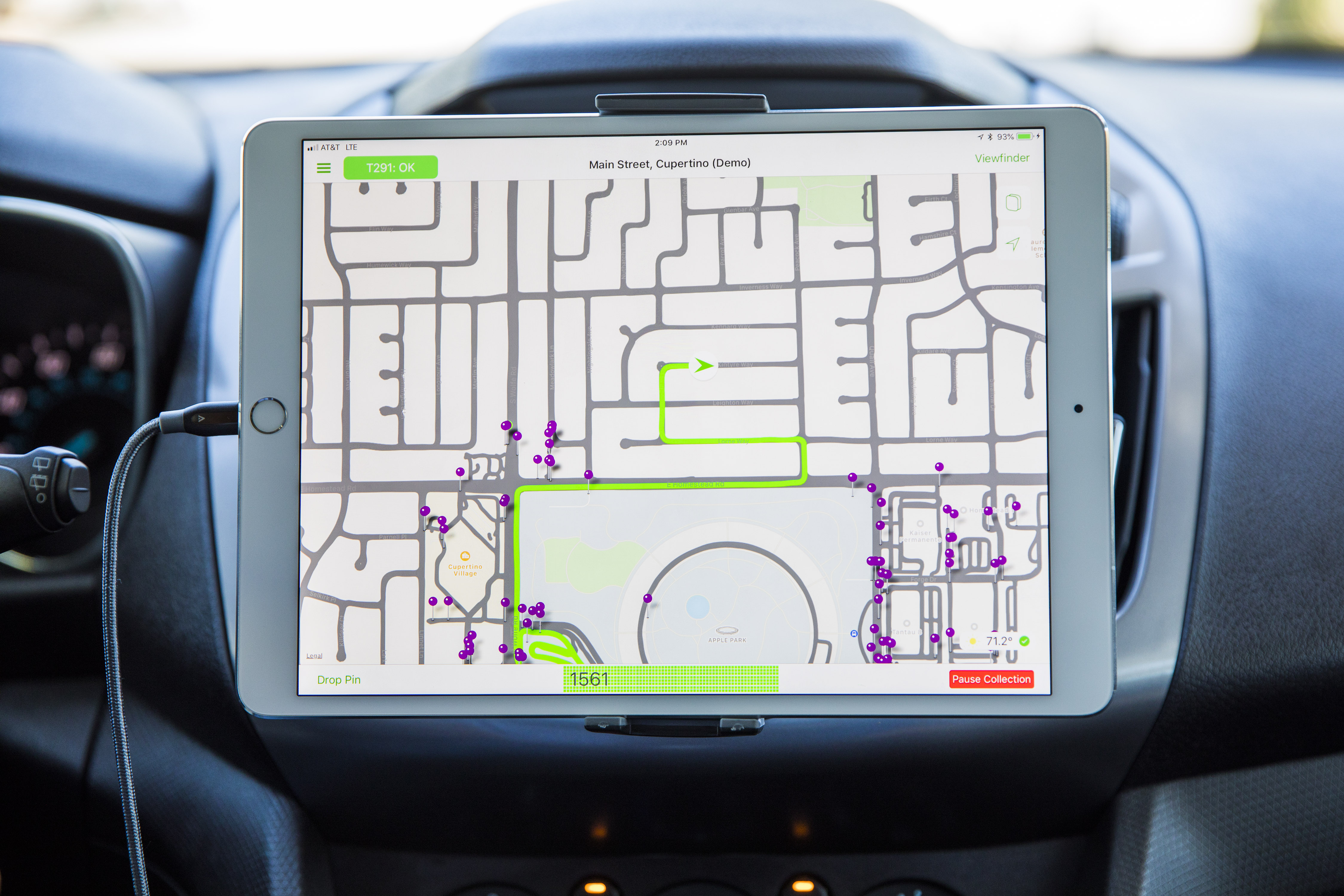
When images and data are captured, they are then encrypted on the fly and saved on SSDs. Once full, the SSDs are removed, replaced and packaged in a case, which is delivered to the Apple Data Center, where a suite of software removes private information such as faces, license plates and other information. From the moment of capture to the moment they are sanitized, they are encrypted with a key in the van and the other key in the data center. The technicians and software that are part of his mapping efforts from there never see any non-anonymous data
This is only one element of the focus put by Apple on the confidentiality of the data that it uses in New Maps. Privacy
Throughout every conversation that I have with a member of the team throughout the day, privacy is evoked, emphasized. This is obviously wanted because Apple wants to impress me as a journalist that it takes very seriously, but that does not change the fact that it's obviously built from scratch and it that I did not find a wrong note in
Indeed, people in charge of data security to people whose job is to make the cards work properly, the constant chorus is that Apple does not feel ] that it is retained in any way whatsoever by not sampling every element of customer-rich data that it can, by storing it and l & # 39; # 39; analyzing.
