[ad_1]
It's time to lift the curtain on the Turing GPU in the all-new Nvidia GeForce RTX 20 Series, the first graphics card designed to handle real-time ray tracing through the inclusion of dedicated toroids and RT cores . But the GeForce RTX 2080 and RTX 2080 Ti have also been designed to dramatically improve the performance of traditional games, with enough power to power these high-speed 4K, 144Hz HDR G-Sync gaming monitors.
Nvidia revealed many figures when announcing the GeForce RTX 2080 Ti. The clock speed, the memory bandwidth, the CUDA kernel count, everything was there. This deeper dive explains the underlying architectural changes that make Nvidia's Turing GPU more powerful than its predecessor Pascal. We will also highlight some of the new Nvidia tools that developers can use to further accelerate performance, or integrate the AI-powered power of Nvidia's Saturn V supercomputer into your graphics card.
This is not a review of the GeForce RTX 2080 or the GeForce RTX 2080 Ti, which should be released on the street on September 20th. But with RTX pre-orders already open, we hope this will give you a better idea of what you are spending. Again, be sure to read our coverage of the GeForce GTX 2080 Ti announcement regarding the flow, speed and details of the graphics card products themselves.
Overview of the GPU Nvidia Turing
Before you begin, here is an overview of the Turing TU102 GPU's top-level specifications in the flagship product GeForce RTX 2080 Ti.
 Nvidia
NvidiaThe GPU TU102 from Nvidia, present in the GeForce RTX 2080 Ti. (Click on an image of this article to enlarge.)
Here is Nvidia's high-level overview, in case what you are looking at is not clear:
"The TU102 GPU includes six graphics processing clusters (GPCs), 36 texture processing clusters (TPCs) and 72 multiprocessors (SMs). Each GPC includes a dedicated raster engine and six TPCs, each TPC including two SMs. Each SM contains 64 CUDA cores, eight voltage cores, a 256-KB register file, four texture units, and 96 KB of shared memory / L1 that can be configured for different capacities based on computing or graphics loads. eight ROP units and 512 KB of L2 cache.
