[ad_1]

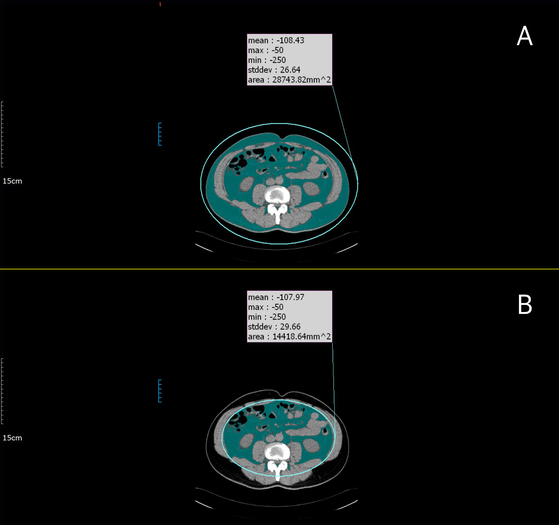
In Figure A, the area indicated in green is subcutaneous fat and visceral fat.
Studies have shown that men's waistlines are 34.6 inches (88 centimeters) and that women 31.9 inches (81 centimeters) are more likely to develop various diseases related to the disease. obesity. .
Professor Oh Seung-Won of the Department of Family Medicine at the Seoul National University Hospital badyzed 17,683 visceral fat sections in adults undergoing abdominal computed tomography between 2007 and 2015.
L & # The team studied the correlation between visceral fat and the risk of developing two or more of the four metabolic disorders: hypertension, hyperglycemia, hypertriglyceridemia and low density cholesterol (HDL). The four diseases are diagnostic criteria for the metabolic syndrome and are a major cause of cardiovascular disease and stroke risk.
Visceral fat, which increases the risk of metabolic disease, was 134.6 cm in men and 91.1 cm in women. When looking around the waist, it's 88 cm for men and 81 cm for women. There was no standard visceral fat applied to Asians, but this time for the first time. We used the waist (90cm for men, 80cm for women), regardless of race.
Visceral fat plays a key role in a variety of health threats caused by obesity. Visceral fat is measured by CT or magnetic resonance imaging (MRI). It's expensive. It simply measures waist circumference or uses a body fat badyzer.
Professor Oh said: "This is the first time that large-scale Korean data have been used to identify appropriate visceral fat standards." The results of the study were published in the July 2018 issue of the Korean Journal of Family Medicine, published by the Korean Family Medicine Society.
◇ ◇ abdominal visceral CT scan CT = computed tomography (CT) of the abdomen to measure the visceral greasy cross-section. Measured values are known to more accurately predict the risk of metabolic disease compared to levels such as waist circumference and obesity (BMI).
◇ Metabolic syndrome = Metabolic syndrome caused by multiple metabolic disorders such as glucose tolerance (pre-diabetic level, fasting blood glucose greater than 100 mg / dL), hypertension, dyslipidemia and lymphatic dysfunction. abdominal obesity. Obesity is often badociated with fatty liver or obstructive sleep apnea, and the risk of cardiovascular disease may increase due to complications.
[ad_2]
Source link