
[ad_1]
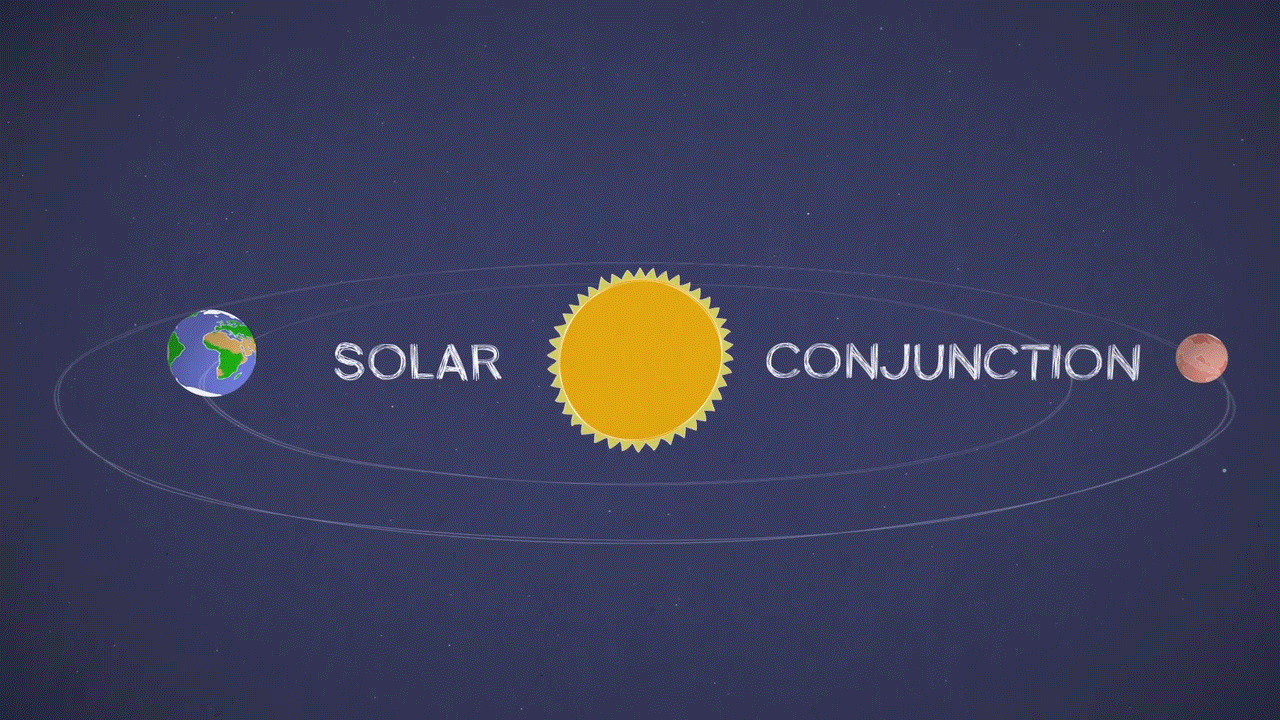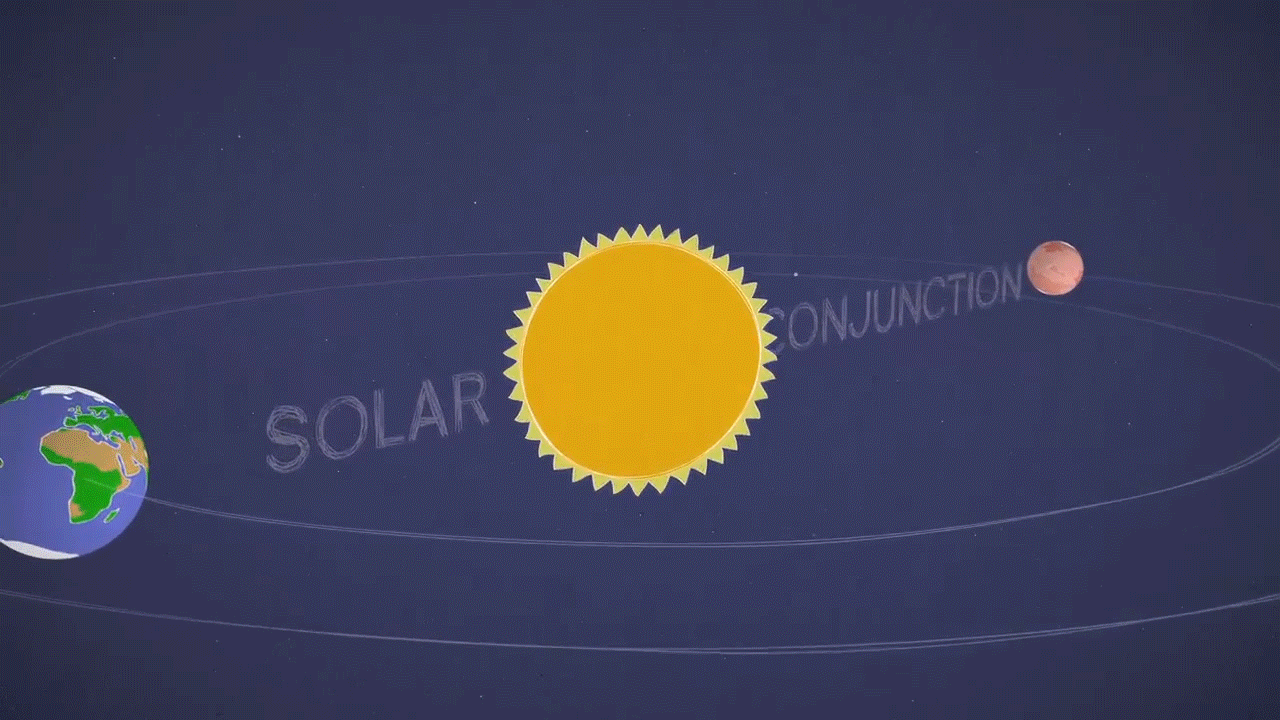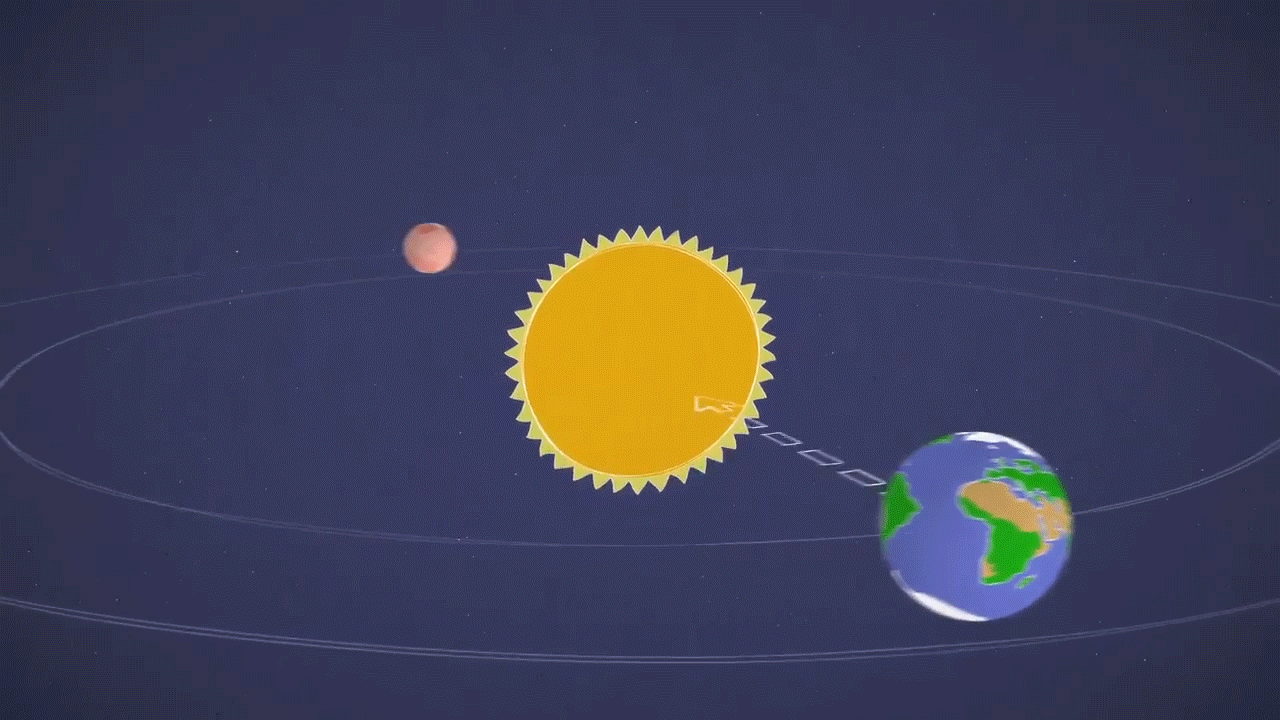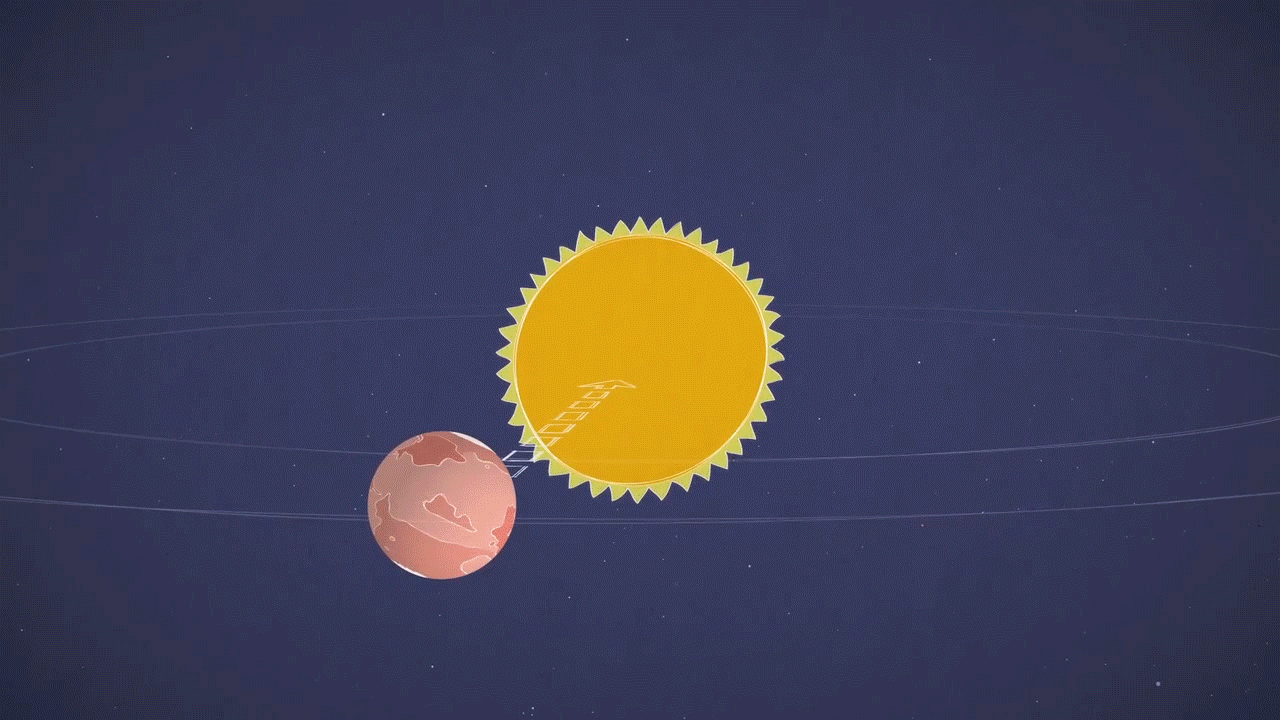
This animation illustrates the solar conjunction of Mars, a period when Mars is on the opposite side of the Sun to the Earth. Meanwhile, the Sun can interrupt spacecraft radio transmissions on and around the red planet. Credit: NASA / JPL-Caltech
The daily conversations between the antennas here on Earth and those on NASA's probe in Mars are about to become much quieter for a few weeks.
Indeed, Mars and Earth will be on opposite sides of the Sun, a period known as Mars' solar conjunction. The Sun expels the ionized hot gases from its crown that extends far into space. During the solar conjunction, this gas can interfere with radio signals as engineers attempt to communicate with a spacecraft installed on Mars, altering commands and causing unexpected behavior on the part of our deep space explorers.
For added security, engineers refrain from sending commands when Mars disappears far enough behind the solar corona to increase the risk of radio interference.