You will also find a unique RT core in each SM, so there are 72 in the GeForce RTX 2080 Ti. Since RT and tensor cores are built into each broadcast multiprocessor, the lower you are in the GeForce RTX 20 family, the less you will find. The RTX 2080 has, for example, 46 cores and 368 cores, and the RTX 2070 will have 36 cores and 288 cores.
With all these advanced items packed, all requiring dedicated material, it should not be surprising that Turing is absolutely massive. The matrix measures 754 mm, compared to the Pascal GPU of 471 mm in the GTX 1080 Ti.
Inside GPU Nvidia Turing: Improved Shading and Memory
Let's explain the improvements made to what has been established for a long time before plunging into the new tensor nuclei and exotic RTs.
 Nvidia
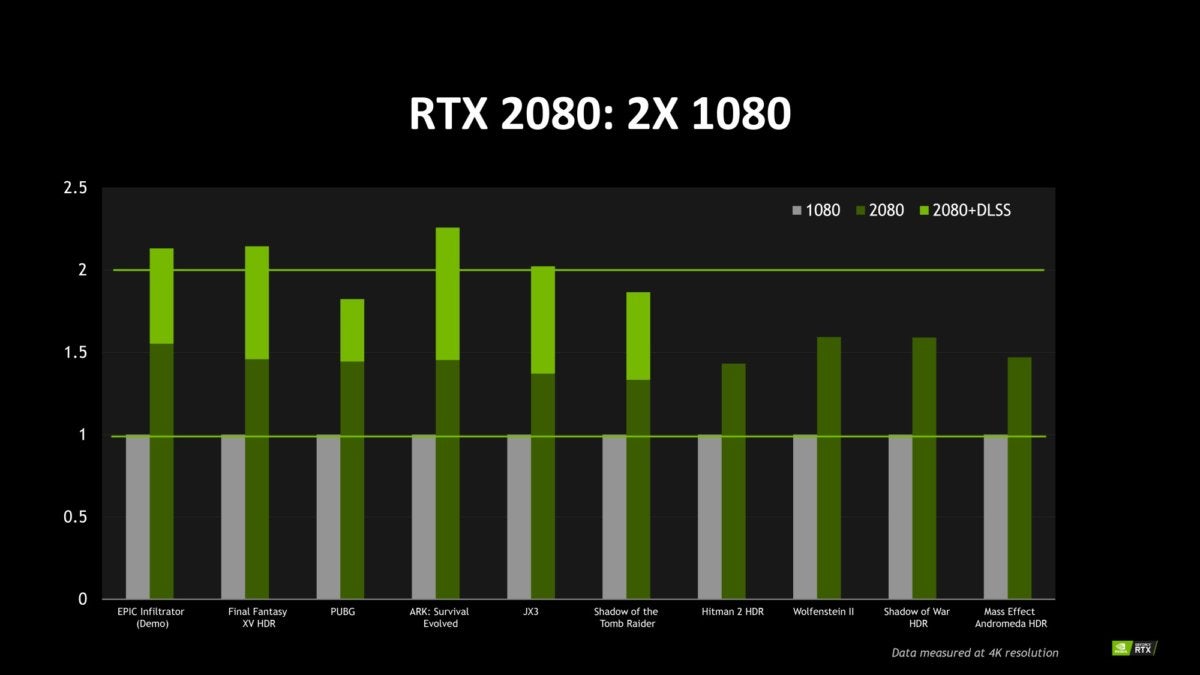
NvidiaNvidia claims that the GeForce RTX 2080 can be about 50% faster than the GTX 1080 in traditional games. Most comparisons occur in games where HDR is enabled, which has a positive impact on current GTX 10 cards. The GeForce RTX 2080 can be twice as fast as the GTX 1080 in games that support Nvidia's DLSS technology, says Nvidia (we'll talk about it later), and exceed 60 frames per second in several triple A games at 4K resolution. with HDR images enabled.
 Nvidia
NvidiaThe actual performance of Nvidia's high-end RTX duo remains to be seen. Nvidia did not talk about the performance of the GeForce RTX 2080 Ti in traditional games. We still do not know how the GeForce RTX 2080 compares to the old GTX 1080 Ti in non-HDR games. The frame rates of Nvidia in the 4K / 60 HDR games listed above do not mention the graphical parameters with which they were tested.
Because the RTX 2080 is at least In the same performance environment as the GTX 1080 Ti, despite overall CUDA cores down nearly 20%, it is clear that CUDA cores have been upgraded.
 Nvidia
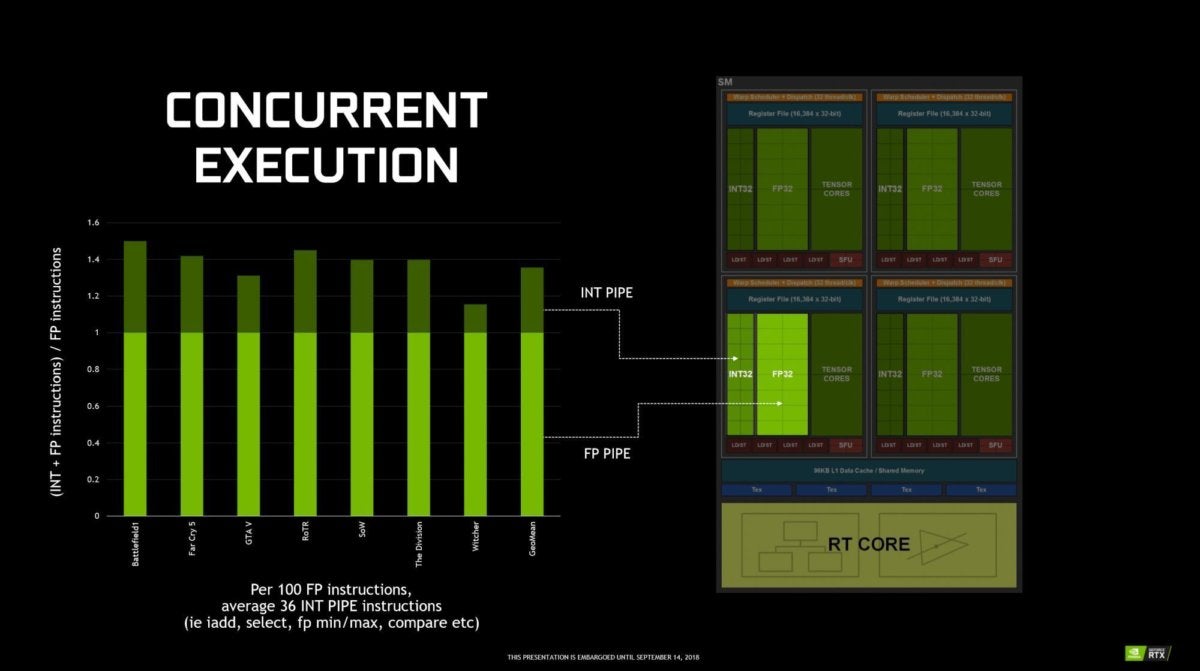
NvidiaScratch: The simultaneous multiprocessors of the Turing GPU are not just upgraded, they have been revised. Beyond the addition of tori and cores RT, Nvidia has also added a new integer pipeline (INT32) next to the floating-point pipeline (FP32) traditionally used to process shadows.
