[ad_1]

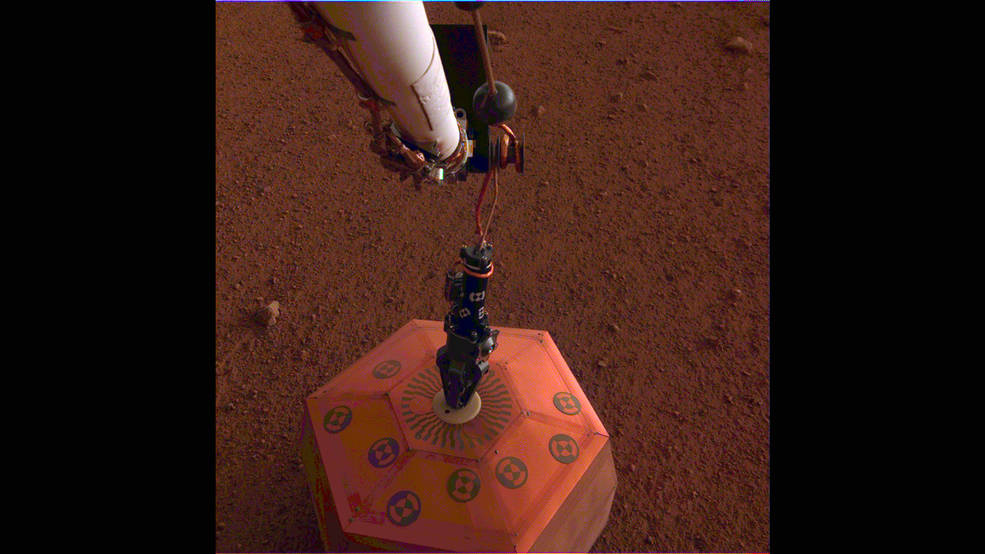
Mechanical arm operating the seismograph. With its robotic arm, the InSight satellite carefully positioned a hexagonal device gently on the Martian surface this Wednesday (19). This act marks the first time in history that a seismograph is placed on Mars – or on the surface of a planet other than the Earth.
InSight landed on Mars on November 26 and is now starting to perform tasks. serious. After checking her new work area and taking a nice selfie, she will now prepare the SEIS (seismic experience for the inner structure), an instrument considered fundamental to the mission.
• The Brazilian NASA recounts the details of the upcoming mission of "The establishment of the seismograph is as important as the landing of InSight on Mars," said Bruce Banerdt, head of research at the NASA Exploration Laboratory.
• The InSight probe landed on Mars – now what?
InSight mission, in a statement. "The seismograph is the priority instrument of InSight: we need it to reach three quarters of our scientific goals."
It's easy …
Who knew that playing clawed game would be useful for exploration #March ? I grab my seismometer and get ready to put it down.
In view of the implementation of SIX, we will be able to implement the SIS. Mission planners have ensured that the robotic arm of the probe is working properly and that a suitable surface point is chosen for its preparation. And as practice improves, team members trained with a replica in a NASA reaction propulsion laboratory (JPL) test area in Pasadena, California.
 Installation of terrestrial seismograph. At the scheduled time, InSight placed the seismograph gently on the surface as far as possible: about 1.6 meters. This specific location was chosen to keep the device as far away as possible from the InSight feet; It allows the cable of the device to rest on the ground and to even be in contact with the surface. This also leaves room for the thermal probe to be placed later.
Installation of terrestrial seismograph. At the scheduled time, InSight placed the seismograph gently on the surface as far as possible: about 1.6 meters. This specific location was chosen to keep the device as far away as possible from the InSight feet; It allows the cable of the device to rest on the ground and to even be in contact with the surface. This also leaves room for the thermal probe to be placed later.
The copper-colored apparatus is now on the Martian surface, but the implementation is not yet complete. The SIX must be leveled, as it is currently inclined from the ground to 2 or 3 degrees. In the coming weeks, NASA scientists will carefully badyze the data extracted by the device to test the reliability and integrity of the information sent to Earth. For example, the InSight team may need to adjust the S-Lined cable to minimize the noise that causes it. For the final stage of the installation process, InSight's robotic arm will provide thermal and windproof protection to the seismograph to stabilize the environment around its sensors.
Whew – disappears after a long day, but I did: I placed my seismometer on the surface of Mars! With SIX, I will be able to listen to the marsquakes and help reveal the heartbeat of #March . (InSight) December 20, 2018
"The calendar of InSight's activities on Mars was better than we had hoped for," said Tom Hoffman, Project Manager Insight. "Laying the seismograph securely on the floor is an amazing Christmas present."
Once the SIX is operational, it will hear the earthquakes – the "heartbeats" of the red planet. The device must be able to detect the seismic waves that pbad through the lower layers of the surface. Planetary scientists had previously shown that tectonic plates existed on Mars, but not on the existing scale on Earth; Major tectonic changes occur approximately once a million years on Mars. That said, the SIX should be able to detect small seismic ripples. Experts will use this data to know the depth and composition of these layers.
As previously stated, InSight will have to deploy another device: the thermal probe. Also known as heat flux probe and physical properties, the device will be positioned in the eastern part of the Insight work area at a distance similar to that of the SIX. This should happen until the end of January.
[NASA]
[ad_2]
Source link