
[ad_1]
• New images show that NASA's InSight probe landed in a prime location on Mars
• The first InSight self-test, NASA's probe appears to be ready and eager to start . This is the first image taken by the mission InSight on the surface of Mars
This magnificent mosaic, consisting of 11 individual photos, shows the entire probe, resting on the Martian surface. The photos were captured by the instrument deployment camera on InSight's robotic arm. The two solar panels of the LG can be seen with various scientific instruments on their deck, such as a climate sensor and a UHF antenna. InSight landed on Mars on November 26th and the NASA project was very successful in its early days.
A second mosaic, consisting of 52 individual images, shows the immediate place of work of InSight, namely:, the area on which the probe will eventually implant its scientific instruments. The area indicated in the mosaic is approximately 4.26 meters by 2.13 meters. The lavender color areas indicate the best places to place his seismograph: the seismic experience for interior structure, in the seismic experience of origin (SEIS).
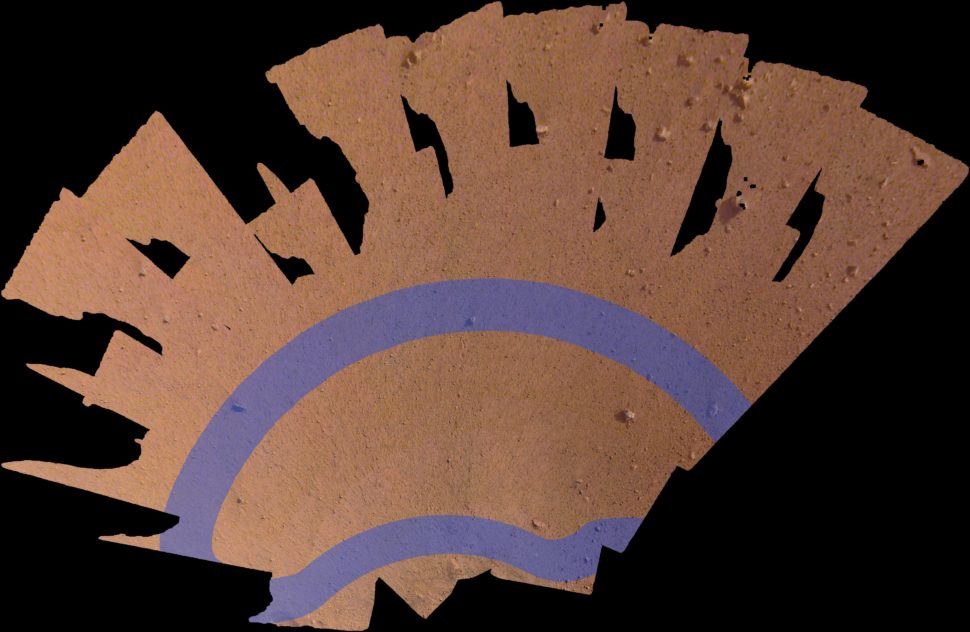
A mosaic of the InSight workplace. The lavender color represents the ideal areas for the placement of the probe seismograph. Fortunately, it is in this area that the stationary probe will do its job. NASA chose this place on Mars, Elysium Planitia, because it is relatively free of rocks. But to further improve things, the probe landed on a rock-free hole – created by an old meteorite impact and slowly filled with sand – that appears to be exceptionally rock-free, with the exception of a few scattered rocks. "The near-absence of rocks, hills and potholes means that our instruments will be extremely safe," said InSight's chief investigator, Bruce Banerdt, in a statement.
"This may seem like a relatively flat terrain if there was not Mars, but we are happy to see it."
Mission planners will now have to decide where, in this area, the probe should place its detection instruments. earthen. Once a point is located, they transmit commands to the probe, which instructs InSight's robotic arm to carefully set up the SEIS and its heat flow probe, called the heat flow and heat flow set. physical properties, at preselected locations.
The flatter the surface, the better, because these instruments work more effectively on flat ground. InSight will also be interested in avoiding rocks more than about 1.3 cm. Once drilling has begun, the heat flow probe can dig up to five meters below the Martian surface.
With so many potential points of failure, he is relieved to see this project start so easily. We are touching the woods so that NASA and its new intrepid probe continue to work well.
[NASA]
Source link