When Nvidia examined the behavior of actual games, he found that for every one hundred floating point instructions executed, 36 floating point instructions and no less than 50 were being processed. The entire new pipeline handles these additional instructions separately and at the same time as the FP32 pipeline. According to Jonah Alben, vice president of GPU engineering at Nvidia, performing both tasks at the same time translates into a considerable acceleration.
 Nvidia
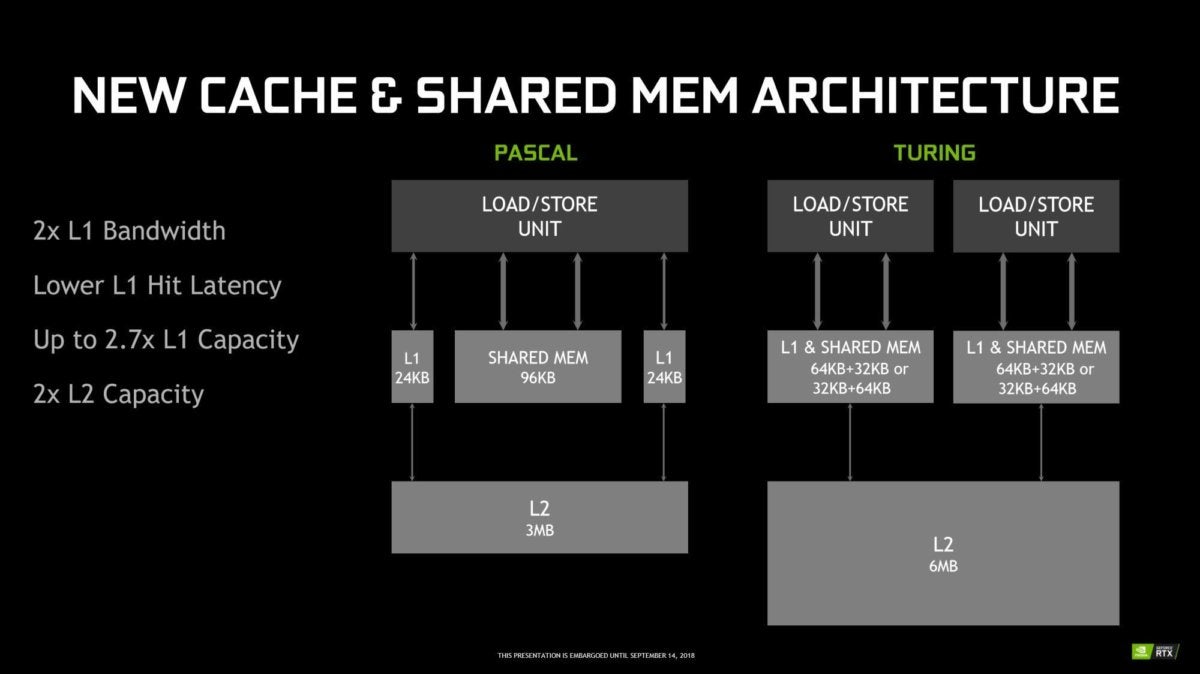
NvidiaNvidia also reviewed how the cache in its concurrent multiprocessors work. Now, smaller SMs each feed a unified pool of L1 and shared memory, which in turn powers an L2 cache twice as large as before. The reworking means that Turing has nearly three times more L1 memory than GTX Series 10 Pascal GPUs, with twice the bandwidth and lower latency.