The consistent message is that the team believes it can provide navigation, location and mapping product without the directly personal data used by other platforms.
"We do not collect data even from A to B," Cue notes. "We collect data – when we do it – anonymously, in subsections from the set, so we can not even say that there is a person who goes from point A to point B. We collect the segments, as you can imagine, this has always been a key part of this process, and honestly we do not think it buys [to collect more]we do not lose any functionality or ability by doing this. "
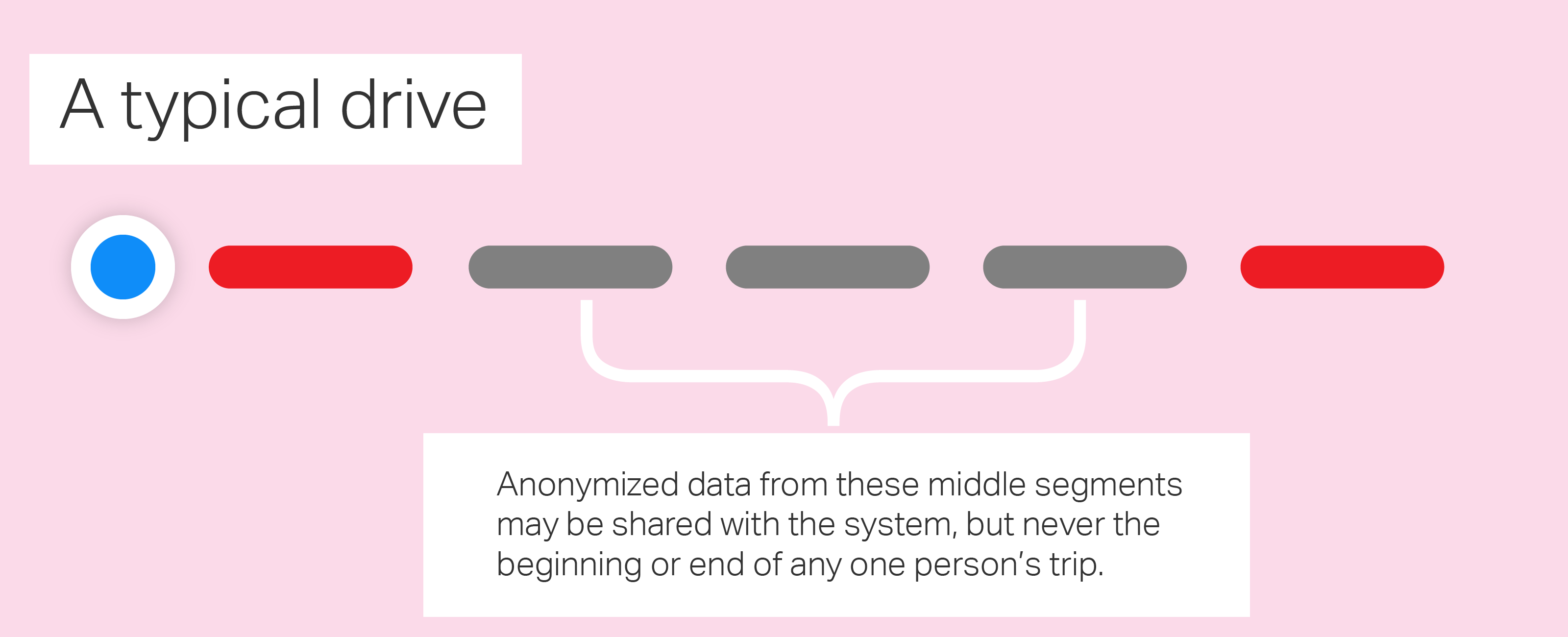
The segments to which it refers are cut off from a person's browsing session. Neither the beginning nor the end of a trip are ever transmitted to Apple. Rotating credentials, not personal information, are assigned to all data or requests sent to Apple and augment the "ground truth" data provided by its own mapping vehicles with that "probe data" returned by iPhones.
