
[ad_1]
The use of sunscreen not only reduces the risk of skin cancer and skin burns, but can also reduce the effects of aging due to sun exposure.
But sometimes we forget the basic things. For example, how should we apply sunscreen? Then, how long do we have to wait before we can really get into the sun after applying sunscreen, and how long can we survive this exposure to the sun, even using sunscreen?
The latter, how does the sunscreen work?
How does the sunscreen work?
There are two main ingredients in all sunscreen products: active ingredients and emulsions.

from shuttersrock.com
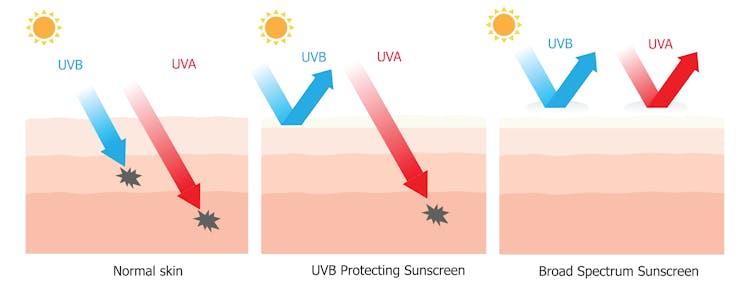
The active ingredients that make sunscreen can act to protect the skin from the sun. The active ingredients are divided into two types: UV absorbers and UV reflectors
UV absorbers are chemicals that can reduce UV radiation and convert it to very low heat levels . A small number of people say that using sunscreen makes them feel an unpleasant heat on the skin.
UV-damaging chemicals can also be called "organic" because they contain carbon atoms.
Some absorb parts of the UVB spectrum, which are known to cause sunburn and increase the risk of skin cancer. While the other party absorbs the UVA spectrum. Numerous studies have shown that more UVA waves can not only penetrate the deeper layers of the skin, but also contribute to skin cancer at the expense of the immune response to damage to the DNA.
For this, sunscreens that have the label "broad spectrum" are more recommended because they offer the best protection.
from shutterstock.com
of some oxides, such as zinc oxide (zinc oxide) and titanium dioxide, which can absorb and disperse UV rays.
In general, sunscreens have more than one active ingredient and can (19659002) Emulsions, lotions, milk, creams, oils, foams or gels are substances that contain substances active. Usually, this is done from a combination of oil and water, as well as other ingredients. The point is that the product is durable on the shelf or in our closet.
Emulsions also help protect the sunscreen, change the taste and aroma of sunscreen and attach to the skin.
What is the FPS and how to measure it?
patron not barrier . Imagine the door with the mosquito net: the wind can still enter, but not the mosquitoes. In the same way, the sunscreen or the herb you use still leaves a small amount of UV radiation penetrating the skin.

Mike Mozart / Flickr, CC BY
SPF can be defined as "sun protection factor". This is used to measure how much UV can cross the shield. The higher the number, the more UV can cross the shield.
SPF 30 allows a third or 3.3% of UV to reach the skin. This means that the lotion can filter up to 96.7% UV. Compare with SPF 50, which can filter 98% UV (and let one for fifty or 2% of UV pbad through the shield).
The difference between SPF 30 and SPF 50 seems big (difference of 20 digits), but that's really not the case. They are only 1.3% different
If your skin can survive 10 minutes without protection until the signs appear on fire, then with SPF 30, the level of appearance will appear 30 times longer, for a total of 300 minutes. SPF 15 can protect up to 150 minutes, while SPF 50, 500 minutes.
But do not be happy. If you linger in the sun for 500 minutes (eight hours) just by using sunscreen, you risk burning!
Read more:
Does eating at night make you fat?
When and how to use it?
At the microscopic level, the skin is a row of peaks and valleys. Coat the skin with sunscreen about 20 minutes before going out, allowing the product to drain into the skin and stick well
from shutterstock.com
Many products suggest you reapply every two hours after use. It's like painting a house wall.
The first layer will certainly adhere well, but reapply after 20-30 minutes of sun exposure – after the first layer is dry – will give you a better layer. And this will cover small parts that may be missed, or are too thin, when first used.
We should also use sunscreen properly. Most people use it too little (between a quarter and three quarters) of the recommended amount on the package.
One teaspoon per body part is a highly recommended rule. Add another teaspoon on the face, front and back. It takes up to seven teaspoons (35ml) if you are on the beach and use only shorts or bikinis.

Photo by rawpixel.com on Unsplash, CC BY
Cover and spread sunscreen around our body. Cover up every two hours, or more often when you move a lot (perspiration, wiping with a towel, putting in physical contact with anything that removes the sunscreen from the skin, even on a sunscreen package that can last up to 10 minutes). At four o'clock).
And we must also pay attention to whether the lotion has not exceeded the expiry date.
Use other items to protect your skin, hat, umbrella, clothes and even stay indoors when the high UV period is in progress. As the sun gets closer to the afternoon, usually between noon and 12:30 pm, the incoming UV rays are high
More:
A "clean" diet can actually harm a child's health
The WHO recommends protecting the skin from sunlight when the UV index reaches 3 or more. The Weather Bureau's report for the UV Index Australia and SunSmart App allows you to get information via a smart phone
How long can I survive the sun?
We must remain wise in the sun necessities. As long as you've used sunscreen as "protective clothing" (but not), it's a bad idea.
Despite the best advice, the normal daily routine – wiping eye water, scratching the itch, hugging children in contact with trees or friends, can eliminate sunscreen and reduce its performance.
And remember that the sunscreen is a filter of sunlight, not a barrier.
Oya, would you be blackened even if you used sunscreen properly? Of course not. If the sunscreen has been used appropriately to reduce exposure to UV rays, it will prevent the biological process of skin whitening.
Update: This article originally states that metal particles reflect UV but that UV is actually dispersed by the oxide.
Source link