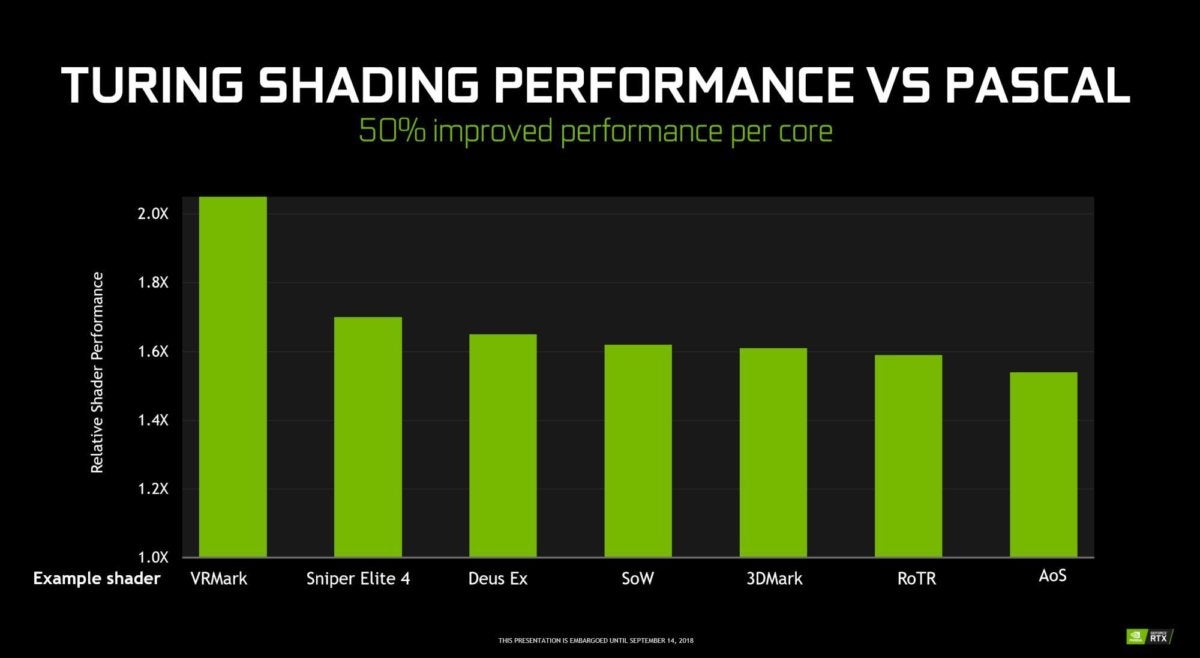 Nvidia
NvidiaAdd it all and Nvidia claims that the Turing GPU performs a traditional gradient 50% higher than Pascal's. It's a massive architectural improvement, although the actual gains vary from one game to another, as shown in the slide above.
But games are not tied only by shading performance. The bandwidth of memory can have a direct impact on the quality of your games. Turing enhances Pascal's superb memory compression technology, as well as the generation of GeForce RTX 2080 and 2080 Ti with the introduction of Micron's next-generation GDDR6 memory – the first time it appears in a GPU. GDDR6 has reached 14 Gbps despite energy consumption 20% lower than that of GDDR5X and Nvidia has optimized the Turing RAM for crosstalk 40% lower than that of its predecessor.