If everyone's reader is sent and the data is completely anonymized, there is never a way to know if a trip was a single individual. The local system signs the IDs and only this one knows who this ID refers to. Apple works very hard here to know nothing of its users. This type of confidentiality can not be added at the end, it must be woven at ground level.
Because Apple's business model does not rely on you, say, an advertisement for a Chevron on your way, it does not even need to link ad IDs to users .
Any customization request or Siri is handled on board by the iOS device processor. So, if you receive a driving notification that tells you it's time to leave for your commute, this is learned, stored and delivered locally, not Apple's servers.
This is not new, but it is important to note the novelty to remember here: Apple is ignoring the power of having millions of passive iPhones and d & # 39; Actively improve their mapping data in real time.
In Brief: Traffic, real-time road conditions, changes in pedestrian walkways are about to get a lot better in Apple Maps.
The secret sauce here is what Apple calls probe data. Essentially small slices of vector data that represent the direction and speed retransmitted to Apple completely anonymized with no way to bind to a specific user or even a given trip. It reaches and absorbs a minuscule amount of data from millions of users, giving it a holistic picture in real time without compromising the user's privacy.
If you drive, walk or pedal, your iPhone can already tell. Now, if he knows you're driving, he can also send relevant traffic and routing data into these anonymous ribbons to improve the overall service. This only happens if your Google Maps app is active, if you check the map, find directions, and so on. If you are actively using your GPS to walk or drive, the updates are more accurate and can help you improve your performance. New walking trails through the parks – the overall quality of the map.
All this, of course, depends on whether you have opted for location services, and can be switched using the Privacy section of the settings.
Apple says that it will have an almost zero effect on battery life or data usage because you already use the maps functions. when probe data is shared and it's a fraction of the power
Starting from the cloud of points
But maps can not live only from ground truth and mobile data. Apple is also collecting new high resolution satellite data to combine with its ground truth data for a solid base map. The next step is to superimpose satellite images to better determine foliage, trails, sports facilities, construction forms and trails.
After cleaning the registration plates and faces, computer vision programming to get out the addresses, signs and other points of interest. These are crossed with data accessible to the public such as addresses held by the city and new constructions of neighborhoods or roads from urban planning services.
But one of the special sauce pieces that Apple adds to The Mix of Mapping Tools is a scatter plot that 3D maps the world around the mapping van. This gives them all kinds of opportunities to better understand what are the road signs (retro-reflective rectangular object about 15 feet off the ground – probably a sign) or stop sign or limitation signs. speed.
allow the positioning of navigation arrows in the 3D space for AR navigation, but Apple declined to comment on "future projects" for such things.
Apple also uses semantic segmentation and Deep Lambertian Networks to analyze the point cloud coupled with data by car and high resolution satellite synchronization. This allows 3D identification of objects, signs, lanes and buildings and separation into categories that can be highlighted to facilitate discovery.
Coupling high-resolution car and satellite image data Apple is now able to produce complete orthogonal reconstructions of city streets with textures in place. It's massively higher resolution and easier to see, visually. And it is synchronized with the "panoramic" images of the car, satellite view and raw data. These techniques are used in autonomous driving applications because they offer a truly holistic view of what is happening around the car. But the ortho view can do even more for human viewers by allowing them to "see" through a cover of brush or trees that would normally obscure roads, buildings and addresses.
