
[ad_1]
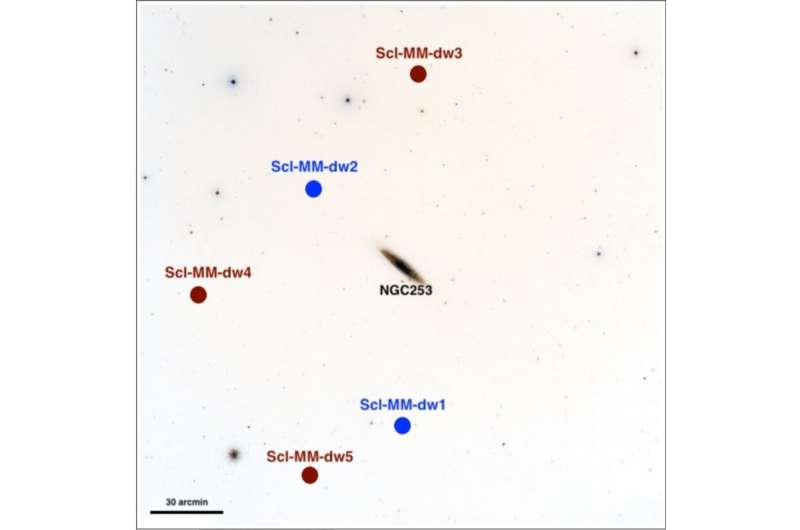
DSS image centered on NGC 253, showing the area explored by PISCeS, extending up to 100 kpc from the center. The solid blue circles represent the position of the dwarves previously discovered in PISCeS. Credit: Mutlu-Pakdil et al., 2021.
Using the Hubble Space Telescope (HST), astronomers have detected three new ultra-weak dwarf galaxies associated with neighboring spiral galaxy NGC 253. The newly discovered dwarfs turn out to be among the weakest systems discovered so far present beyond the local group. The discovery is reported in an article published August 20 on arXiv.org.
Ultra-weak dwarf galaxies (UFDs) are the least luminous, most dark matter-dominated, and least chemically evolved galaxies known. Therefore, they are seen by astronomers as the best candidate fossils in the early universe.
The Panoramic Imaging Survey of Centaurus and Sculptor (PISCeS) project is one of the astronomical surveys aimed at finding new weak satellite galaxies, including UFDs. As part of PISCeS, a team of astronomers led by Burçin Mutlu-Pakdil of the University of Chicago observed the field around NGC 253 with HST, looking for dwarf satellite systems. At a distance of about 11.4 million light years, NGC 253 is the main galaxy in the neighboring Sculptor group.
The team visually inspected all images, looking for spatially compact overdensities of stars around NGC 253 and found three new UFDs, in addition to the two known ones identified in 2014 and 2016.
“In this work, we report the discovery of three ultra-weak dwarf satellite galaxies of NGC 253 in a visual search of Magellan / Megacam images taken as part of PISCeS, our panoramic imaging campaign to find a weak substructure at breast of
The new UFDs received the designations Scl-MM-dw3, Scl-MM-dw4 and Scl-MMdw5. They are uniformly old (ages estimated at around 12 billion years), with almost all of their stars forming in the early universe, so astronomers consider them pristine fossils of the reionization era.
Scl-MM-dw3 is the smallest UFD of the newly detected trio, as its elliptical half-lumen radius along the semi-major axis has been estimated to be around 362 light-years. The galaxy is located approximately 11.34 million light years from Earth and approximately 264,000 light years from NGC 253. Its stellar mass has been calculated to be 110,000 solar masses.
Scl-MM-dw4 turns out to be as massive as Scl-MM-dw3, but is almost 70% larger – its half-light radius has been measured at 613 light years. This UFD is located about 13.37 million light years away, and its distance from NGC 253 is estimated to be some 280,300 light years.
With a half-light radius of about 1,167 and a mass of about 140,000 solar masses, Scl-MM-dw5 is the largest and most massive dwarf of the three new UFDs. The galaxy is located approximately 12.71 million light years from Earth and approximately 313,000 light years from NGC 253.
Astronomers have pointed out that the new dwarfs have luminosities between -7.5 and -7.24 mag, which places them among the weakest galaxies identified outside of our local group.
Astronomers discover three new weak dwarf galaxies
Burçin Mutlu-Pakdil et al, Hubble Space Telescope Observations of NGC 253 Dwarf Satellites: Discovery of Three Ultra-faint Dwarf Galaxies, arXiv: 2108.09312 [astro-ph.GA] arxiv.org/abs/2108.09312
© 2021 Science X Network
Quote: Three new ultra-low dwarf galaxies discovered (2021, August 31) retrieved on August 31, 2021 from https://phys.org/news/2021-08-ultra-faint-dwarf-galaxies.html
This document is subject to copyright. Other than fair use for private study or research purposes, no part may be reproduced without written permission. The content is provided for information only.
[ad_2]
Source link