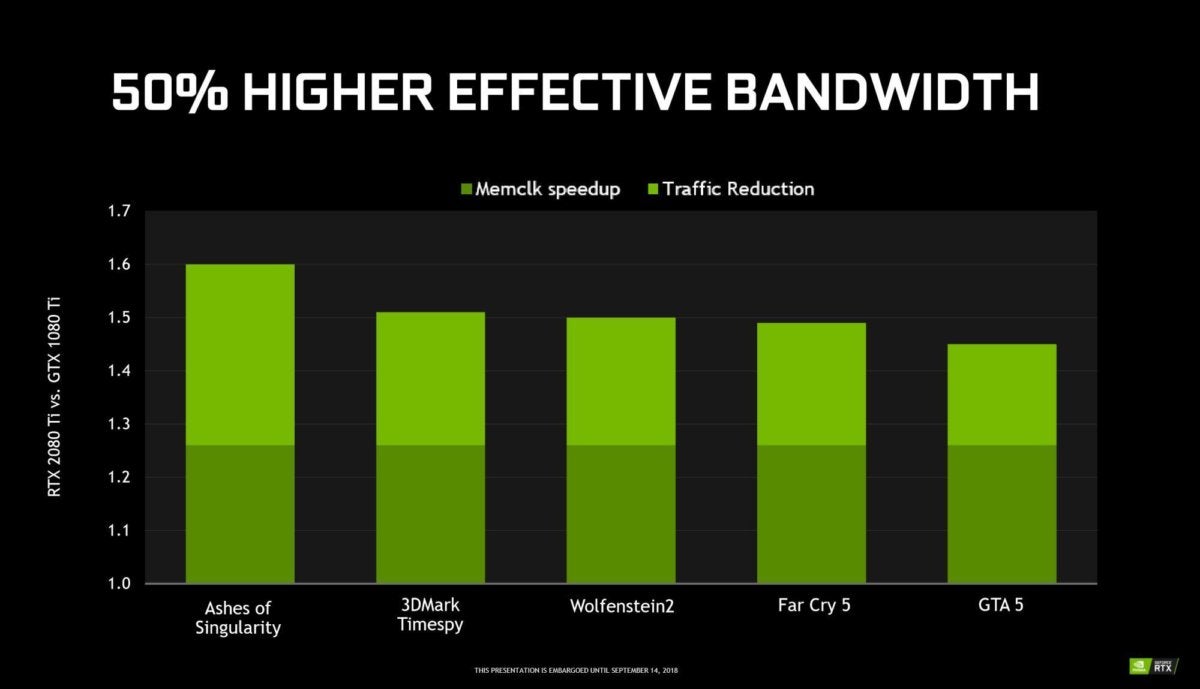 Nvidia
NvidiaAccording to Nvidia, the range of improvements brings to the RTX 2080 Ti a 50% increase in the effective memory bandwidth compared to the GTX 1080 Ti. In real terms, the GeForce RTX 2080 Ti achieves a total bandwidth of 616 GB / s compared to the GTX 1080 Ti's 484 GB / s, even though both cards offer identical memory capacity and bus sizes. That's the power of GDDR6.
New Turing Shading Technologies
As with most GPU launches, Nvidia has also introduced new shading technologies that developers can leverage to improve performance, images, or both.
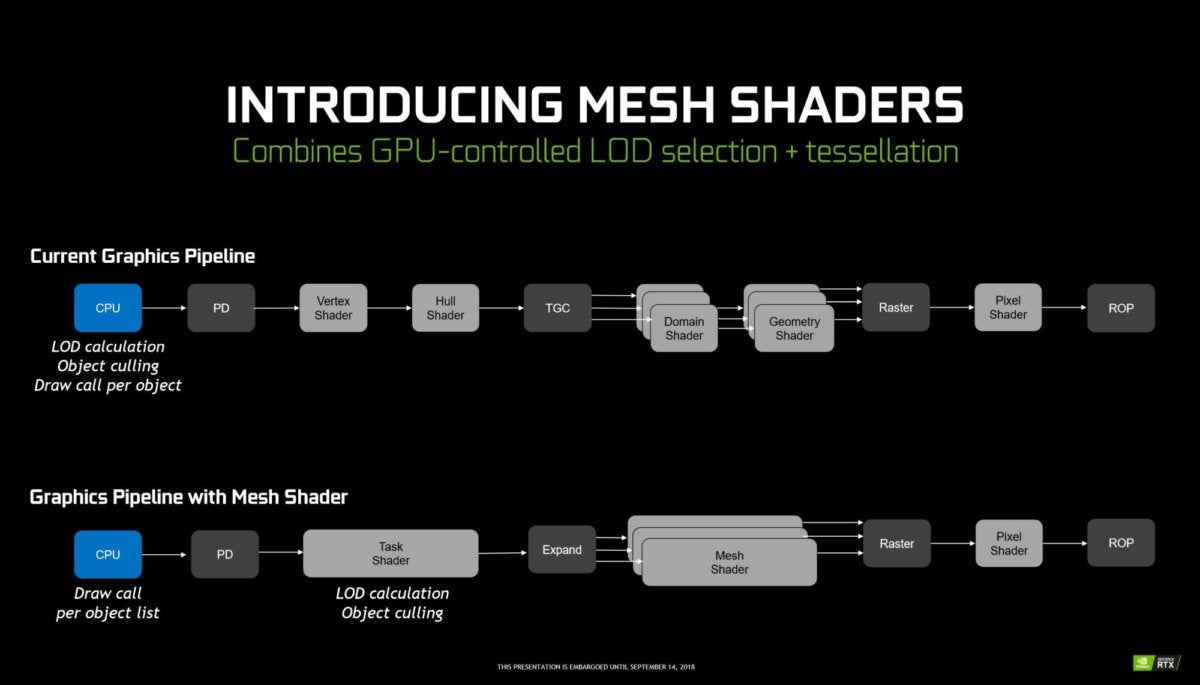 Nvidia
NvidiaThe mesh makes it possible to lighten part of your processor during very visually complex scenes, with tens or hundreds of thousands of objects. It consists of two new shader steps. Task shaders perform object selection to determine which elements of a scene must be rendered. Once this is decided, Mesh Shaders determines the level of detail at which visible objects must be rendered. Those who are farther away need much less detail, while closer objects should be as clean as possible.
Nvidia showed shades of mesh with an impressive playable demo where you stole a spaceship through a vast field of 300,000 asteroids. The demo worked around 50 frames per second despite this number of gargantuan objects, since the mesh shading reduced the number of triangles drawn at a given point to around 13,000, from the original. a maximum of 3 trillion drawn triangles. Intriguing stuff
 Nvidia
NvidiaVariable rate shading is a supercharged version of the multi-resolution shadow supported by Nvidia for years. Human eyes only see the focal points of what is happening in their vision. objects on the periphery or in motion are not as sharp. Variable-rate shading takes advantage of shading the main objects at full resolution, but secondary objects at a lower rate, which can improve performance.
One potential use case of this is adaptive motion shading, where non-critical parts of a moving scene are rendered with less detail. The picture above shows how it could be handled Forza Horizon. Traditionally, each part of the screen was rendered with the details, but with adaptive shading of motion, only the blue parts of the scene enjoy such a high treatment.
 Nvidia