This is extremely important when it comes to the next step In the battle of Apple for supremely accurate and useful maps: the human editors
Apple has had a team of builders in the world. tools specifically working on a toolbox that can be used by human editors to analyze and analyze data street by street. The editor suite includes tools that allow human editors to assign specific geometries to flying buildings (think of the unique ridged dome of the Salesforce tower) that allow them to be immediately recognizable. It allows editors to view real street sign images taken by the car right next to 3D reconstructions of the scene and artificial vision detection of the same signs, recognizing them immediately as accurate or not.
Quickly move an address to the center of a building, determine if they are misplaced and move them. It also allows you to set access points, making Apple Maps smarter on the "last 50 feet" of your trip. You have reached the building, but in which street is the entrance? And how are you in the aisle? In a few clicks, an editor can make it permanently visible.
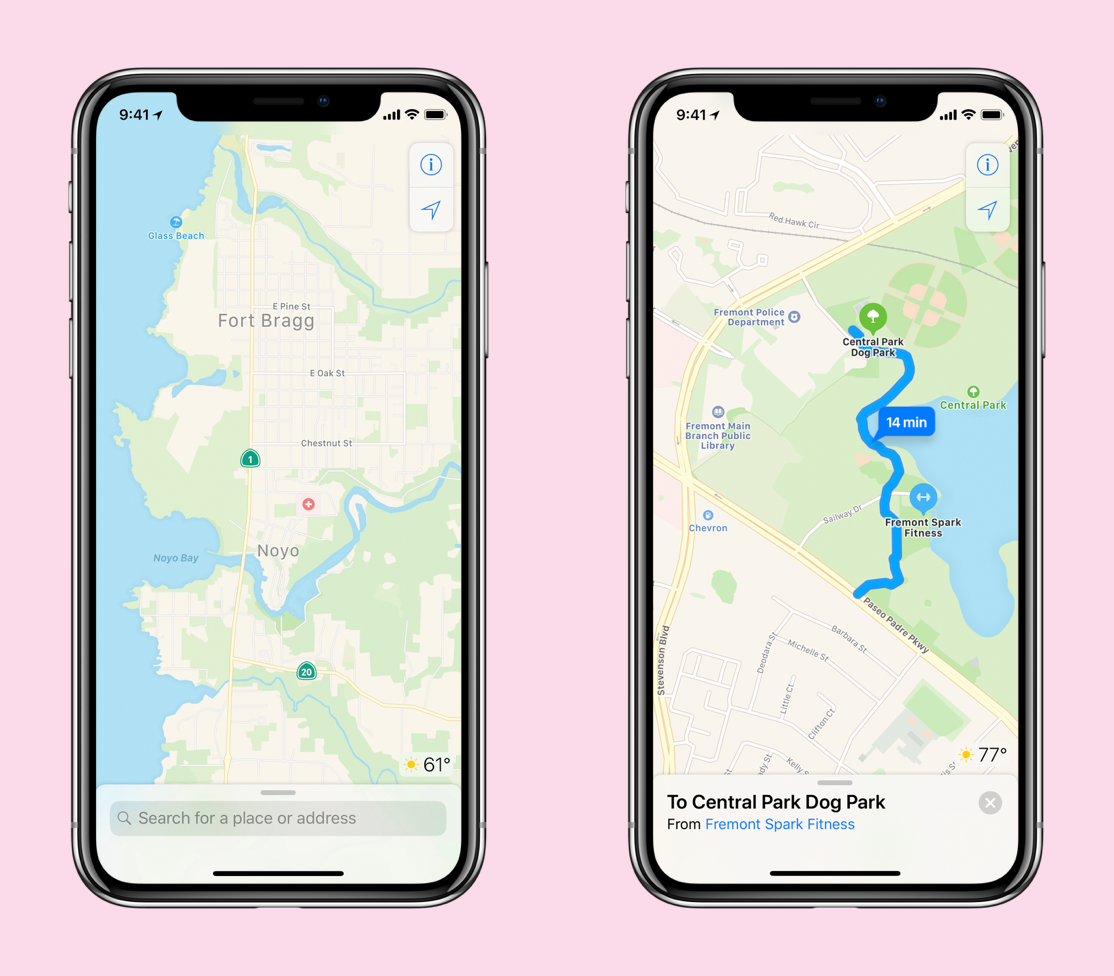
When you look at places like San Francisco or the big cities from this point of view, you have addresses where the name of the address C is a certain street but really, the entrance to the building is in another street. They did it because they want the best street name. These are the kinds of things that our new cards will really shine on. We will make sure that we will bring you exactly to the right place, not to a place that could be very close. "
The water, the swimming pools (all new for Maps), the sports areas and the vegetation are now more important and expanded thanks to the new applications of computer vision and satellite imagery. So Apple had to build editing tools for those too.
