
[ad_1]

On the occasion of a surprising event, the 20th anniversary and the future of research, Google announced a number of new search features. Some are new, others are extensions or adaptations of existing capabilities, and some are borrowed or "inspired by competitors' products" (Snap, Instagram, Pinterest).
Ben Gomes, vice president of research, lThis is with a brief historical overview of Google's mission and approach to information. He then presented conceptual concepts defining the next generation of research capabilities, three "research changes":
- Responses to travel
- From search queries to discovery without query.
- From text to visual content.
Customize the "search path" Years ago, Microsoft determined that research was not a unique behavior. Her research has shown that people usually do multiple queries on many sessions to complete tasks such as finding a job, planning a wedding, buying a car, renting an apartment or planning a vacation. Today, Google has taken up this idea in two related search ads: Activity Sheets and Improved Collections.
Activity cards will appear "where you left off", showing you previous pages / sites visited and previous queries. Google indicates that they are not displayed each time or for each request and that users can edit and delete the results of the maps.
New collections
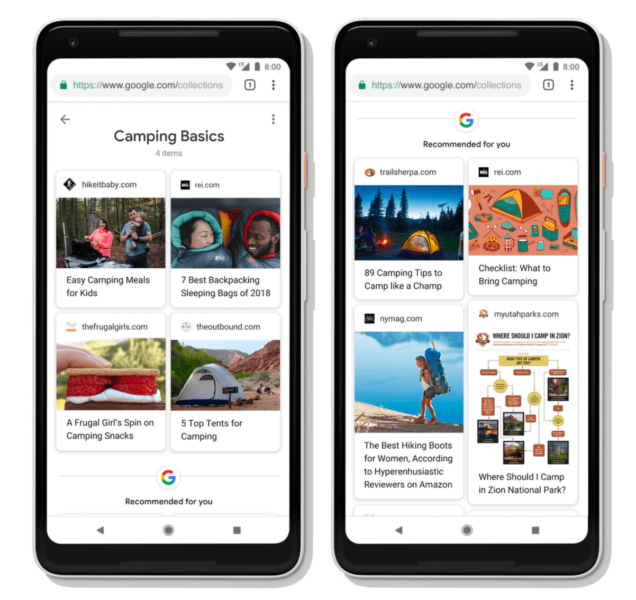
The collections already existed, but we do not know how many people used it. Collections allows users to save and organize content on their phones. The new version of Collections is closely related to the activity sheets.
Users will be able to save pages in their collections from activity cards. There will also be suggestions of related topics. One can imagine the utility of this principle for planning and high-priced purchases (for example, purchase of a car or appliance or a major household appliance).
Google also adds what it calls a "subject layer" to the knowledge graph. This explains his increasing number of suggestions. According to Google:
The subject layer is constructed by analyzing all existing content on the Web for a given topic and developing hundreds and thousands of subtopics. For these subtopics, we can identify the most relevant articles and videos – those that have always been topical and always useful, as well as new content on the subject. We then examine the models to understand how these sub-themes relate to each other, so that we can make the type of content that you want to explore more intelligible.
The "subject layer" in the answer box / featured snippets

In the picture above, you can see that there are separate sub-themes for each dog breed. This is based on Google's understanding of the relationships between these individual races and the queries and related content. These are more structured data in action.
Google Feed becomes 'Discover'. Google has revealed that Google Feed has 800 million active users per month worldwide. He also said the feed is a growing source of traffic for third-party publishers. Today, the company has announced a name change and some improvements to Google Feed.
The new product name is "Discover". It will appear on the mobile version of the Google home page.
Beyond the new name, there are design improvements and the addition of new controls and user features. Each news or content article will now be accompanied by a topic header that effectively constitutes a search query, to learn more about the topic in question.
Users can also track topics and indicate whether they want to see more or less content on a particular topic. Google will also add more video content to the feed.
The Google feed is now Discover

Visual search: borrowing from Snapchat, Pinterest. The third largest set of ads was devoted to visual search and discovery. And these updates and changes are at least inspired by Snap, Instagram and Pinterest.
As a result of AMP stories, Google extends them into search results, initially around celebrities and athletes. Stories is a visually immersive mobile format that includes video and can be dragged, created by a machine:
[W]We start using AI to intelligently build AMP stories and bring that content into Search. We start today with stories about notable people – like celebrities and athletes – providing insight into the facts and important moments of their lives in a rich visual format. This format allows you to easily access the articles for more information and offers a new way to discover the content of the Web.
Separately, Google has stated that it uses computer vision to identify relevant segments of videos for quick display in search results. Called "Featured Videos", it will help users to identify videos that match their interests more quickly by presenting one-off sections.
Google also said it was updating Google images this week to "show more context around images", to give users more information and better empower them to take action, on desktop and mobile devices.
The company added that Google Lens is coming to Google Images to allow a visual search for any item or object in a photo. If Lens gets the desired product or image, users will be able to manually specify (draw a circle) the specific search object to redirect Lens to that item.
Other stuff Google has finished with improvements to its job search capabilities, which will show job seekers nearby educational or job training opportunities related to particular positions. This new initiative is called Pathways.
The company announced initial partnerships with the State of Virginia, the Virginia Community College System, and local Virginia employers. She has also collaborated with Goodwill to help this organization expose its professional training opportunities to research.
Finally, Google is expanding its SOS and public alerts to include flood alerts, using sophisticated data modeling to illustrate the potential extent and progression of flood trajectories and the resulting damage. It launches the program in India in partnership with the Central Water Commission of this country.
What does this mean for marketers? Google brings much more structured content to search results and, in some cases, preempts queries or suggests queries that will generate additional search sessions. The classic "blue links", especially on mobile devices, will be even less highlighted. All these new features also create a new inventory of potential contextual ads for marketers.
Google has not discussed monetization or ad placements in any of these features or content areas. However, at least some of them are likely to see advertising spots in the short or medium term.
[ad_2]
Source link