"It's still the moment," said Roy Gladden, Mars Relay Network Manager at NASA's Jet Propulsion Laboratory in Pasadena, California. "Our engineers have been preparing our spacecraft for the conjunction for months, they will always collect scientific data on Mars, and some will try to send them home, but we will not command this spacecraft because they could act on a corrupt command. ".
When does this happen?
The solar conjunction takes place every two years. This time, the suspension of orders, called "moratorium on orders" – will take place from August 28 to September 7, 2019. Some missions will have stopped ordering their spacecraft earlier in the preparation of the moratorium.
What happens to the spaceship?
Although some instruments on board spacecraft – especially cameras generating large amounts of data – are inactive, all NASA spacecraft will continue their scientific activity; they will just have lists of things to do much simpler than they normally would.
On the surface of Mars, the Curiosity rover will stop driving, while the InSight lander will not move his robotic arm. Over Mars, the Odyssey Orbiter and the Mars reconnaissance orbiter will continue to collect data from Curiosity and InSight for their return to Earth. However, only Odyssey will attempt to relay this data to Earth before the end of the conjunction. Meanwhile, another orbiter, MAVEN, will continue to collect its own scientific data but will not support any relays during this period.
All this means that there will be a temporary break in the raw image feed available in Curiosity, InSight and other Mars missions. The solar conjunction of Mars is affecting the operations of all spacecraft currently on Mars, not just those of NASA.
What happens when the solar conjunction ends?
Once the connection is complete, the spacecraft will transmit the data it has collected to NASA's Deep Space Network, a large-scale land-based antenna system managed by JPL. Engineers will spend about a week downloading information before resuming normal spacecraft operations.
If the teams responsible for monitoring these missions determine that the collected scientific data is corrupt, they can usually have them retransmitted after the end of the moratorium on 7 September.
For a moratorium on sending orders to Mars, blame the Sun
Quote:
What is Mars' solar conjunction and why is it important? (August 24, 2019)
recovered on August 24, 2019
from https://phys.org/news/2019-08-mars-solar-conjunction.html
This document is subject to copyright. Apart from any fair use for study or private research purposes, no
part may be reproduced without written permission. Content is provided for information only.
[ad_2]
Source link