Several hundred publishers will use these tools, in addition to the thousands of employees that Apple has already worked on cards, but the tools had to be built first, now Apple no longer depends third parties to check and correct problems.
And the team also had to build artificial vision tools and machine learning allowing it to determine if there are problems to be solved.
Anonymous Sonder the data of iPhones, visualized, looks like thousands of points, moving and flowing through a network of streets and walkways, like a network of luminescent colors. At first, chaos. Then, the models emerge. A street opens for business, and nearby ships pump orange blood into the new artery. A flag is triggered and a publisher tries to see if a new route needs an assigned name.
A new intersection is added to the web and an editor is marked to ensure that the left-turn lanes connect properly across the overlapping layers. directional traffic. This has the added benefit of a massively improved route guidance in the new Apple Maps.
Apple is counting on this combination of human signaling and AI to enable publishers to develop base maps and maintain them as biomass changes constantly. havoc on roads, addresses and the occasional park.
Here, there is Helvetica
The new Apple cards, like many other digital cards, display very differently depending on the scale. If you zoomed out, you get less detail. If you zoom in, you get more. But Apple has a team of cartographers working on more cultural, regional and artistic levels to make sure its maps are readable, recognizable and useful.
These teams have objectives that are both concrete and a little out of the ordinary. the best traditions of Apple that cross the technical and the artistic.
Cards must be usable, but they must also fulfill cognitive objectives on cultural levels that go beyond what a user can know. For example, in the United States, it is very common to have cards that have a relatively low level of detail even at a medium zoom. In Japan, however, the cards are absolutely packed with details at the same zoom, because this increased information density is what is expected by users.
This is the details department. They have reconstructed replicas of hundreds of actual road signs to ensure that the shield of your navigation screen matches the one you see on the road sign. Regarding public transport, Apple has licensed all the types of faces you see on your favorite subway systems, such as Helvetica for NYC. And the line numbers are in the same order as you will see them on the platform boards.
It is about reducing the cognitive burden needed to translate the physical world that you have to navigate in the digital world represented. by Maps.