NvidiaAdaptive Content Filtering applies the same principles, but it dynamically identifies those parts of the screen that have little detail or broad bands of similar colors, and nuances in more detail, and even more so when you're moving . It seemed damned good in action during a playable Wolfenstein II demo that allows you to enable or disable the feature. I did not see any change in visual quality, but Nvidia's Alben says that activating CAS increases the frame rate by 20 frames per second or more in situations where you shoot at 60 frames per second on a mainstream GPU. The developers who crossed their fingers support this type of technology with more dynamism than they did in multi-res shading, which Warrior of Shadows 2 but did not gain traction beyond that.
Variable rate shading can also help in virtual reality workloads by adjusting the level of detail to where you are. Another new VR system, Multi-View Rendering, expands the simultaneous Multi-Projection technology introduced with the GTX 10 series to allow "developers to efficiently draw a scene from multiple viewpoints or even draw multiple instances of multiple scenes." a character in different positions. in one pass. "
Finally, Nvidia also introduced Texture Space Shading, which makes an area appear around an object rather than a single scene to allow developers to reuse shading in multiple perspectives and frames.
What's going on in a frame with Turing
For a standard GPU architecture, that's all you need to know. But we are just starting with Turing. In fact, before we begin, let's take a quick look at how Turing handles workloads that take advantage of all of its features, such as ray games.
 Nvidia
NvidiaThe lines at the top marked "1 frame of rotation" are the key. For the other GPUs of Nvidia, it would have only one part, the yellow line of the FP32. But it's more complicated in Turing.
Although FP32 standard shader processing takes place, dedicated RT cores and the entire dedicated pipeline execute their own specialized tasks at the same time. Once everything is done, everything is transferred to the hearts of tensors for the remaining 20% of an image, which perform their auto-learning magic, such as denoising images or the Super Learning application. Super Sampling in games using Nvidia RTX technology. stack.
Next page: RT cores, tensor cores, and video / display upgrades.
Source link