Conclusion
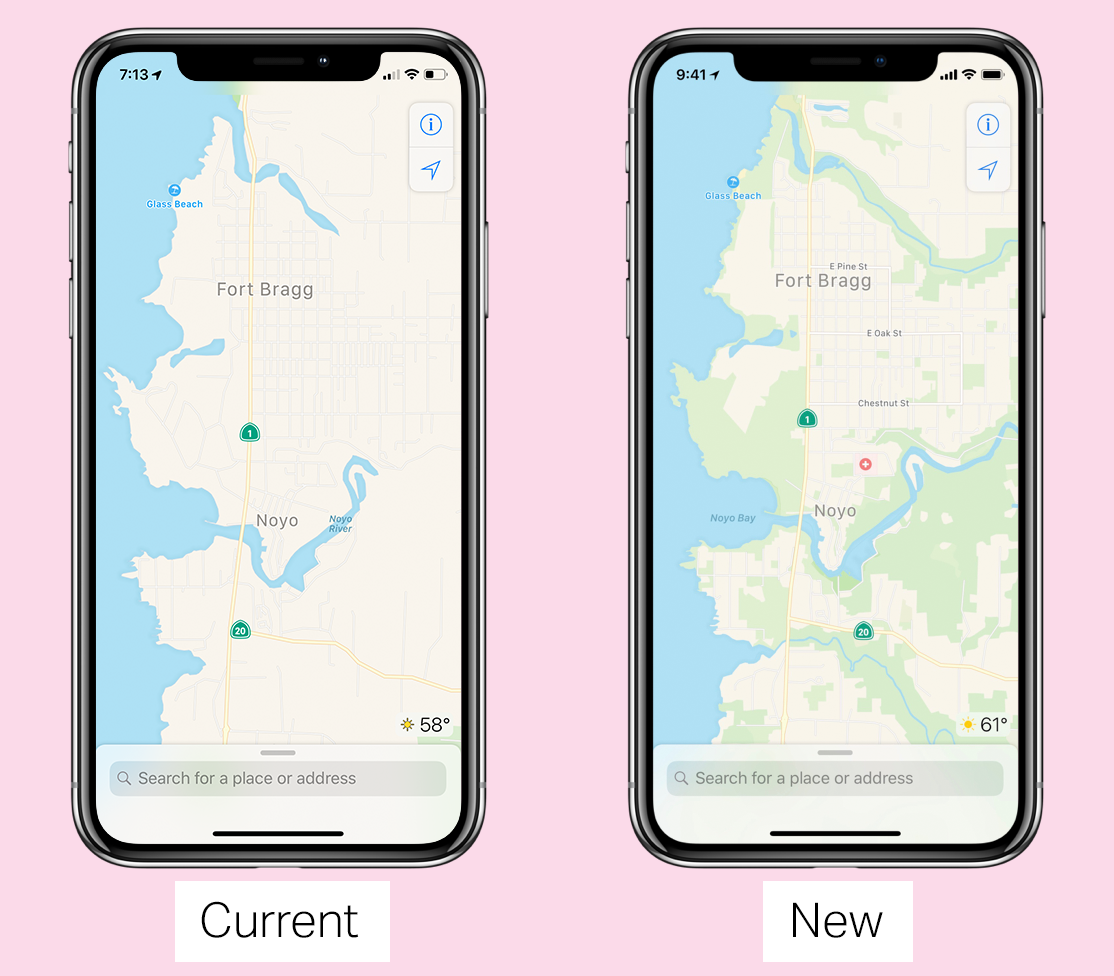
The new version of Apple Maps will be preview next week with the release of the Bay Area of California. It will be seamlessly integrated into the "current" version of Maps, but the difference in quality level should be immediately visible based on what I've seen up to here.
Better road networks, more pedestrian information, sports areas like baseball and basketball courts, more land cover, including grass and trees, represented on the map, as well than buildings, forms of construction and more precise sizes. A map that looks more like the real world you are going through.
Research is also being reorganized to make sure you get more relevant results (on the correct continents) than ever before. The navigation, especially pedestrian guidance, also enjoys a big boost. Parking areas and construction details to get you the last meters up to your destination are also included.
What you will not see, for the moment, is a complete visual overhaul.
"You will not see huge design changes on the cards," says Cue. "We do not want to combine these two things at the same time because that would cause a lot of confusion."
Apple Maps receives the much-awaited attention that it really deserves. By totally embracing the project, Apple is committed to creating the map that users have been waiting for from the beginning. This is a persistent shadow on iPhones, in particular, where alternatives like Google Maps have offered more robust feature sets that are so easy to compare to the native app, but impossible to access at the deep system.
nauseam, but it's worth saying again that if Apple thinks that mapping is important enough to own, it should have it. And that's what we are trying to do now.
"We do not think anyone does this level of work that we do," adds Cue. "We have not announced this, we have not talked to anyone about it, it's one of those things we've been able to keep pretty much a secret, nobody really knows it. Pleased to have it there.In the next year, we will implement it, section by section, in the United States. "
Source link